1. Power and obedience
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
What is the Hogg and Vauhgan definition of power?
Capacity to influence others while resisting their attempts to influence
Fiske and Berdahl, 2007 definitions of power
The relative control over another’s valued outcomes
outcomes can be physical, financial, social and etc
people who control others’ outcomes have power, like it or not
What kinds of outcomes do harsh bases of power use?
economic and physical outcomes
work with outcomes that are more tangible and explicit
What kind of power differentials do harsh bases of power rely on?
rely on power differentials that are more obvious
When are harsh bases of power more likely to exist?
more likely to exist when power is illegitimate
What do harsh bases of power require?
they require surveillance
less power when not present
What kind of outcomes do soft bases of power use?
social outcomes
work with outcomes are more subjective and intangible
What kind of power differentials do soft bases of power rely on?
rely upon power differentials that may be less obvious
are soft bases of power weaker than harsh ones?
no they are not weaker than harsh bases of power
What kind of influence does soft bases of power produce?
tend to produce influence that is self-sustaining, without surveillance
Definition of coercive power?
harsh
the ability to give or threaten punishment for non-compliance
e.g. a bully
definition of reward power?
harsh
the ability to give or promise rewards for compliance
e.g. a donor
Definition of legitimate power?
both harsh and soft
the target’s belief that the influencer is authorised by a recognised power structure to command and make decisions
e.g. a judge or police
Definition of informational power?
soft
The target’s belief that the influencer has more information than oneself
e.g. spy
Definition of expert power?
soft
the target’s belief that the influencer has generally greater expertise and knowledge than oneself
e.g. doctor
definition of referent power?
soft
identification with, attraction to or respect for the source of influence
e.g. celebrity
What does the approach/ inhibition theory of power suggest about how people behave when they are in a position of high power?
High power → approach
attention to rewards
positive emotions (desire, enthusiasm, pride)
automatic cognition
disinhibition
state/ trait driven behaviour
What does the approach/ inhibition theory of power suggest about how people behave when they are in a position of low power?
Low power → inhibition
attention to threats
negative emotions (awe, embarrassment, fear, guilt, shame)
systematic, controlled cognition
inhibition
situationally constrained behaviour
What are 8 aspects that we may be more likely to observe in people who feel powerful?
be more willing to engage in action
act in line with their own preferences
express their opinions openly
experience and express more positive emotions
have a decreased motivation to affiliate with low power individuals
make more sinister attributions about the intentions of low-power individuals
be less likely to engage in perspective-taking and to show empathic concern (particularly towards subordinates)
have lower basal cortical levels and lower cortisol reactivity to stressors
What was found in Galinsky, Gruenfeld and Magee’s study when participants were places in a high or low power position during a task and then a game of blackjack?
in task either manager or builder of a lego structure
in game of blackjack players can ask for additional cards to reach 21
those previously put in power → took more cards (more action)
What was found in Galinsky, Gruenfeld and Magee’s study when participants were places in a high or low power position during a task and then placed in a room with an annoying fan?
ppts either allocated lottery tickets or predicted allocation
when placed in a room with an annoying fan, those previously put in power dealt with the fan
What was found in Galinsky, Gruenfeld and Magee’s study when participants were places in a high or low power position during a task and then asked how much money they want to take/ return to the pool?
ppts either allocated lottery tickets or predicted allocation
those previously in power took more AND returned more to the pool
whether action given is selfish or prosocial, people in power are more likely to take it
Finish this phrase to define Dominance?
The degree of deference, respect and attention one receives as a consequence of…
the perceived ability to coerce, intimidate and impose costs and benefit
Finish this phrase to define Prestige?
The degree of deference, respect and attention one receives as a consequence of…
perceived attractiveness as a cultural model or coalition partner
What was the procedure used by Cheng et al to determine whether one’s impression as dominant and/or prestigious lead to social influence within small groups?
given imaginary scenario of moon crash-landing. Had to prioritise which things should be prioritised on the journey to the base
task completed alone then in a group. in order to compare alone and group response to see who was most influential
participants were then asked to rate their group members in terms of dominance and prestige
What were the measures of dominance and prestige and measures of social influence used by Cheng et al to determine whether one’s impression as dominant and/or prestigious lead to social influence within small groups?
measures of dominance and prestige
group member evaluations of each other
third-party evaluations of each group member
Measures of social influence
behavioural change: how much were group decisions moved toward each individual’s rankings
third party eye gaze: to whom did third-party gaze while watching videos of groups discussions?
What were the results of Cheng et al who determined whether one’s impression as dominant and/or prestigious lead to social influence within small groups?
both dominance and prestige independently predict influence
both independently predict visual attention toward the dominant or prestigious target
What are some dominance motives?
i like to give orders and get things going
i would enjoy having authority over people
I enjoy planning things and deciding what other people should do
What are some prestige motives?
I like to have people come to me for advice
I like to be admired for my achievements
I would like an important job where people look up to me
What are conflicts that leaders face?
followers give leaders the power to make decisions that benefit the group
leaders are ostensibly bound to act in the group’s interests
but the group’s interests may be at odds with the leader’s self interest
a key conflict can arise when power is unstable - when the leaders’ interest in keeping power may be more important for them than group interests
What was the design used by Maner and Mead to examine whether dominance-motivated individuals act in their own self-interest to maintain power, when a position of power is unstable?
teams completed a puzzle
each player could be granted clues
performance earned them money that the group split
Participants could secretly select clue quality for each member of their group
Ps told that they had stable leadership, equal authority with all or unstable leadership (could be reassigned based on performance)
would unstable leadership lead dominance-motivated individuals to withhold information from group members?
What were the results of Maner and Mead? Would unstable leadership lead dominance-motivated individuals to withold information from group members
Yes, unstable leaders high in dominance shared less quality clues
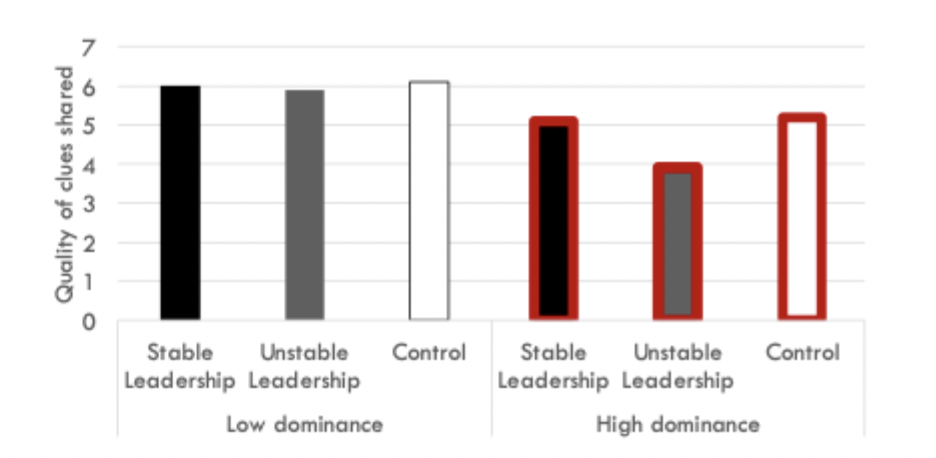
How was Maner and Mead’s design adjusted to see if unstable leadership lead dominance-motivated individuals to exclude highly-skilled group members?
pre-task ppts completed a test and received a high score, so did one other player
told that too many people showed up for the experiment
Ppts could anonymously tell experimenter how much they felt other members should be excluded
leader could be reassigned based on performance in unstable leadership
What were the second results of maner and mead? Would unstable leadership lead dominance-motivated individuals to exclude highly-skilled group members?
Yes, high dominance individuals with unstable leadership had greater desire to exclude other skilled player
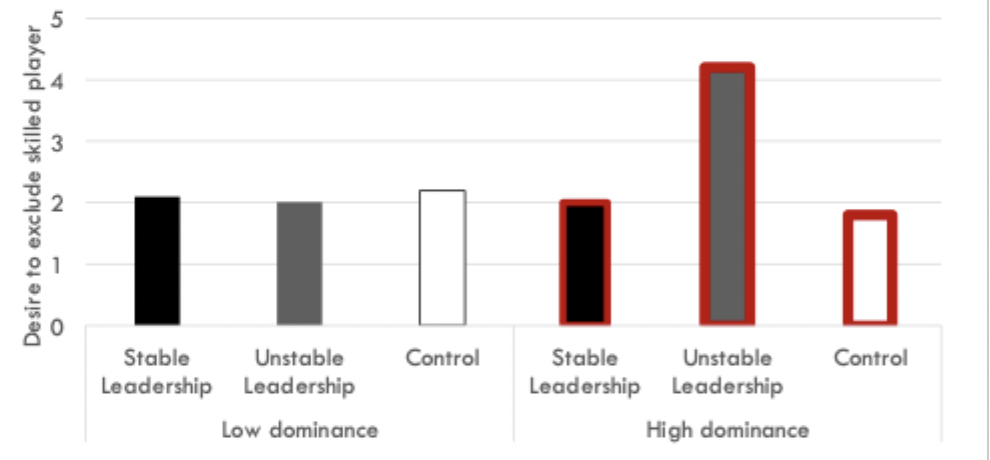
What can be concluded from Maner and Mead’s unstable leadership study?
Unstable leadership led dominance-oriented individuals to act in their own self interest, undermining group member performance and excluding highly skilled individuals
Group-based dominance occurs across many societies, based on…
ethnicity
religion
gender
etc
What are 3 ways in which group base dominance exerts itself
via force (e.g. internment camps)
outgroup derogation (e.g. disproportionate punishment of specific groups)
ingroup bias (e.g. better provisions for healthcare or education)
What are the three theories that try to account for group-based dominance?
Social identity theory
social dominance theory
system justification theory
What is the theoretical basis of social identity theory?
Groups provide us with a social identity
who we are
who we ostensibly should be
What are the three things that group identity/ salience increased through a process of categorisation?
(self-)stereotyping: think of ourselves as possessing the traits of the group
depersonalisation
perceived intergroup difference
What are the three ways we strive for positive distinctiveness within the social identity approach?
individual mobility (if groups are permeable)
social creativity (change the rules)
social competition (ingroup favouritism)
How do minimal group paradigms provide support for the Social Identity Approach?
manipulation with group assignment into arbitrary groups. For example, based on: high vs low estimators, estimation accuracy, aesthetic preferences or even scarf colour
and then measured using monetary distribution to see if in-group favoured
What is the theoretical basis of social dominance theory?
Group-based hierarchies exist across societies
some have positive social value (access to power, wealth, healthcare, etc)
some have negative social value (substandard housing, underemployment etc)

How is discrimination coordinated in social dominance theory? The assymmetry hypothesis
Discrimination coordinated via legitimising myths
the asymmetry hypothesis: asymmetrical ingroup bias, more likely to endorse legitimising myths
What is social dominance orientation?
an individual orientation toward group-based dominance
What are some example items from the social dominance orientation scale? (screenshot)

What is the system justification theory?
system justification is the process by which existing social arrangements are legitimised, even at the expense of personal and group interest
What does system justification theory argue?
there is a general ideological motive to justify the existing social order
this motive is at least partially responsible for the internalisation of inferiority among members of disadvantaged groups (outgroup favouritism)
it si observed most readily at an implicit, nonconscious level of awareness
it is sometimes strongest among those who are most harmed by the status quo
System justification theory from the perspective of ego?
The desire to maintain a favourable self image, to feel valid, justified and legitimate as an individual
System justification theory with focus on system?
desire to imbue the status quo with legitimacy and to see it as good, fair, natural, desirable and even inevitable
System justification theory with focus on group?
the desire to maintain favourable images of one’s group and to justify the actions of ingroup members
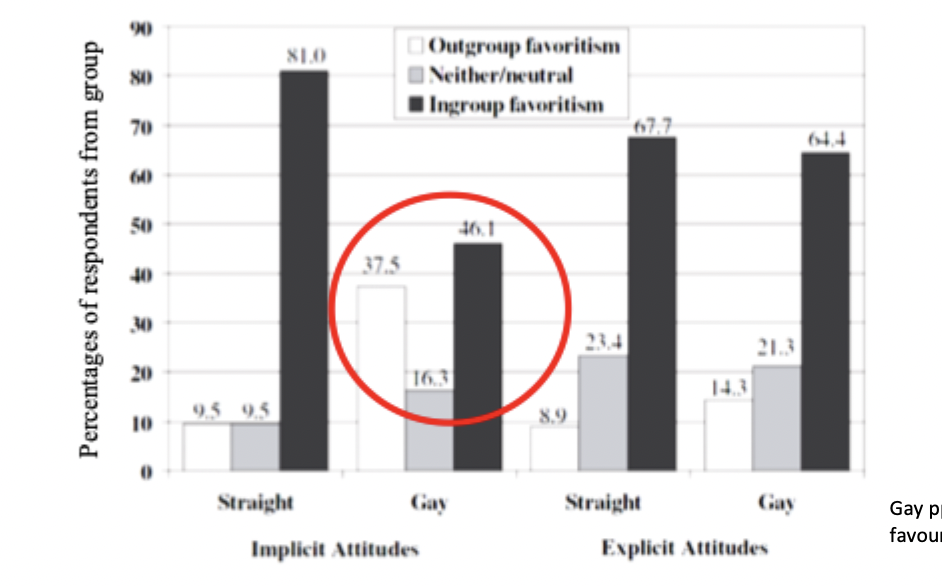
What was found studying gay and straight participants on outgroup favouritism among disadvantaged groups
gay ppts more likely to show outgroup favouritism on implicit measures
as political conservatism increases, members of high status groups will exhibit increased ingroup favouritism and members of low status groups will exhibit increased outgroup favoritism
Definition of obedience or coercive compliance?
a change in behaviour or expresses attitudes and beliefs
in response to the direct request of a powerful person or group
does not require internalisation
Definition of conformity
a change in behaviour or expressed attitudes or beliefs
in response to social norms or others’ behaviour
does not require internalisation
persuasion definition
a change in attitude, beliefs or behaviour
in response to direct messages
requires internalisation
What was the procedure in Milgram’s classic experiments?
An experimenter a teacher and a learner
the ppt is the teacher. The learner is a confederate
the learner is completing a memory test. for every wrong answer, the teacher is instructed to deliver the learner a shock, which gets stronger each time
critical measure: how far does the teacher go before he/she refuses to continue
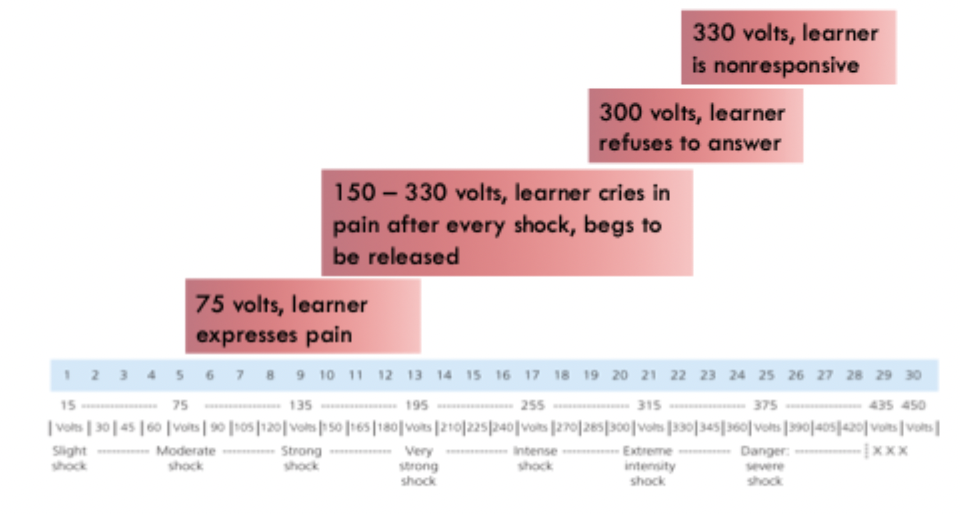
What were milgram’s key results?
experts predicted that few people would complete the experiment
but 65% in the original studies continued to deliver the shocks until the end
this pattern has been replicated, even in recent years
When did disobedience increase in Milgram’s variations?
disobedience increased when
experimenter provided no explicit direction to increase shocks
a group of teachers (confeds) pressured the participant to disobey
the teacher was proximal to the learner
the experimenter was no physically present
the teacher and learner were friends or relatives
experimenters were inconsistent (providing conflicting instructions)

What are 5 explanations that could be applied to milgrams findings?
blind obedience to powe
diffusion of responsibility
the psychology of sunk cost
conformity to group norms (SIT)
persuasion
What is the situationist account for Milgram’s findings?
often it is not so much the kind of person a man is as the kind of situation in which he finds himself that determines how he will act
Hannah Arendt’s account of Milgram’s findings
her writings on Eichmann and the “the banality of evil” are often associated with the Milgram studies
but personal responsibility was central to her arguments
“there is no such thing as obedience in political and moral matters”