refraction
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
what is refraction
refraction is the change in speed of a wave in a new medium
speed of light in a vacuum?
3 × 10^8 ms-1
what is the normal
the normal is an imaginary line that is drawn at 90 degrees to a surface It serves as a reference line to measure the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction
what is angle of incidence
angle of incidence is the light entering from a medium to another
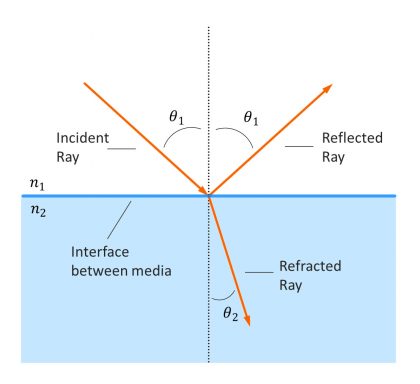
what is angle of refraction
angle of refraction is the refracted ray and this light bends as it hits a new medium as the light slows down when the new medium has a different refractive index
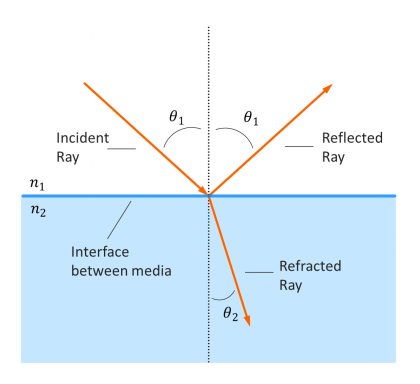
what is refractive index
refractive index is how much light slows down in a material
explain what happens when light goes from a less dense medium to a more dense and what happens when it goes from more dense to less dense
when light goes from a less dense to a more dense medium it bends towards the normal slowing down however when going from a more dense to less dense for example light going from water into air the refracted ray will speed up and bend away from the normal
why does the refracted bend towards the normal when light goes from air to water but bends away from the normal when going from water to air
the reason for this is because when light goes from a less dense to more dense medium it slows down making it bend towards the normal however when the opposite happens the light speeds up and bends away from the normal
whats the formula for refractive index
n=c/v c=speed of light and v= speed of light in that material
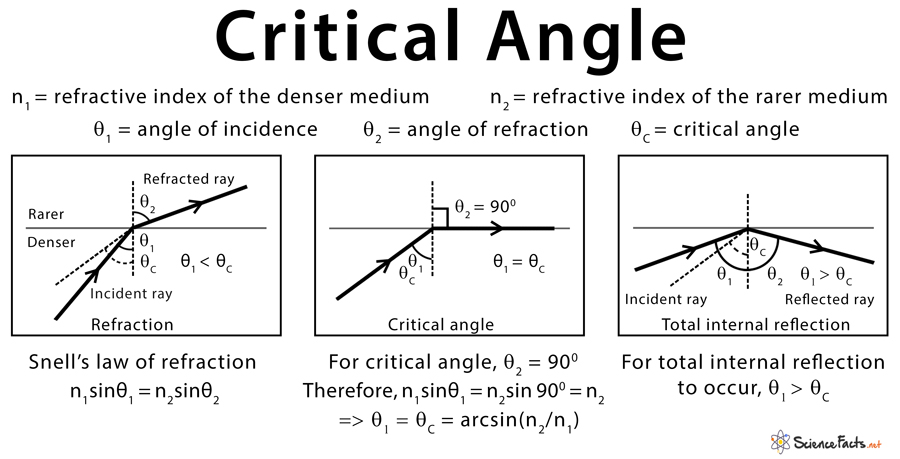
what is the critical angle
the critical angle is when the angle of incidence is in the denser medium and the angle is big enough that the refracted ray is bending away from the normal at 90 degrees to the boundary to the point where it becomes a straight line and if the angle of incidence becomes even larger the refracted ray goes below the boundary and reflects internally this is called total internal reflection in short the criticle angle is when the refracted ray is at 90 degrees to the boundary
what is Snells law
snells law tells you how much light bends when entering a new medium
what is the formula for Snells law
n₁sin(θ₁) = n₂sin(θ₂)
n1 means refractive index of first medium
sin(θ₁) means angle of incidence
n2 means refractive index of second medium
sin(θ₂) means angle of refraction
light travels from water n=1.33 into glass n=1.50 and the angle of incidence is 35 find the angle of refraction
1.33 sin i (35)=1.50 sin i(?)
1.33 x sin i (35) /1.50 = 0.509
sin -1 inverse (0.509) = 31
the angle of refraction is 31 sin r (31)
if the sin value is more then 1 it cannot refract and does TIR and shows a error in the calculator as sin-1(1) = 90 degrees which is critical angle
formula for critical angle
sin c = 1/n
n = refractive index
a type of glass has n = 1.50 calculate the critical angle
1/1.50=0.6
sin-1(0.6) = 41.8
41.8 is the critical angle
what are optic fibers used for
they are used for information and carry digital signals in the form of pulses of light
what is cladding
cladding is a layer of glass or plastic that has a lower refractive index then the core
explain the process of TIR in a optic glass fiber
TIR can happen only when the light is in the denser medium, because the angle of incidence has to be large enough that the refracted ray would bend past 90° (the critical angle). When this happens, the light is reflected back into the denser medium instead of escaping. In an optical fiber, the core has a higher refractive index than the cladding, so when light hits the claddings boundary at an angle greater than the critical angle, total internal reflection occurs. This keeps the light trapped inside the core. The cladding’s lower refractive index is essential because it prevents the light from refracting out of the fiber. There is also an outer protective coating, but this layer does not affect the optics; it is only there to protect the fiber physically.
what is the reason for using optic fibers for communication
Optical fibres are used for communication because total internal reflection keeps the light trapped inside the fibre, so signals travel long distances with very little loss. They can carry very high data rates because light has a very high frequency. Optical fibers are also lightweight, secure, and not affected by electrical interference, making them reliable for internet and telephone communication.