Halogenoalkanes
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is a haloalkane
An alkane where at least one hydrogen has been replaced with a halogen
What is primary halogenoalkane
If carbon boned to halogen is bonded to 1 carbon
What is secondary halogenoalkane
If carbon boned to halogen is bonded to 2 carbon
What is tertiary halogen
If carbon boned to halogen is bonded to 3 carbon
Whta is general formula for halogenoalkane
CnH2n+1X. X=halogen
What IMF forces do halgoalkanes
Experience permant dipole-dipole forces and Van der Waals so polar molecules
What happens to MP and BP as length of carbo chain increases
Van der Waals strength increases so MP and BP increases
Solubility of halogenoalkanes
halogenoalkane are polar so slightly soluble in water - hydrogen bond between water molecules tend to be stronger than permeant dipole-dipole forces
What happens to solubility as length of carbocation increases
Solubility decreases
What reaction mechanism for halogenoalkane
nucleophile substation
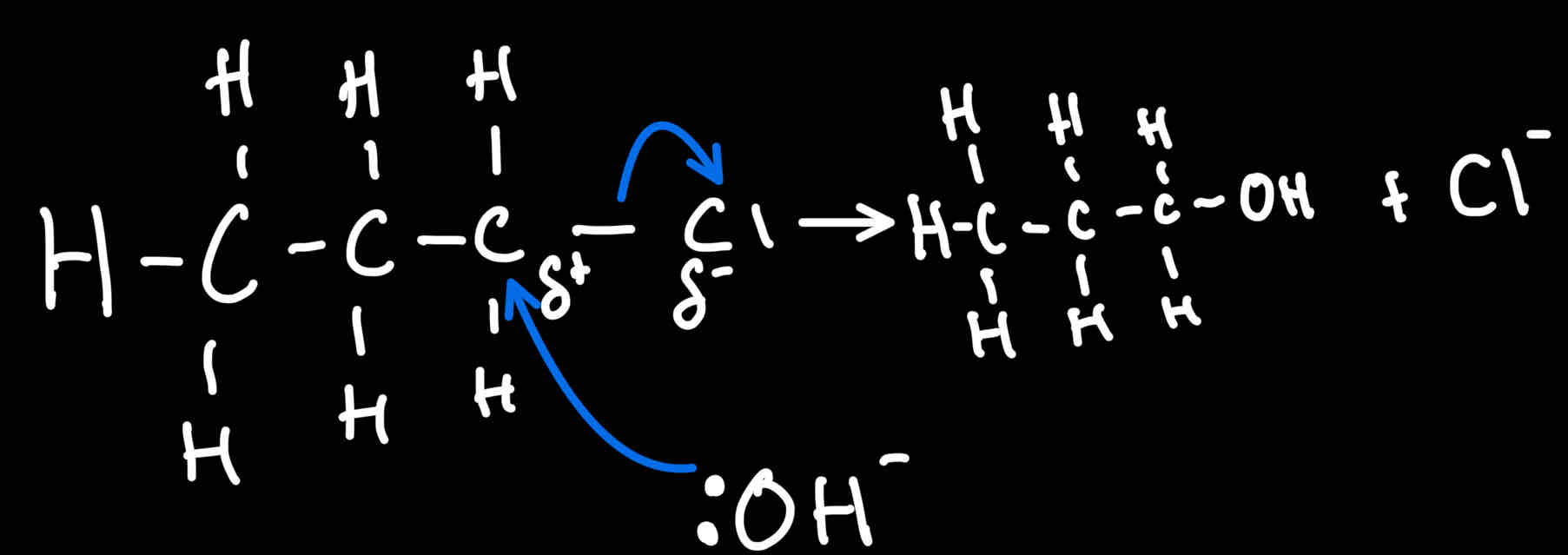
What conditions for reaction of halogenoalkanes → alcohols
-NaOH/KOH
Heat
What conditions for reaction of Halogenoalkane → nitrile
NaCN / KCN dissolved in ethanol
And heat
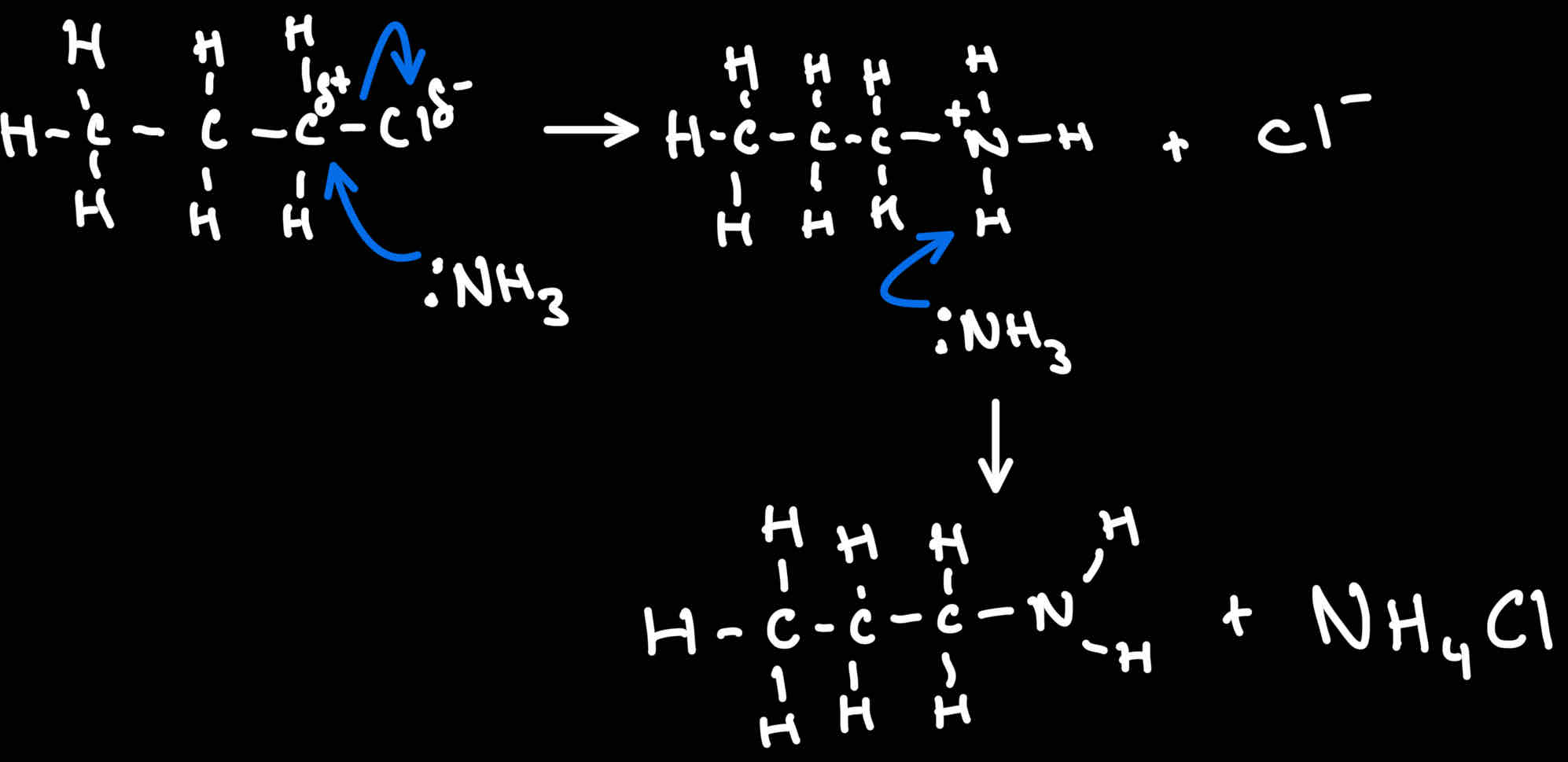
What conditions for Halogenoalkanes → 1 degree Amine
Heat under pressure
Excess ammonia
Why must have excess ammonia for Halogenoalkanes → 1 degree Amine
Excess to prevent further reaction of amine product
Reaction mechanism for Halogenoalkanes → Alcahol
Reaction mechanism for Halogenoalkanes → Nitrile
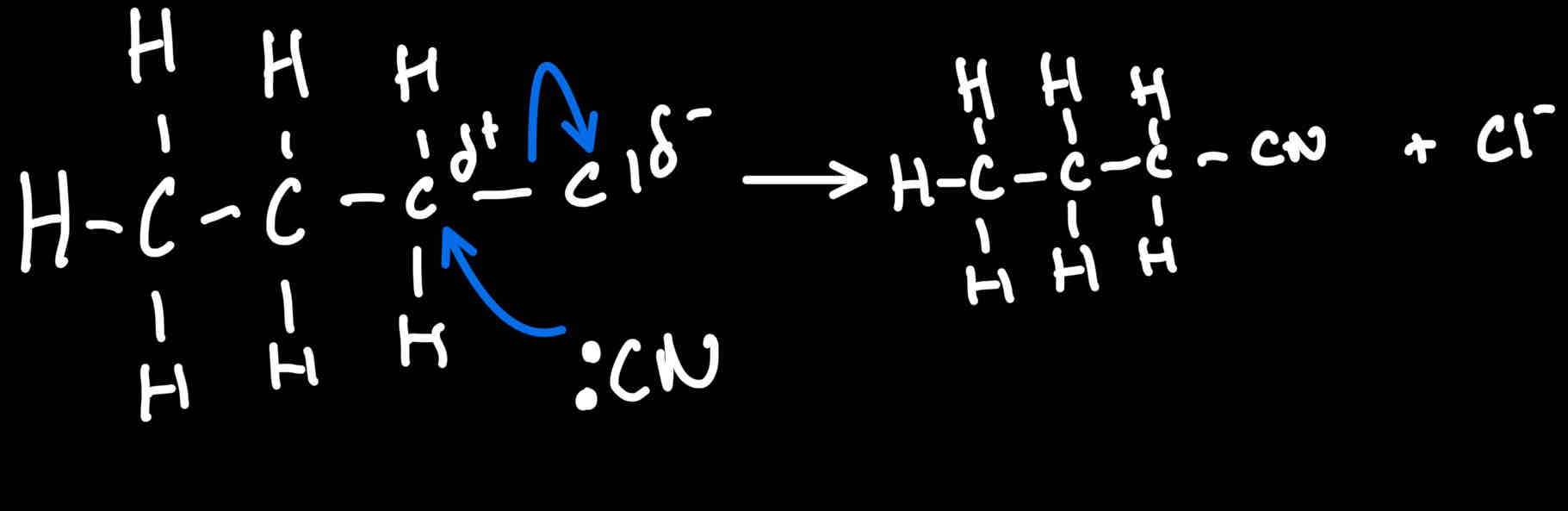
Reaction mechanism for Halogenoalkanes → 1 degree amine
Rate of reaction for halogenalkanes
The lower the bond enthalpy → less energy for activation energy → more collisions will be successful→ increase rate of reaction
List of hughest enthalpy to lowest enthalpy
C -F → highest enthalpy - slowest reaction
C - Cl
C - Br
C - I → lowest enthalpy - fastest reaction
How to measure reactivity
Dissolve compound in ethanol
Add AgNO3 and water
Measure time taken for silver nitrate and halogen precipitate to form
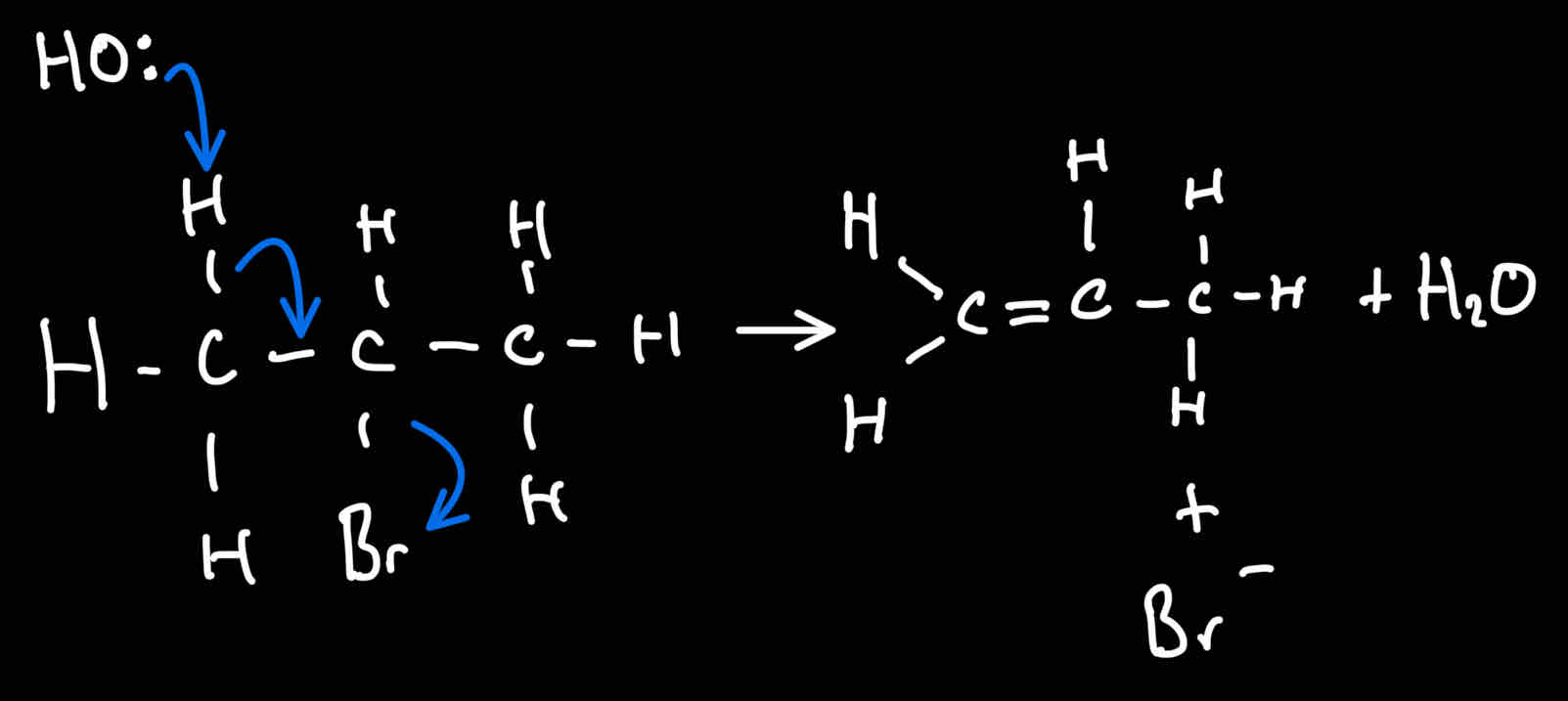
Elemimatiom reaction of halogeno alkanes
Halogenoalkane → alkene
Conditions for halogenoalkene → alkenes
NaOH/akOH dissolved in ethanol
Reaction is heated
Reaction mechanism for elimination reaction for elimination reaction of halogenoalkenes
What is hetrofission and what does it form
If a covalent bond breaks and both bonding electrons go to one atom
2 ions formed
Shat is homolytic fission and what does if form
If a covalent bond break and a electron goes to each atom
Product:2 free radicals
What is a free radical
Any species that contains unpaired electrons
X•
What is easiest way to form free radicals
UV light or high temp
What makes the it more likely a bind to go homolytic fission
The lower the bond enthalpy
Property of free radicals
Incredibly reactive
What forms when 2 free radicals
A molecule
A• + B• → A-B
What forms when a free radical and a molecule collide
A free radical and a new molecule
A• + B-B → A
Alkanes react with halogens in prescene of of UV loght to form
Halogenoalkane
What are 3 steps of free radical susbistition
Initiation
Propagation
Termination
What happens in initiation for CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
X2 → 2X•
What happens during propagation for CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
Cl• + CH4 →HCl + CH3•
CH3• + Cl2 → CH3Cl + Cl•
Termination step for CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl
Any of the free radicals react together
Cl• + Cl• → Cl2
Cl• + CH3• → CH3Cl
CH3• + CH3• → CH3CH3
Disadvantage of free radicals substitution
Very hard to control ( free radical too reactive)
In reality multiple products are formed
What is a chlorofluorocarbons
Compound that contains chlorine fluorine and carbon
What were chlorofluorocarbons used for
Refrigerators , solvents
Initiation for O zone deple
C2F4Cl2 → C2F4Cl• + Cl•
Propagation for ozone depleted
Cl• + O3 → ClO• +O2
ClO• + O3 → 2O3 + Cl•
Termination for Ozone depletion
2 free radical reacting
What is alternative of hydro fluorocarbons
Hydrocarbons
Why are hydrocarbons better
Contain stronger bond → less likely to break under UV light
Cannot produce Cl•