Anatomy Lecture Quiz 2
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Osteogenic Cells
(Osteoprogenitor) Mitotically active stems cells found in the membranous periosteum and endosteum
Osteoblast Cells
bone forming cells that secrete the bone matrix
Osteocytes Cells
Mature bone cells that occupy Lacunae (space within the bone matrix) of which they monitor and maintain
Bone Lining Cells
flat cells found on the bone surface thought to help maintain the matrix
Osteoclasts
giant multinucleate cells located at the sites of cell resorption and are generated from the same hemopoietic stem cells that differentiate into macrophages
What are bone lining cells called on the external surface?
Periosteal cells
What are bone lining cells called on the lining on the internal surface?
Endosteal cells
Which cells contributes into making bone-lining cells?
osteoblasts and osteocytes
Reticular (Connective) Tissue
These fibers wrap around adipocytes
Where is the reticular tissue located?
Lymphatic tissue (Lymph nodes), Hematopoietic Tissue (Liver), and Spleen
Cartilage
Made up of collagen and elastin fibers embedded in a matrix
Which cartilage is the strongest and where is it found?
Fibrous Cartilage and it is found in the pelvis, skull, and vertebral discs
Which Cartilage is the weakest and where is it found?
Hyaline Cartilage and it is found at the end of long bones and on the ventral ends of ribs,
Loose Connective Tissue
Fibers and many cell types in gelatinous matrix, found in skin, and surrounding blood vessels, nerves, and organs
Dense Connective Tissue
Bundles of parallel collagen fibers and fibroblasts, found in tendons and ligaments
Areolar Connective Tissue (loose) Function
Wraps and cushions Organs; its macrophages phagocytize bacteria; plays important role in inflammation; holds and conveys tissue fluid
Adipose Tissue (loose) Function
Provides reserve food fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs
Adipose Tissue (loose) Location
Under skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, within abdomen and in breasts
Adipose Tissue
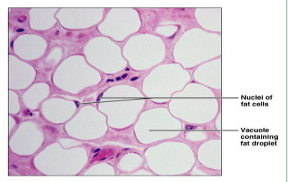
Areolar (Connective) Tissue Location
Widely distributed under epithelia of body e.g. forms lamina propria of mucous membranes; packages organs; surrounds capillaries
Areolar Tissue
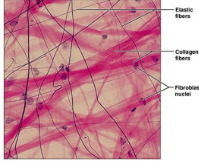
Fibers
Reticular, Collagen, and Elastic
Reticular
A fishing net structure web of interreacted fibers (bone marrow, kidney, spleen, liver, lymph nodes
Collagen
Thick and Juicy (skin, bones, tendons, ligaments)
Elastic
Thin yet strong and scattered (skin, lungs, viens)
Extra Cellular Matrix
Made up one 1 collagen
Neuroglial cells
Cells that provide metabolic support and immune protection for neurons
How many muscle tissues are there?
3
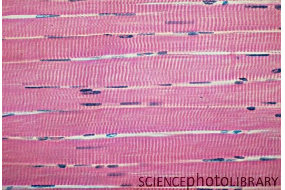
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary, striated, striations perpendicular to the muscle fibers and it’s mainly found attached to the bones
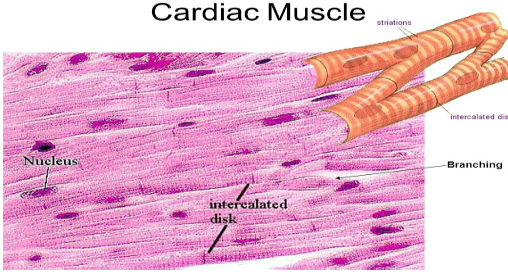
Cardiac Muscle
Involuntary, straited, branched and has intercalated discs
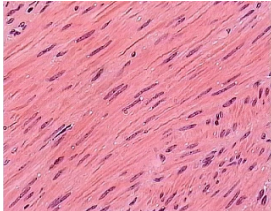
Smooth Muscle
Involuntary, nonstriated, spindle shaped and is found in blood vessels and the G1 tract. (Nuclei is elongated)
Smooth Muscle
Cardiac Muscle
Skeletal Muscle
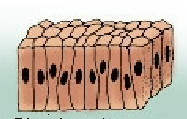
Epithelial Tissue
Made of cells arranged un a continuous sheet with one or more layers, has apical and basal surfaces
Simple Squamous

Simple Cuboidal

Simple Columnar
Includes Stillia and is a tall or cylindrical cell
True or False: All Ciliated cells are columnar but not all columnar cells are ciliated
True
White Blood cells are also called what?
Leukocytes or Leucocytes
Neutrophils
Mulit-load nuclei cell, and a bright blue/pinkish background which is lighter
Eosinophils
By load, and dark vein background
Basophils
Looks like a mass cell and cancel in granulations
Lymphocytes
Dark on the inside and on the outside, there is a clear fluid
Monocytes
Takes up 2/3 of cell and rest is clear
Connective Tissue Matrix is made up of what?
Ground Substance and Fiber
Ground Substance is made up of what?
Proteins and Polysaccharides
Fibroblasts
Type of cell that is responsible for making the extracellular maxtrix and collagen
Basophil characteristics
Responsible for inflammatory reactions during immune response