Chapter 8: Intelligence and Creativity
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Psychometric approach (to intelligence)
intelligence is a trait or set of traits that characterizes some people to a greater extent than others
Piaget’s Intelligence and others
piaget’s — thinking or behavior that is adaptive to the demands of your situation or environment
others’ — to think abstractly or to solve problems effectively
General Mental Ability (g) Spearman 1927
Ability to reason, plan, solve probems, think abstractly, comprehend complex ideas, learn quickly, learn from experience.
Fluid Intelligence vs Crystallized Intelligence
fluid — ability to use your mind to actively solve new problems WITHOUT any prior knowledge (new creative flexible)
crystallized — use of knowledge acquired from schooling and other life experiences
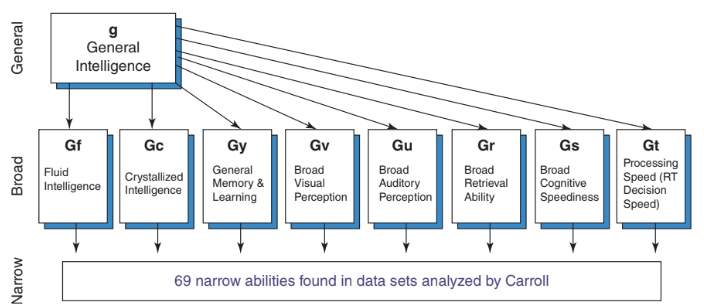
Cattell-Horn-Carroll theory of Intelligence
3 layers
1 - general intelligence, kind of like spearman’s g
2 - 8 abilities that are correlated with each other to some extent (fluid int., crystallized int., general memory and learning, broad visual perception, broad auditory perception, broad retrieval ability, broad cognitive speediness, processing speed/decision making)
3 - 69 narrow specialized abilities
Alfred Binet's IQ Test
Age-graded test to compare children, to identify kids needing extra attention.
first “IQ” test aimed at children
MA (mental age) — the level of age-graded problems that the child is able to solve
classroom skills: attention, perception, memory, reasoning, verbal comprehension
WW1 IQ tests
army alpha — literate recruit test
army beta — illiterate recruit test
they were testing IQs to see who was capable of leading during war time
Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale (TERMAN)
comparing MA with chronological age (CA)
MA/CA x 100 = IQ (int. quotient)
test norms — standards of normal performance expressed as average scores and the range of scores
Wechsler Scales
set of intelligence scales
established a normal distribution of IQ
Mean and Standard deviation of IQ Scores
Mean: 100, Standard dev: 15
Intellectual disability
IQ < 70 (2 SD below mean). Deficits in 2 or more adaptive behaviors which affect daily, general living. 2~3% of the general population, of which 25% due to genetic disorder.
Gifted
IQ of 130 or higher; there are fitness indicator such as physical symmetry and sexual selective, but also usually comes with a sense of burden. Other individuals treat gifted as robots
Savant Syndrome
A syndrome in a developmentally disabled person who has some remarkable talent that contrasts with his low level of general intelligence. Sometimes happens after incidents.
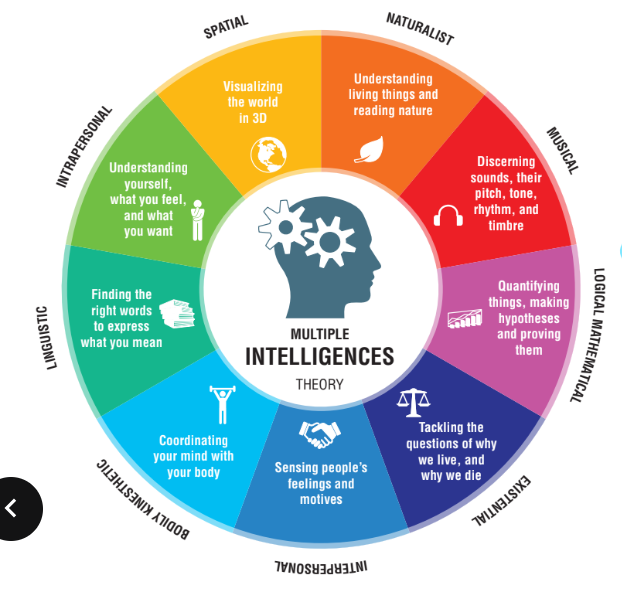
Gardener’s theory of multiple intelligences
Focus on “how are you smart” rather than “how smart are you”
spatial
naturalist
musical
logical mathematics
existential
interpersonal
bodily kinesthetic
linguistic
intrapersonal
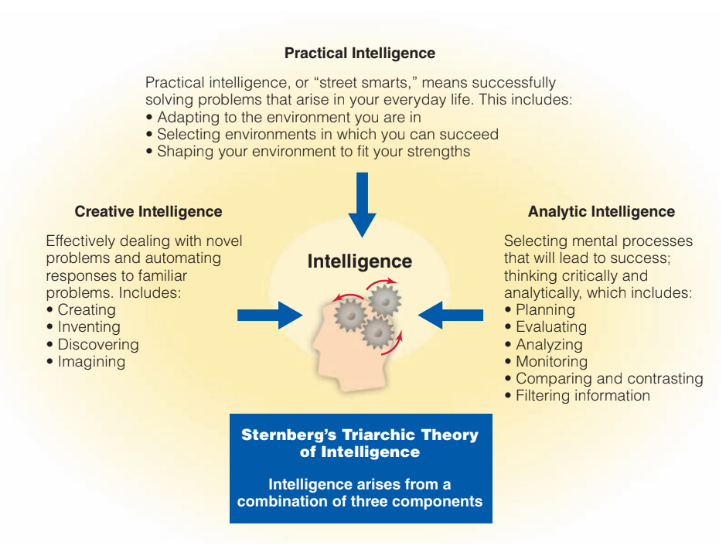
Sternberg’s Theory of successful intelligence
argument: IQ tests ignore how people produce intelligent answers
theory of successful intelligence: 3 components that jointly contribute
practical intelligence: using your abilities to solve the problems encountered in everyday life
creative intelligence: response to new experiences, requires active information processing
analytical intelligence: focuses on information processing skills, traditional IQ test things
IQ in infancy — Bayley Scales
« IQ » tests can't be administered until 3 years old, but before that there is Bayley scales of infant development: it does not accurately predict IQ (it does not assess the same abilities)
motor scale — infant ability to grasp and throw stuff
language scale — budding vocabulary skills and communication
cognitive — how does the kid think, look for objects, follow directions
Intelligence of time and contexts
Intelligence is relatively stable but CAN vary across the lifespan, and it is malleable; You can train for intelligence tests, and IQ is influenced by environmental influences such as education, home environment, socioeconomic status; IQ is also affected by momentary aspects such as tiredness, concentration, and strategy to approach task.
Criticism on IQ measures
-> Arbitary construct; is measures concepts that are important in western education system?
-> Does not fully describe intelligence?
-> Other conceptualization of intelligence possible?
Flynn Effect
The rise in average IQ scores that has occurred over the decades in many nations; it is slower nations still developing.
IQ test difference: males vs females
Men's IQ tend to score higher than females, albeit that trend is decreasing, but that is probably due to a lot of factors including traditional gender roles.
Prodigies
A child with extraordinary talent, displaying ability levels comparable to adult professional; may be related to exceptional working memory and elevated attention to details.
Convergent Thinking vs Divergent Thinking
Convergent Thinking- A pattern of thinking in which individuals produce one correct answer; characteristic of the items on conventional intelligence tests
Divergent Thinking- A pattern of thinking in which individuals produce many answers to the same question; more characteristic of creativity than convergent thinking
Cumulative-Deficit Hypotheses
Describes how impoverished environments inhibit intellectual growth and these negative effects accumulate over time.
Stereotype Threat
The apprehension experienced by members of a group that their behavior might confirm a cultural stereotype (E.g.: Asian American women perform better in math tests when their identity as Asian American is made evident, as opposed to performing worse when identity as women was made evident.
IQ and its effects on Health, success
both health and occupational success positively correlated
fluid int. decreases while crystallized int. increases with age
only a few older adults experience wisdom — exceptional insight into complex life problems