Understanding Addiction and Substance-Related Disorders
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
What is drug addiction characterized by?
Compulsive, uncontrollable drug seeking and use despite harmful consequences.

What does the term 'addiction' derive from?
A Latin term for 'enslaved by' or 'bound to'.

True or False: People who are addicted to substances are morally flawed and lack willpower.
False.
True or False: There are functional changes to brain circuits involved in reward, stress, and self-control with addiction.
True.
True or False: The best way to treat addiction is to publicly shame and punish those who are afflicted.
False.
What are some reasons people take drugs?
To feel good (euphoria), feel better (cope with stress), do better (improve performance), experimentation, curiosity, social pressure, and loneliness.
Is the initial decision to take drugs typically voluntary or involuntary?
Typically voluntary.
What happens to a person's ability to exert self-control with continued drug use?
It can become impaired.
What is the reward pathway in relation to addiction?
It motivates a person to repeat behaviors needed for survival, such as eating and sex.
What neurotransmitter is involved in the euphoria experienced from drug use?
Dopamine.
How does repeated drug use affect the brain's reward circuit?
The brain adapts by reducing the cells in the reward circuit to respond, leading to tolerance.
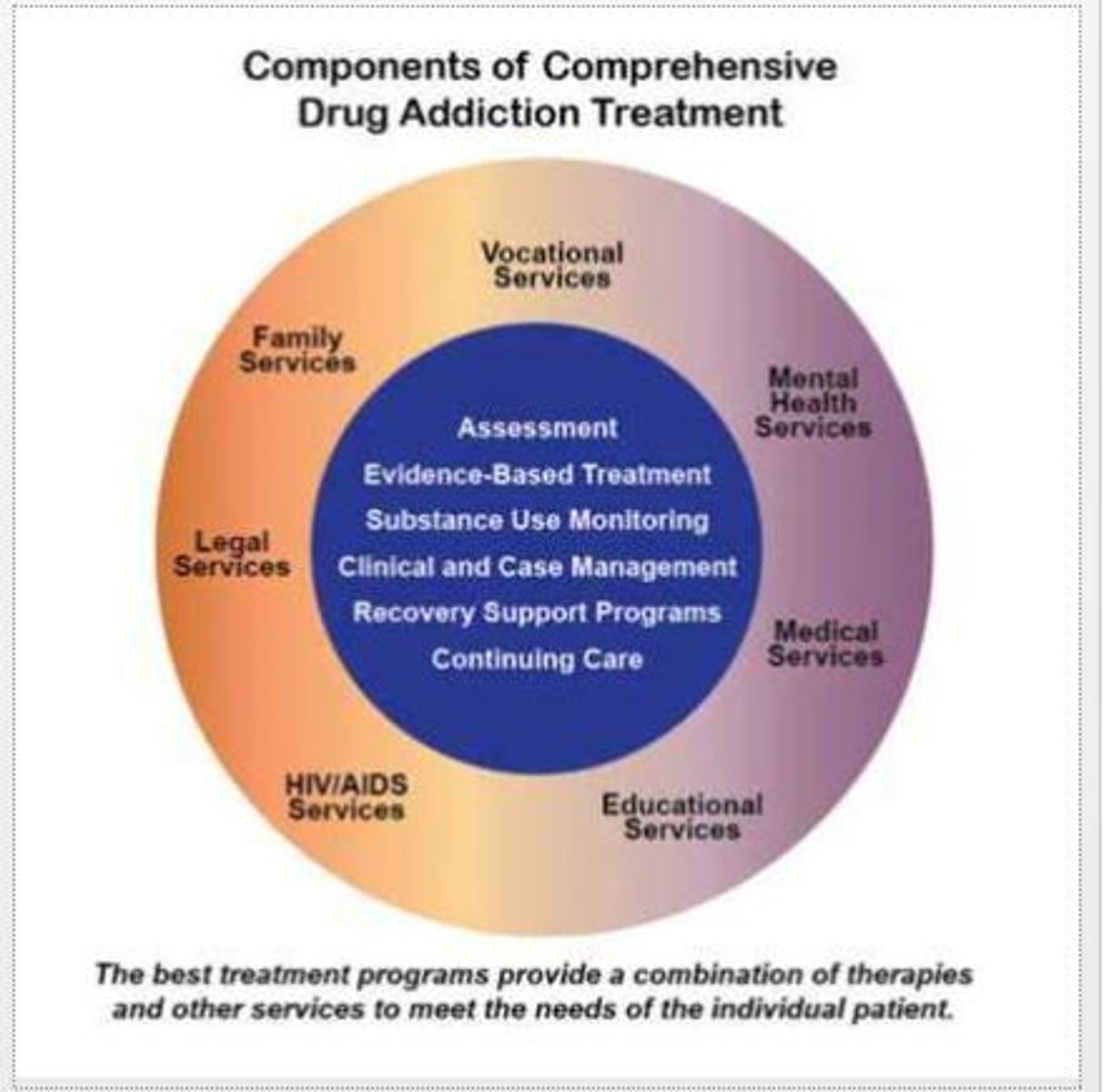
What does tolerance mean in the context of drug use?
The need to take more of the drug to achieve the same effect.
What happens to a person's ability to derive pleasure from other activities with continued drug use?
They become less able to derive pleasure from activities once enjoyed, such as food, sex, and social interactions.

What is the relationship between drug use and reinforcement of pleasurable behaviors?
Surges of dopamine reinforce pleasurable behaviors, making them more likely to be repeated.
What is the impact of addiction on behavior?
It can lead to harmful behaviors and a relapsing disease.
What is the role of social pressure in drug use?
It can contribute to experimentation and curiosity about drugs.
Can a single factor determine whether a person will become addicted to drugs?
No, no single factor determines addiction.
What are some functional changes that occur in the brain due to addiction?
Changes in circuits involved in reward, stress, and self-control.
What is the significance of euphoria in drug use?
It is a primary reason why people initially take drugs.
What does addiction lead to in terms of personal behavior?
It leads to compulsive drug-seeking behavior despite negative consequences.

What is the chronic nature of addiction?
It is a relapsing disease that can lead to long-term changes in brain function.
What are the diagnostic characteristics of substance use disorders related to impaired control?
Impaired control includes taking the substance in larger amounts or over a longer period than intended, persistent desire to cut down or regulate use, spending a great deal of time obtaining, using, or recovering from effects, and experiencing cravings.
What social impairments are associated with substance use disorders?
Social impairments include recurrent use resulting in failure of work, school, or home obligations, continued use despite social or interpersonal problems, and giving up or reducing important social, occupational, or recreational activities.
What are the risks associated with the continued use of substances despite knowledge of problems?
Risks include using substances in physically hazardous situations and continuing use despite knowing it causes physical or psychological problems.
What pharmacologic effects are noted in substance use disorders?
Tolerance develops, requiring more of the substance to achieve the desired effect, and withdrawal syndrome may occur when blood or tissue concentration declines.
List the ten diagnostic categories of substances.
Alcohol, Caffeine, Cannabis, Hallucinogens, Inhalants, Opioids, Sedatives/Hypnotics/Anxiolytics, Stimulants, Tobacco, and Unknown.
What are the most commonly abused substances and their user statistics?
Commonly abused substances include Alcohol (136.7 million users), Cigarettes (63.4 million), Marijuana (23.9 million), Painkillers (3.5 million), and others like tranquilizers, cocaine, and stimulants.
What is comorbidity in the context of substance use disorders?
Comorbidity refers to the presence of other mental health disorders in individuals who abuse substances, which may result from long-term substance use or predispose individuals to substance abuse.
What are the effects of alcohol on the nervous system?
Effects include diminished brain size and functioning, organic brain disorders, blackouts, neuropathies, and gait disturbances.
What are the signs and symptoms of alcohol withdrawal?
Signs include autonomic hyperactivity, hand tremor, insomnia, nausea/vomiting, transient visual or tactile hallucinations, psychomotor agitation, anxiety, and generalized tonic-clonic seizures.
What nursing interventions are important for managing alcohol withdrawal?
Nursing interventions include assessing vital signs, using CIWA-Ar for monitoring, and administering medications such as benzodiazepines, anticonvulsants, thiamine, and magnesium.
What are the long-term cardiovascular effects of alcohol?
Long-term effects include cardiomyopathy, hypertension, arrhythmias, and stroke.
What are the gastrointestinal effects of long-term alcohol use?
Gastrointestinal effects include liver diseases, pancreatitis, GI ulcers and bleeds, esophageal varices, and cancers of the upper GI tract.
What are the effects of stimulants like cocaine and methamphetamine?
Stimulants increase dopaminergic activity causing euphoria and psychotic symptoms, and can lead to tachycardia, hypertension, and elevated body temperature.
What are the withdrawal symptoms associated with amphetamines?
Withdrawal symptoms include fatigue, vivid unpleasant dreams, insomnia or hypersomnia, increased appetite, and psychomotor retardation or agitation.
What are the effects of marijuana (cannabis) use?
Effects include euphoria or dysphoria, relaxation, heightened perception, poor coordination, cravings, and disorientation.
What withdrawal symptoms are associated with marijuana?
Withdrawal symptoms include irritability, anxiety, sleep difficulties, decreased appetite, restlessness, and depressed mood.
What are synthetic cannabinoid compounds and their effects?
Synthetic cannabinoids like Spice and K2 are human-made chemicals that can produce stronger effects than marijuana and have unpredictable and dangerous outcomes.
What are the effects of phencyclidine (PCP) use?
Effects include dissociation, numbness, disorientation, hallucinations, and increased blood pressure and heart rate.
What are the signs of intoxication from PCP?
Signs include nystagmus, hypertension, ataxia, muscle rigidity, and seizures.
What are the effects of hallucinogens like MDMA and LSD?
Effects include increased heart rate, nausea, intensified experiences, and changes in the sense of time.
What is the significance of the CIWA-Ar scale?
The CIWA-Ar scale is used to assess the severity of alcohol withdrawal symptoms.
What role does thiamine play in alcohol withdrawal treatment?
Thiamine (Vitamin B1) is administered to decrease ataxia and other symptoms of deficiency during alcohol withdrawal.
What are the potential medical problems associated with substance use?
Medical problems include overdose, homicide, suicide, infections, and various health complications.
What are the effects of alcohol on the immune system?
Alcohol impairs immune functioning, leading to increased susceptibility to infectious diseases.
What are the effects of alcohol on the integumentary system?
Effects include skin lesions and increased risk of traumatic injury.
What are the effects of alcohol on the musculoskeletal system?
Effects include traumatic injury and myopathy.
What are the effects of alcohol on the genitourinary system?
Effects include hypogonadism and erectile dysfunction in men.
What are common symptoms of Other Hallucinogen Use Disorder intoxication?
Pupillary dilation, tachycardia, sweating, palpitations, blurring of vision, tremors, and incoordination.
What is Persistent Psychosis in the context of hallucinogen use?
A series of continuing mental problems including visual disturbances, disorganized thinking, paranoia, and mood changes.
What is Hallucinogen Persisting Perception Disorder (HPDD)?
Flashbacks of certain drug experiences, including hallucinations or other visual disturbances, which can occur without warning.
What substances are classified as opioids?
Heroin, codeine, morphine, and opioid pain medications.
What are the effects of opioids on the body?
They produce pleasure and pain relief, cause tolerance and physical dependence.
What are the signs of opioid overdose?
Respiratory depression, stupor, and coma.
What are the symptoms of opioid intoxication?
Pupillary constriction or dilation, drowsiness, slurred speech, and impairment in attention or memory.
What are common withdrawal symptoms of opioids?
Dysphoric mood, nausea, muscle aches, lacrimation, pupillary dilation, sweating, diarrhea, yawning, fever, and insomnia.
What is the purpose of opioid detoxification?
To gradually reduce the dose of opioids over several days or weeks.
What medications are used in opioid detoxification?
Methadone (full opioid agonist) and buprenorphine (partial opioid agonist) to reduce cravings.
What are the symptoms of sedative, hypnotic, or anxiolytic withdrawal?
Autonomic hyperactivity, hand tremor, insomnia, nausea, visual or tactile illusions, psychomotor agitation, anxiety, and grand mal seizures.
What are the signs of intoxication from sedatives, hypnotics, or anxiolytics?
Slurred speech, incoordination, unsteady gait, nystagmus, impairment in cognition, and stupor or coma.
What are inhalants and their effects?
Organic solvents that are CNS depressants, causing dizziness, nystagmus, incoordination, and euphoria.
What is 'sudden sniffing death' associated with inhalants?
Inhaled fumes replace oxygen in the lungs and CNS, causing suffocation and may lead to cardiac arrhythmia.
What are common withdrawal symptoms from inhalants?
Anxiety, tremors, hallucinations, and sleep disturbances.
What are the effects of tobacco use disorder?
Nicotine stimulates the adrenal glands, increasing blood pressure, breathing, and heart rate.
What are withdrawal symptoms of nicotine?
Irritability, anxiety, difficulty concentrating, increased appetite, restlessness, depressed mood, and insomnia.
What are the symptoms of caffeine intoxication?
Tachycardia, periods of inexhaustibility, psychomotor agitation, restlessness, and insomnia.
What are common withdrawal symptoms from caffeine?
Headache, marked fatigue, dysphoric mood, difficulty concentrating, and flu-like symptoms.
What are anabolic steroids and their effects?
Synthetic substances related to male sex hormones that promote muscle growth and can cause increased irritability, aggression, and mood swings.
What constitutes prescription and OTC drug abuse?
Taking medication prescribed for someone else, in higher quantities, or for nonmedical purposes.
What is gambling disorder?
Persistent and recurrent maladaptive gambling behavior that disrupts personal, family, and vocational pursuits.
What are some key nursing assessments in addiction treatment?
Determine level of use, patient's denial or acceptance of treatment, and involve family/friends.
What is motivational interviewing in addiction nursing?
A therapeutic intervention that elicits self-motivational statements from patients to support behavior change.
What is the role of psychoeducation in addiction treatment?
Educating patients about medications, signs of intoxication, overdose, withdrawal, and available treatment programs.
What is denial in the context of substance use?
The patient's inability to accept their loss of control over substance use or the severity of consequences associated with it.
What are effective nursing interventions for confronting denial?
Gentle and direct approaches that encourage expression of feelings without being judgmental or punitive.
What are the four stages of the Transtheoretical Model?
Pre-contemplation, Contemplation, Preparation, Action, Maintenance.
What characterizes the Pre-contemplation stage in the Transtheoretical Model?
Individuals typically don't consider their behavior to be a problem.
What happens during the Contemplation stage of the Transtheoretical Model?
Individuals might be thinking about making a change in their behavior.
What does the Preparation stage involve in the Transtheoretical Model?
The person has moved forward to planning and preparing for carrying out changes.
What occurs during the Action stage of the Transtheoretical Model?
The change of behavior starts to happen.
What is the focus of the Maintenance stage in the Transtheoretical Model?
Sustaining the behavior change.
What is a key predictor of whether individuals will change their substance use behavior?
Motivation.
How is motivation described in the context of behavior change?
A goal-oriented attitude that propels action for change, helps sustain new activities and behaviors, and is fluid and modifiable.
What is ambivalence in the context of motivation for change?
Ambivalence about change is normal.
What does treatment for substance use involve?
A partnership between health care providers, the individual, and family.
What is the purpose of detoxification in substance use treatment?
To manage physical and psychological withdrawal symptoms.
What is a relapse in the context of substance use?
Recurrence of substance use behavior after a period of abstinence.
What are some common treatments for substance use?
Detox, Medication Assisted Treatment (MAT), Behavioral counseling, modifying attitudes and behaviors, increasing healthy life skills, evaluating co-occurring mental health issues, and long-term follow-up.
What is Disulfiram (Antabuse) used for in alcohol misuse treatment?
It interferes with the degradation of alcohol, causing unpleasant reactions if alcohol is consumed.
What precautions must be taken when administering Disulfiram?
Never administer to an intoxicated patient or without the patient's knowledge; abstain from alcohol for at least 12 hours.
What is the role of Naltrexone in alcohol misuse treatment?
It binds to opioid receptors in the CNS, reduces cravings, and helps maintain abstinence.
What is Campral used for in alcohol treatment?
To maintain abstinence from alcohol by reducing symptoms of insomnia, anxiety, restlessness, and dysphoria.
What is Naloxone and when is it used?
An opioid antagonist given as a rescue drug for extreme drowsiness, slowed breathing, and loss of consciousness.
How does Naloxone work in emergency situations?
It reverses respiratory depression.
What medications are used for Opioid Use Disorder in Medication Assisted Treatment?
Methadone and Buprenorphine.
What effects do Methadone and Buprenorphine have?
They suppress opioid withdrawal and block the effects of illicit opioids.
What is Naltrexone and its role in opioid treatment?
Naltrexone is a long-acting opioid antagonist that reduces opioid cravings, blocks the effects of opioids, and requires detoxification before use.
What are the goals of Brief Interventions in substance use treatment?
The goal is to reduce risky substance use before individuals become dependent or addicted, through negotiated conversations and harm reduction strategies.
What is the focus of Group Interventions in substance use treatment?
Group Interventions focus on maintaining sobriety and using problem-solving skills to deal with stressful events that threaten abstinence.
What is the purpose of Individual Therapy in substance use recovery?
Individual Therapy discusses treatment goals, reviews fears and anxieties related to recovery, and devises healthy responses to stressors.