Meiosis
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/24
Last updated 5:00 AM on 12/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
1
New cards
What is needed in sexual reproduction?
2 parents (one sperm and one egg)
2
New cards
What is the point of meiosis?
to reduce the number of chromosomes in half
3
New cards
How many cells are made in meiosis?
4
4
New cards
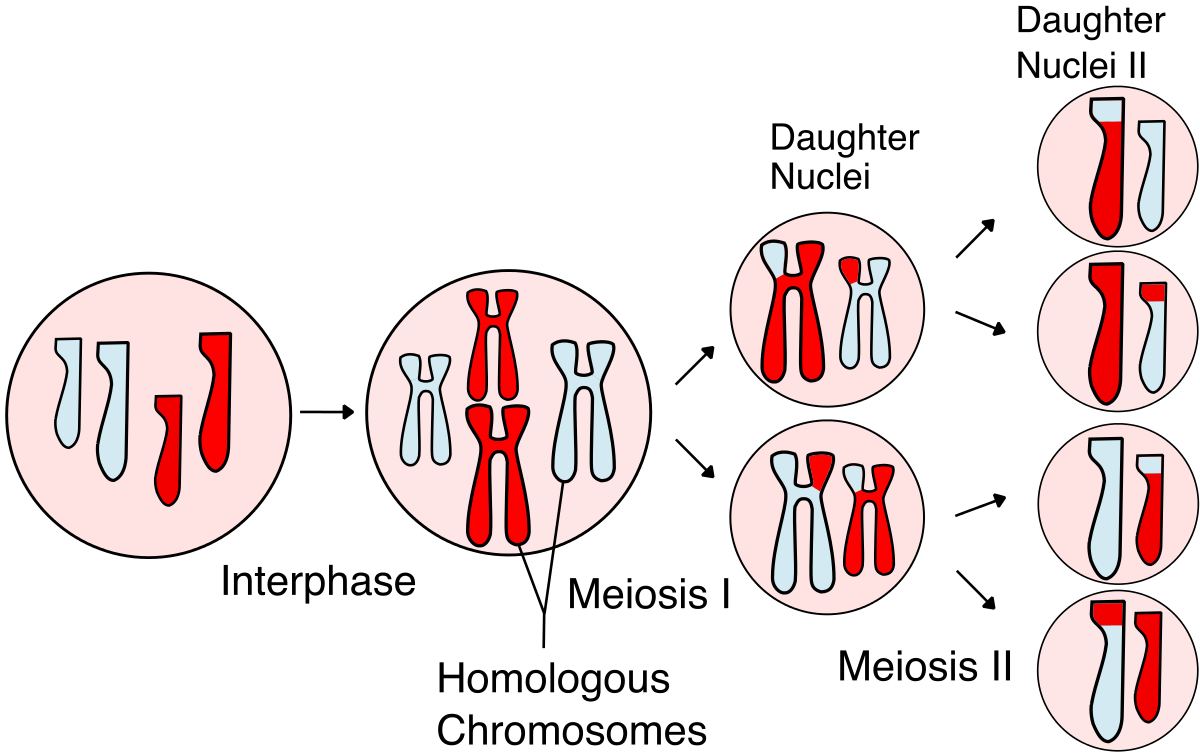
What is the difference in Meiosis I and II?
Meiosis I- 1 cell gets divided into 2
Meiosis II- 2 cells get divided into 4
Meiosis II- 2 cells get divided into 4
5
New cards
What are the stages in Meiosis I?
Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, and Telophase and Cytokinesis I
6
New cards
What are the stages in Meiosis II?
Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and Telophase and Cytokinesis II
7
New cards
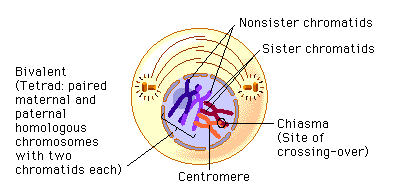
What happens in Prophase I?
the spindle fibers are present, the nuclear membrane disappears, synapsis pairing of the tetrad homologous chromosomes, and crossing over
8
New cards
What does synapsis mean?
pair of homo. chromosomes (tetrads) that are extremely close to each other
9
New cards
What is crossing over?
portions of chromatids break off and attach adjacent chromatids which results in genetic recombination
10
New cards
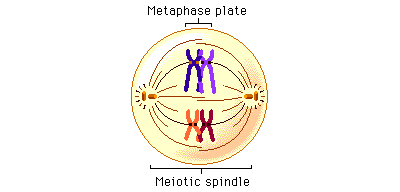
What happens in Metaphase I?
the tetrads line up in the equator of the cel and the kinetochore fibers from the centrioles attach to the centromere of the chromosomes
11
New cards
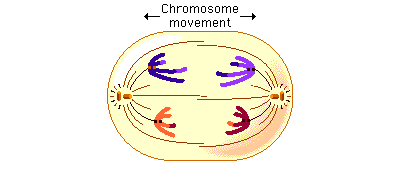
What happens in Anaphase I?
the homo. chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite poles with the pairs being separated and independent assortment allows the random separation of the homo. chromosomes (more genetic variation)
12
New cards
What happens in Telophase +Cytokinesis I?
there are now the haploid number of chromosomes in the cell and 2 new cells with one chromosome from the homo. pair
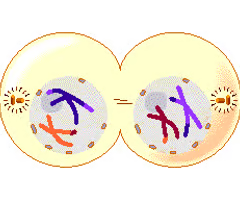
13
New cards
What happens in the stages of Meiosis I?
DNA gets copied in this stage and there is only one cell
14
New cards
What happens in Meiosis II?
dna is NOT being copied, and the two cells get split into four
15
New cards
What happens in Prophase II?
The opposite pairs of the tetrads are in the individual cells. The centrioles appear and nuclear membrane is also disappearing
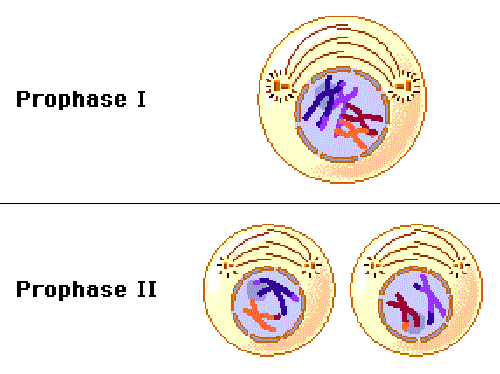
16
New cards
What happens in Metaphase II?
The opposite pairs of the homo. chromosomes are lined up at the equator of the cell and the centrioles release spindle fibers. The kinetochore fibers attach themselves to the centromere of the chromosomes.
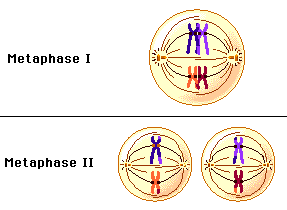
17
New cards
What happens in Anaphase II?
The chromosomes get pulled apart into sister chromatids to polar opposite sides. The cells will now get split in telophase + cytokinesis II.
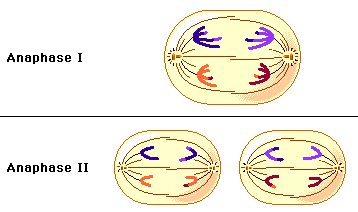
18
New cards
What happens in Telophase+Cytokinesis II?
The end result contains four haploid daughter cells which are gametes (sperm or egg cells).
19
New cards
What are the haploid cells for male referred to as?
spermatids
20
New cards
What are spermatids?
4 haploid cells
21
New cards
What do spermatids become?
spermatoza (sperm)
22
New cards
What are the haploid cells for female referred to as?
ovaries
23
New cards
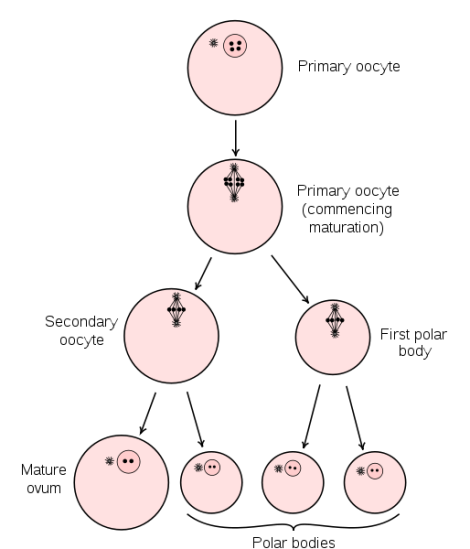
What are polar bodies?
These are three of the haploids from the diploids that are non functional
24
New cards
What is the ovum?
The only functional egg which will have 23 chromosomes
25
New cards
What occurs in sexual reproduction?
sperm+egg= fertilized egg
* referred as a zygote or offspring
* referred as a zygote or offspring