Gait and Walking
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
sensory; motor
gait is an interaction between _____ and _____ functions
true
T/F: the gait cycle is a repetitive pattern involving steps and strides
heel strike
the gait cycle begins at _____ _____
same
the gait cycle ends with the ______ heel strike
stride
sequence of movements between successive heel strikes of the same foot
stride length
distance between two successive heel strikes of the same foot
step
sequence of movements between successive heel strikes of opposite foot
step length
sequence of movements between heel strikes of opposite foot
step width
the lateral distance between heel centers
3-4 in
what is normal step width when walking?
foot angle
the amount of toe out during gait cycle
5-7 degrees
what is the normal amount of toe out during gait?
3 mph
what is normal walking speed?
110 steps/min
what is normal step rate?
28 in
what is normal step length?
2-3 in
what is normal step width when running?
0%
the first heel strike is at what percent of the gait cycle?
100%
the second heel strike is at what percent of the gait cycle?
60%
stance phase makes up what percent of the gait cycle?
40%
swing phase makes up what percent of the gait cycle?
10%
only ______ percent of the gait cycle is double limb contact/support
AP
the pelvis has a small short arc rotation in _____ tilt during gait
- subject to hyper/hypo mobility of SI joints and lumbar spine
30; 10
what is the normal amount of hip flexion and extension during gait?
pelvic; lumbar
hip restrictions during gait usually manifest as _____ and ______ deviations
5 degrees
how many degrees of knee flexion is there at heel strike?
20 degrees
after heel strike, how much does the knee flex during the stance phase?
35 degrees
how many degrees of knee flexion is there during toe-off?
0-5 degrees
how many degrees of PF is there at the ankle during heel strike?
10 degrees
how many degrees of DF is there during the stance phase at the ankle?
20 degrees
how many degrees of PF is there during push off at the ankle?
extended
the first MTP is slightly _______ at heel strike
60 degrees
what is the normal amount of MTP extension during heel off?
consequences
______ to great toe abnormality:
- toe out gait pattern
- inefficient push off phase
- medial knee and medial foot arch strains
true
T/F: at heel strike, the joints and muscles of the LE (and trunk) are reaching forward to propel the body
upper
at stance phase, controlled ankle and knee motions cushion weight transfer to the _____ kinetic chain
extend
during stance phase, the LE joints and muscles _____ to allow swing phase of the other limb
half
toe clearance at swing phase is less than _____ an inch
shortens
the swing limb (opposite to stance limb) _____ to clear the ground (hip/knee flexion)
drops
at right heel strike the left iliac crest ______ slightly before progressively moving upward
lowering
during the second half of the gait cycle, the relatively higher left iliac crest during the initial part of right swing phase reflects the controlled _____ of the right iliac crest by the left hip abductors when a person initially stands on the left LE
adduction
a drop in the left iliac crest contributes to right hip _____
abduction
a raise in the left iliac crest contributes to right hip _____
falls
during right LE weight acceptance the left iliac crest ____ due to gravity and eccentric contraction of the R hip abductors
concentric
when the left iliac crest is elevated above the right side after weight acceptance on the right, this is due to _____ hip abductor contraction
weakness
_____ of the hip abductors:
- poor eccentric control of contralateral glute med
- compensated trendelenburg
hip hiking
this occurs to clear the toe during the swing phase
limb
_____ length discrepancy:
- due to coxa valga/vara, congenital, h/o fx
-can be observed via palpation of iliac crests or supine to sit SI testing
- results in increased side flexion during each portion of gait cycle
small
due to ligaments and knee geometry, the total motion in the frontal plane at the knee is usually ______ but can have a large impact on regions above and below
valgus
we tend to have more _____ at the knee during swing
inverted; everts
the subtalar joint is _____ 2-3 degrees at heel strike and then rapidly _____ throughout stance phase (about 2 degrees)
inverts
the subtalar joint ______ just before heel off
internally
during heel strike through stance phase the pelvis, femur, and tibia all ____ rotate
externally; neutral
during toe-off through swing phase the femur and tibia _____ rotate and the pelvis gets closer to _____ rotation
internally; externally
during stance the hip ____ rotates and in toe off through the swing phase the hip ____ rotates
hypomobility
if there is no rotation at the hip it may signal _____ from OA, joint infection, capsular tightness, etc.
externally; internally
during heel strike the tibia _____ rotates and then from heel off to toe off the tibia ____
everts; inverts; everts
the subtalar joint _____ from heel strike to stance and then ____ from heel off to swing and then _____ again
pliability; stability
the midfoot has increased _____ from heel strike to mid-stance and has increased ____ from mid stance to heel off
1.33
the lowest energy expenditure per meter walked is at a speed of approximately _____ m/s (80 m/min)
increased
at higher and lower walking speeds there is _____ energy expenditure due to more muscle and ventilation force and co-contraction of muscles
decrease
canes/crutches/walkers can _____ efficiency of gait
high; increase
vertical GRFs are _____ at heel strike and then dip during stance due to forces being dispersed and then _____ again during push-off
anterior; posterior
AP GRFs are more _____ during heel strike and more ______ during push-off
increased
if there is rearfoot dysfunction there will be _____ ML GRF curves and higher energy expenditure
medial
the CoP follows the contours of the _____ arch of the foot
medially
if someone has pes planus the CoP moves ______
medial arch
tendons and plantar fascia work with bony structures to maintain the ______ _____ guiding the CoP path
posterior; PF
at heel strike the GRF falls _____ to the axis of rotation of the talocrural joint creating a ____ torque at the ankle. this requires an opposing DF torque to control the motion
laterally; eversion
at heel strike the GRF on the calcaneus is located _____ to the axis of rotation causing an _____ torque at the subtalar joint. this is partially controlled by the action of tib anterior (supinates/inverts foot)
PF; flexion; flexion
GRF at heel strike promotes ankle _____, knee ______, and hip ______
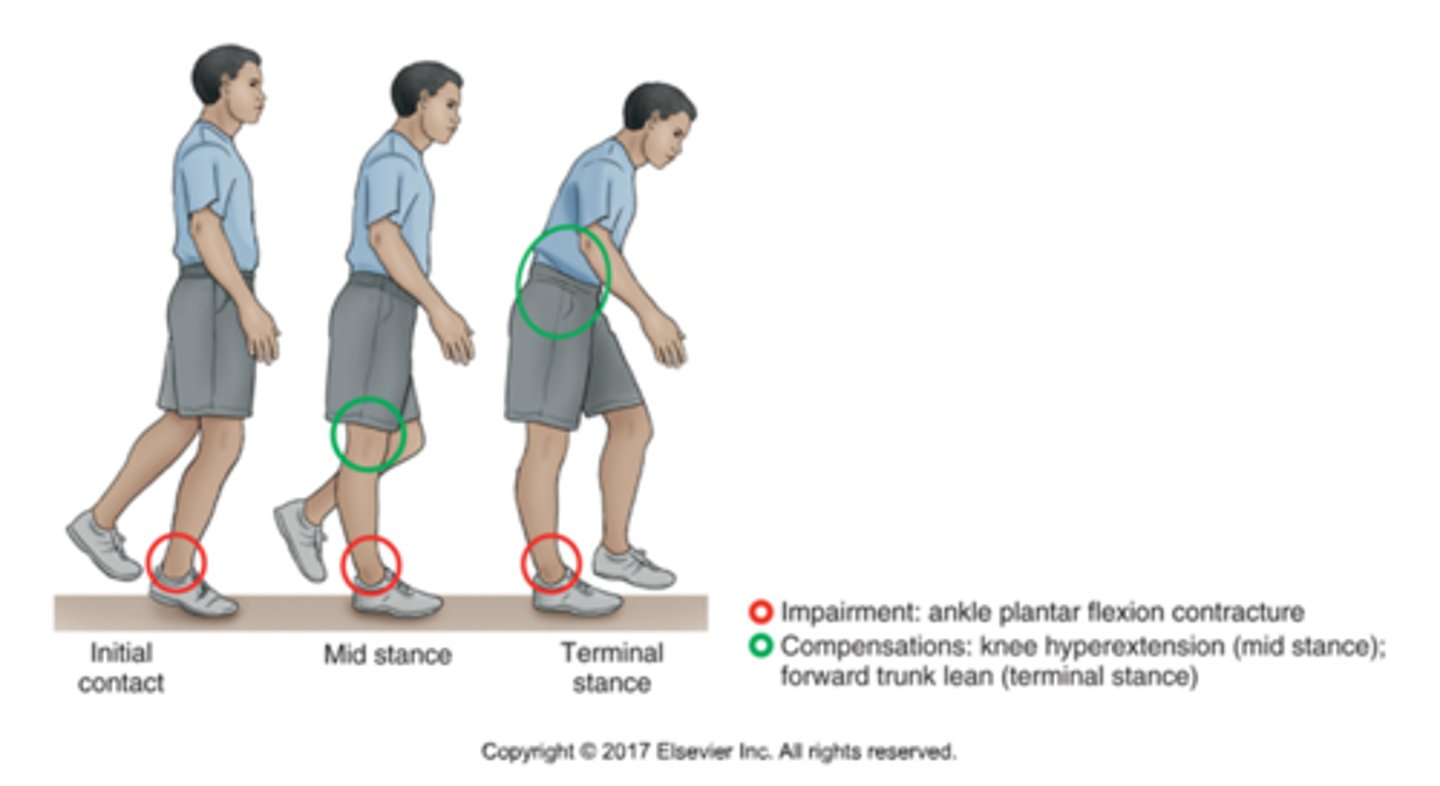
PF contracture
patient makes initial contact with the ground with the forefoot region
at mid-stance , bringing heel to the ground will result in knee hyperextension
forward lean of the trunk occurs in terminal stance as a strategy to maintain forward progression of the COM
will also have lumbar extension compensation at initial contact
weak ankle DF
may result in foot drop during swing phase
requiring excessive hip flexion for the toes to clear the ground during swing phase (hip hike on impaired side as well)
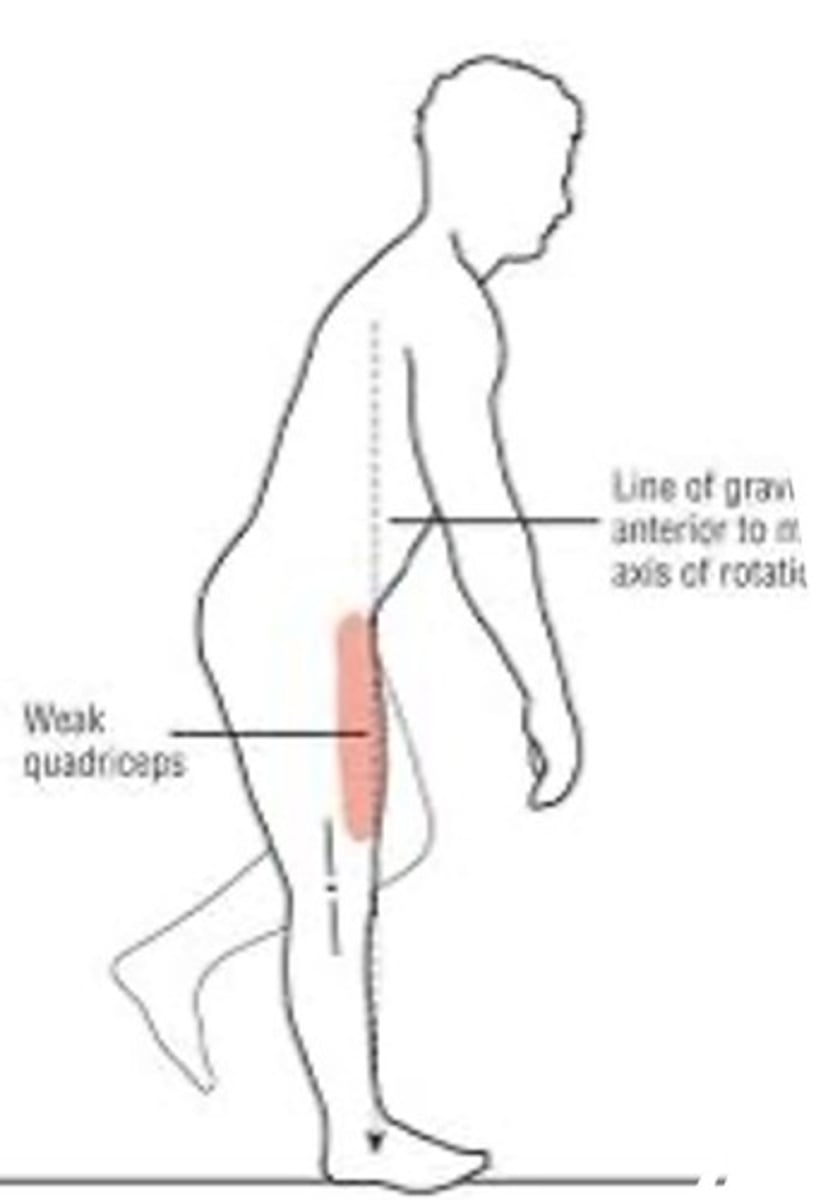
quad weakness
weakness in this muscle leads to anterior trunk lean to move COM of the body anterior to the axis of rotation of the knee
- weakness with active hip flexion
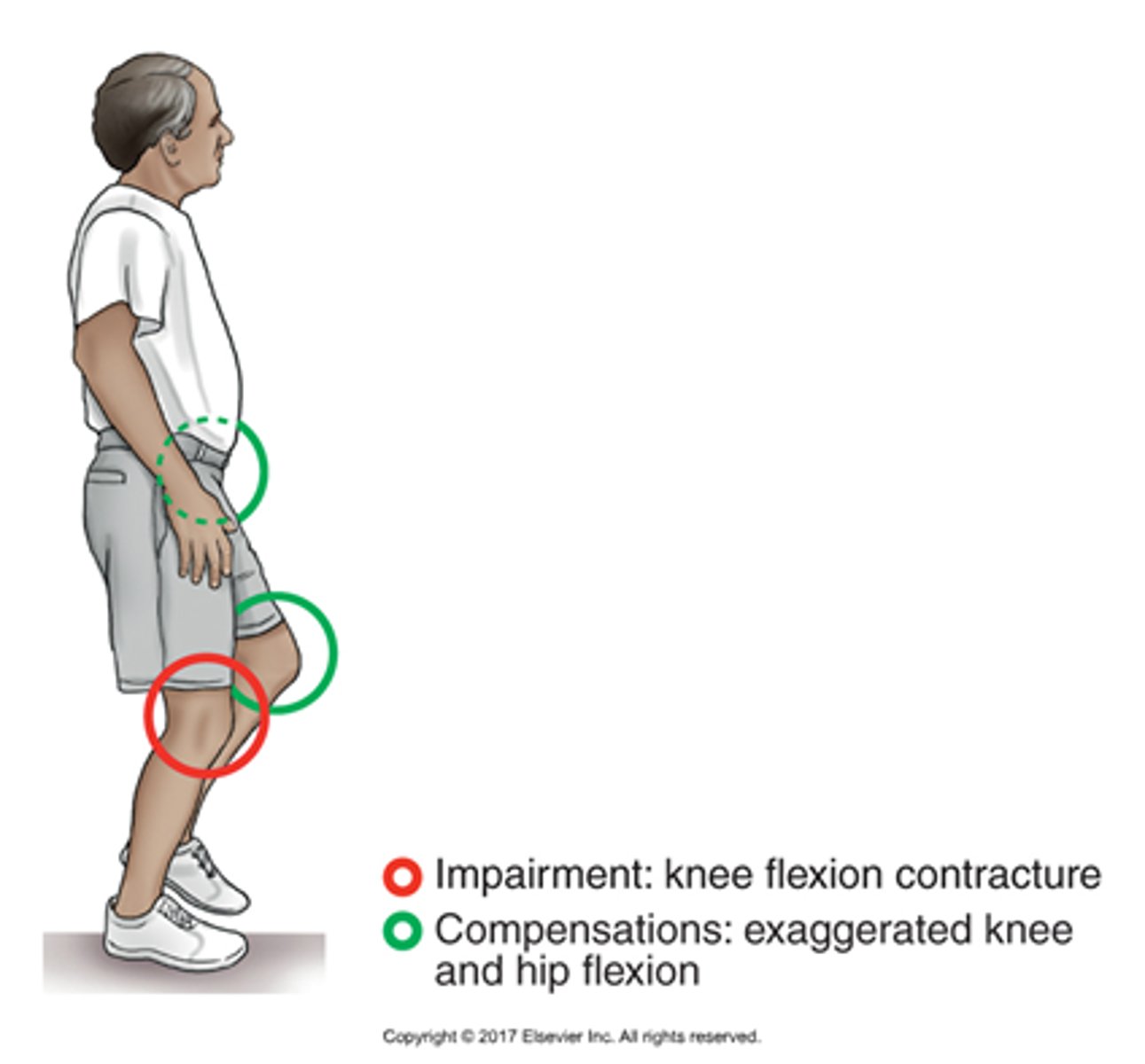
knee flexion contracture
results in a crouched gait of the stance limb
to clear the toes during swing the unaffected CL side must compensate with exaggerated knee and hip flexion
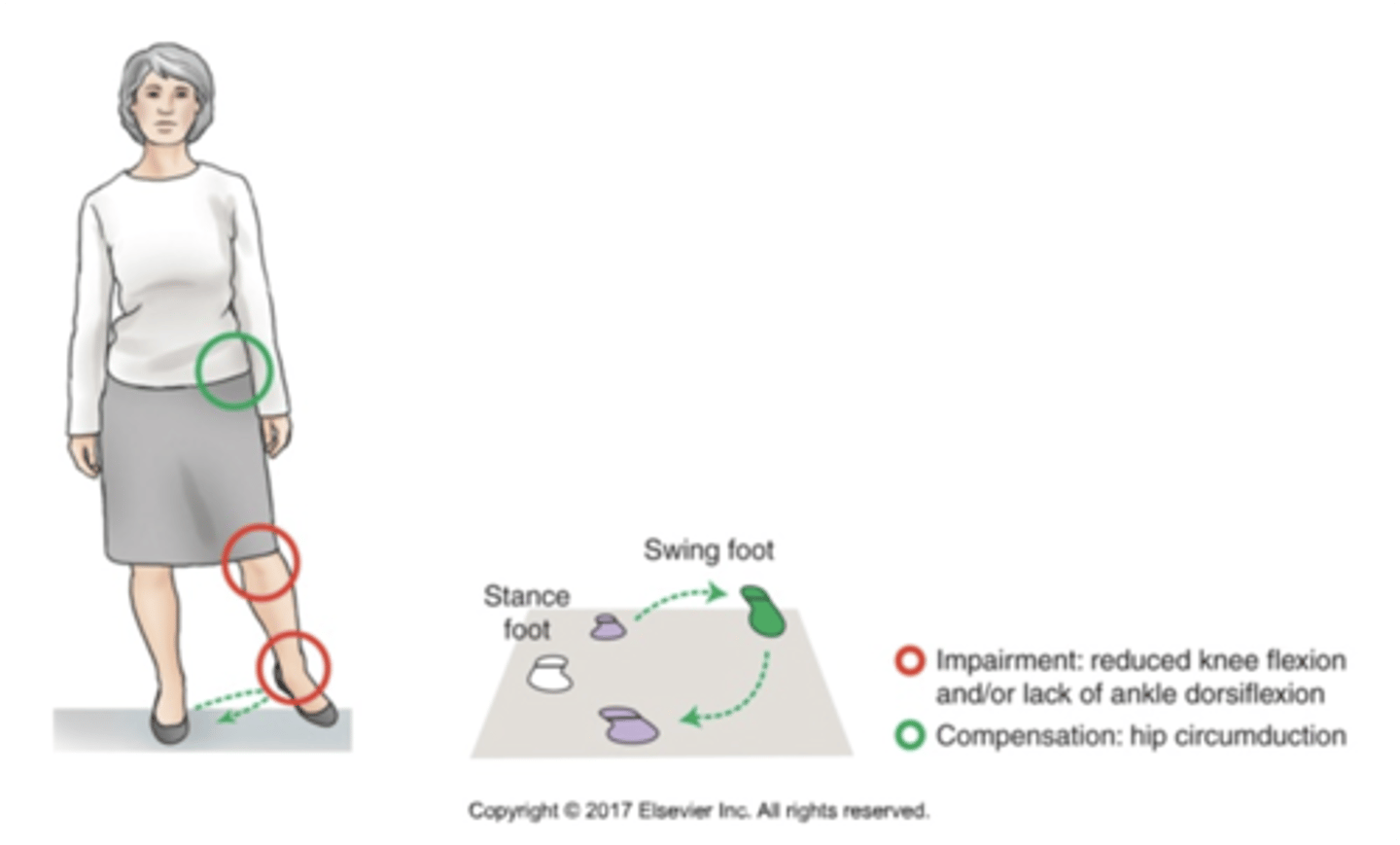
hip circumduction
used to compensate for the inability to shorten the swing limb because of inadequate knee flexion or ankle DF