i hate math save me
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
arcsin restriction of range
[-π/2, π/2]
arccos restriction of range
[0, π]
arctan restriction of range
(-π/2, π/2)
arccsc restriction of range
[-π/2, π/2] except 0
![<p>[-π/2, π/2] except 0 </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2fa01415-fc47-40db-9c51-f5988d87b6a7.png)
arcsec restriction of range
[-π/2, π/2] except 0
![<p>[-π/2, π/2] except 0 </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/70ce4cf3-993d-4f97-8675-1d525d1def12.png)
arccot restriction of range
[-π/2, π/2] except π/2
![<p>[-π/2, π/2] except π/2 </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ba4d32e8-0ea0-4524-9243-2a39311ccf61.png)
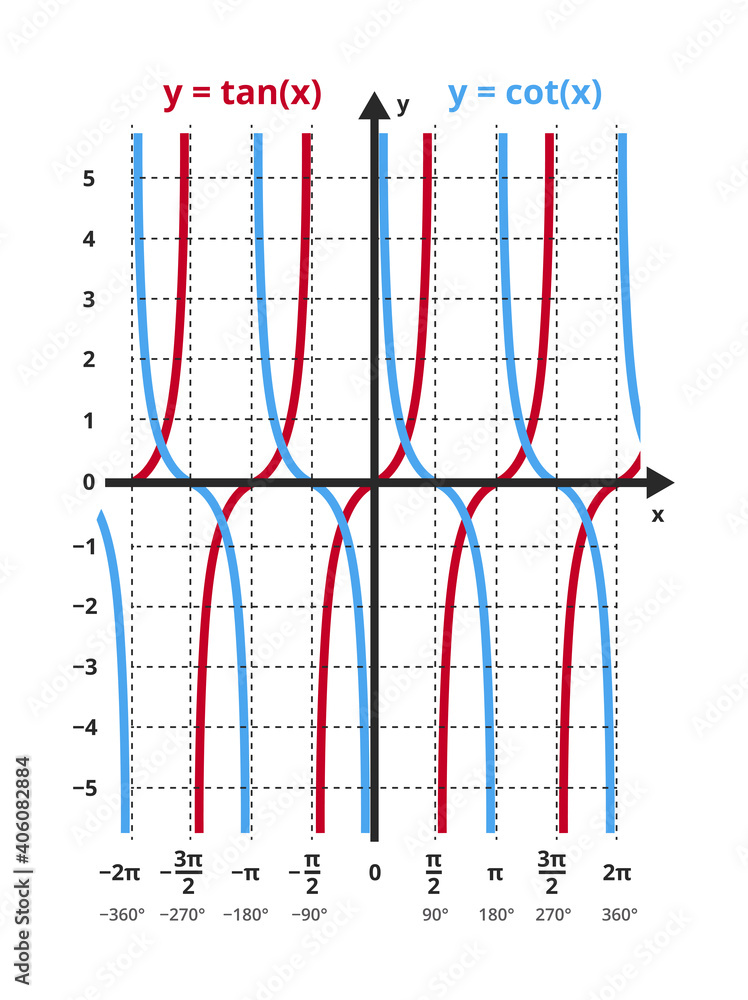
y=tanx vs. y=cotx
The functions y=tanx and y=cotx are reciprocal trigonometric functions; tanx is defined for all real numbers except odd multiples of π/2, while cotx is defined for all real numbers except integer multiples of π.
formula to convert radians to degrees
radians/π = degrees/180
half angle identity → cos²x=
cos²x = ½ + ½ cos (2x)
half angle identity → sin²x=
sin²x = ½ - ½ cos (2x)
double angle identity → cos2u =
cos 2u = cos²u - sin²u = -2sin²u+1 = 2cos²u-1
double angle identity → sin 2u =
sin 2u = 2 sin cosu
double angle identity → tan 2u =
(2 tan u)/(1-tan²u)
compound angle identity → sin (x±y) =
sin x cos y ± cos x sin y
cos (x±y) =
cos x cos y ∓ sin x sin y
tan (x±y)=
tan x ± tan y / 1 ∓ tan x tan y
terminal side
side that determines the angle
coterminal angles
angles that have same terminal side (210° and -150°)
period formula
2π/b = period
y=sin(1/2x) would stretch by ___
scale factor of 2
sin²x+cos²x=?
1
sin(90°-x) =
cosx
cscx
1/sinx
1/cosx
secx
1/tanx
cotx
sin(90-x)
cosx
cos(90-x)
sinx
tan(90-x)
cotx
sec(90-x)
cscx
csc(90-x)
secx
odd trig function identities
-(sinx)=sin(-x)
-(cscx)=csc(-x)
-(tanx)=tan(-x)
-(cotx)=cot(-x)
even trig function identities
cosx=cos(-x)
secx=sec(-x)
even function
y=x²
y=x^6+1
y=x²-2
odd function
y=x²+x
y=2x
even function properties
symetrical over y-axis
even number of exponents
f(-x)=f(x)
odd function properties
rotation of 180° about origin
odd number of exponents
f(-x) = -f(x)