Dermatology Lecture 4 Bacterial Infections (Sandy)
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Lesions are triggered by minimal trauma such as insect bite, needle stick, or biopsy. This is a nonspecific reaction with the formation of pustules, papules, ulcerations.
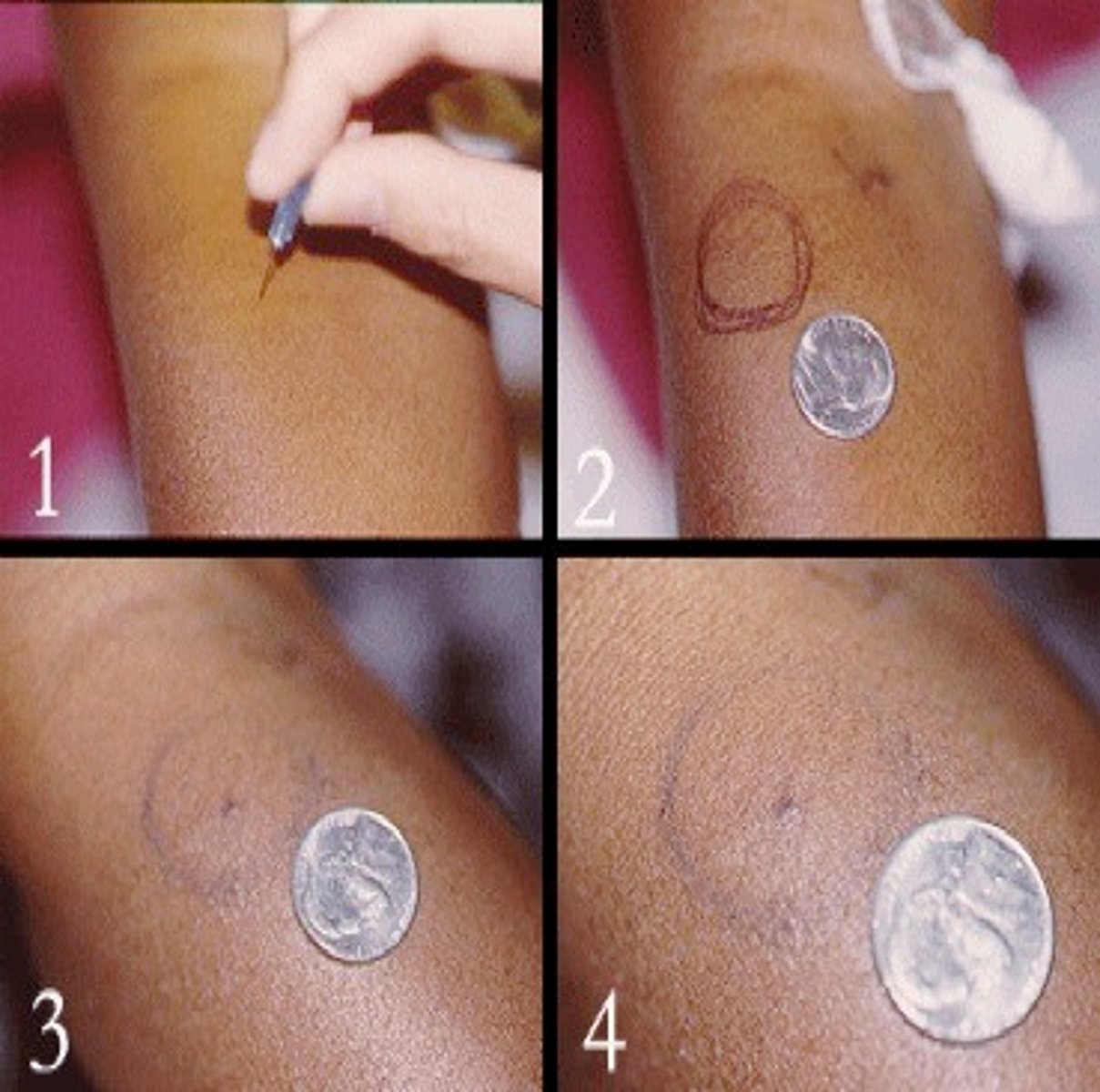
Phenomenon of Pathergy
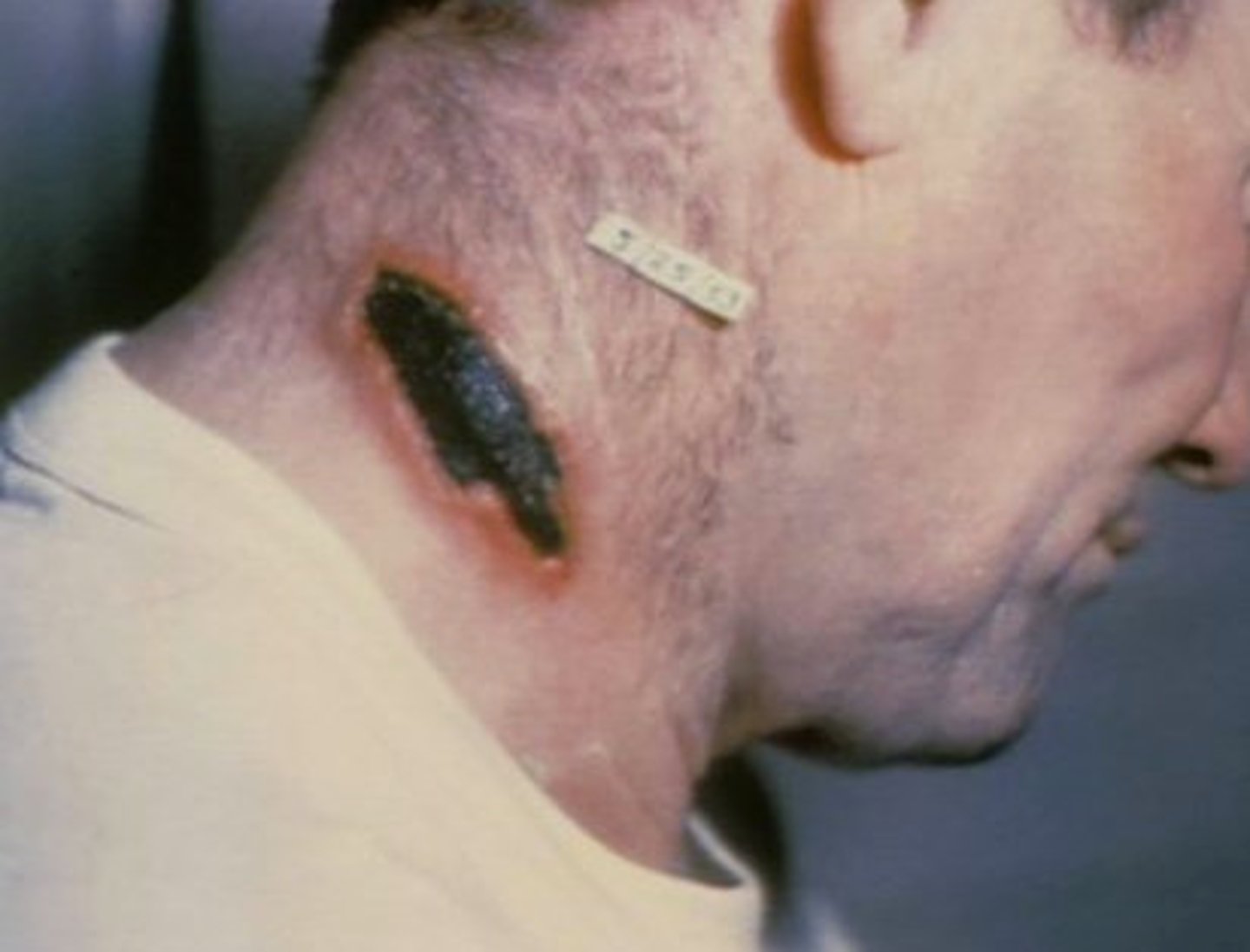
Type of necrotic tissue which appears a thick, black, dry scab
Eschar
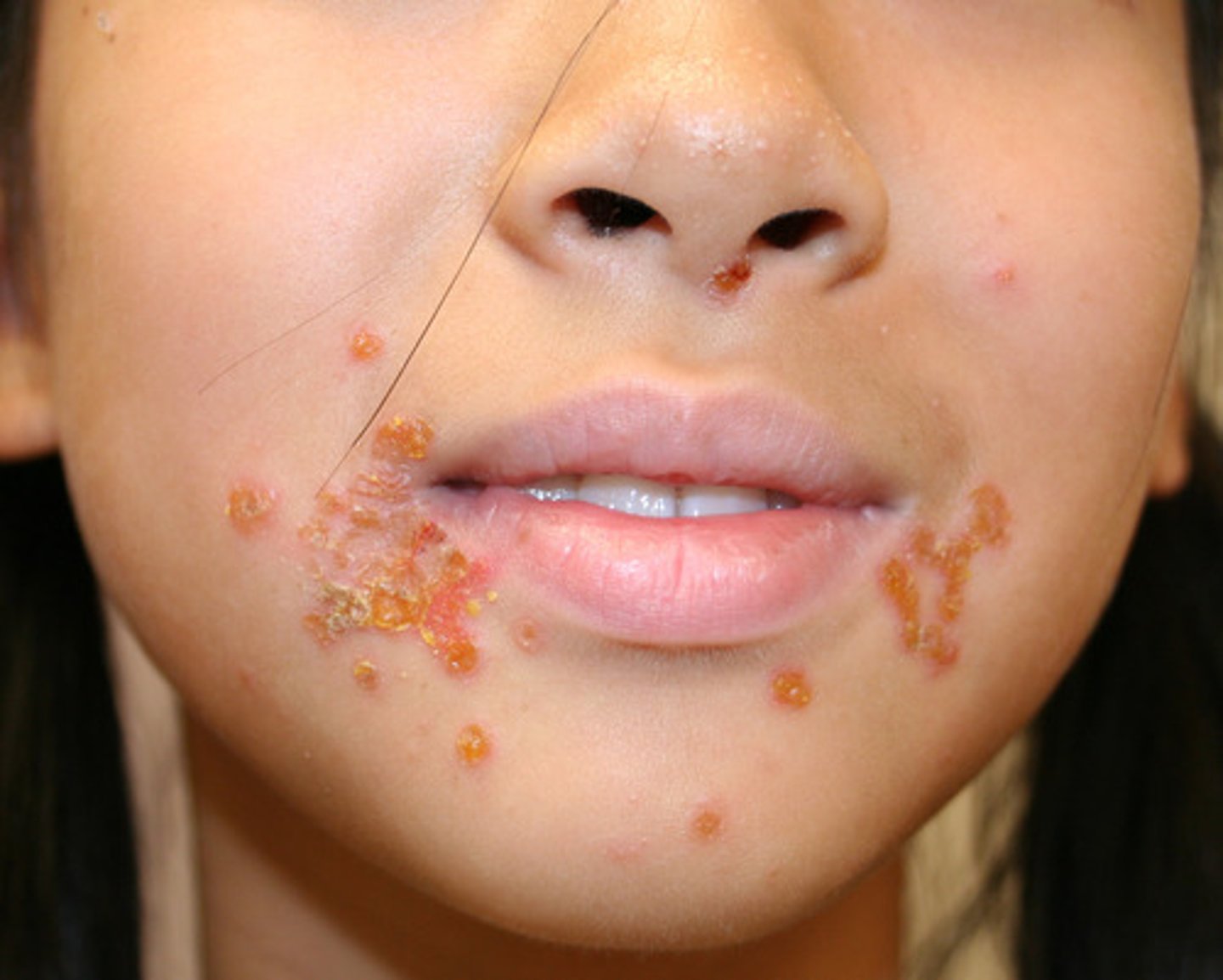
Contagious bacterial skin infection characterized by isolated pustules that become crusted and rupture. MC on Face and arms but can happen anywhere.
Impetigo
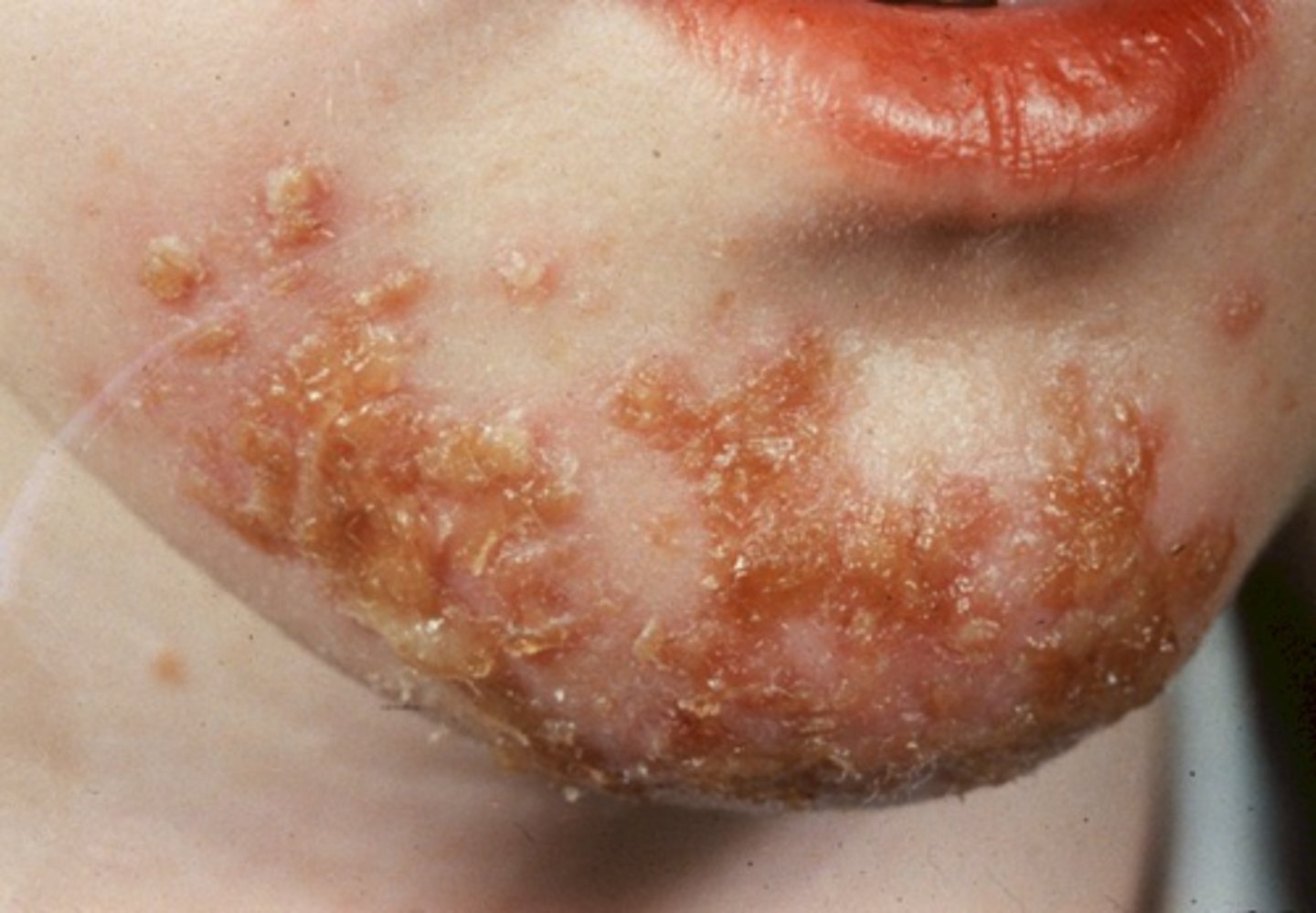
Contagious bacterial skin infection characterized by erythematous papules and honey-colored crusting. May also present with small vesicles and pustules
Non-bullous impetigo
Contagious bacterial skin infection characterized by vesicles and bullae containing clear fluid. Shallow erosions and crusting result when the lesions break. Common in wrestlers
Bullous impetigo
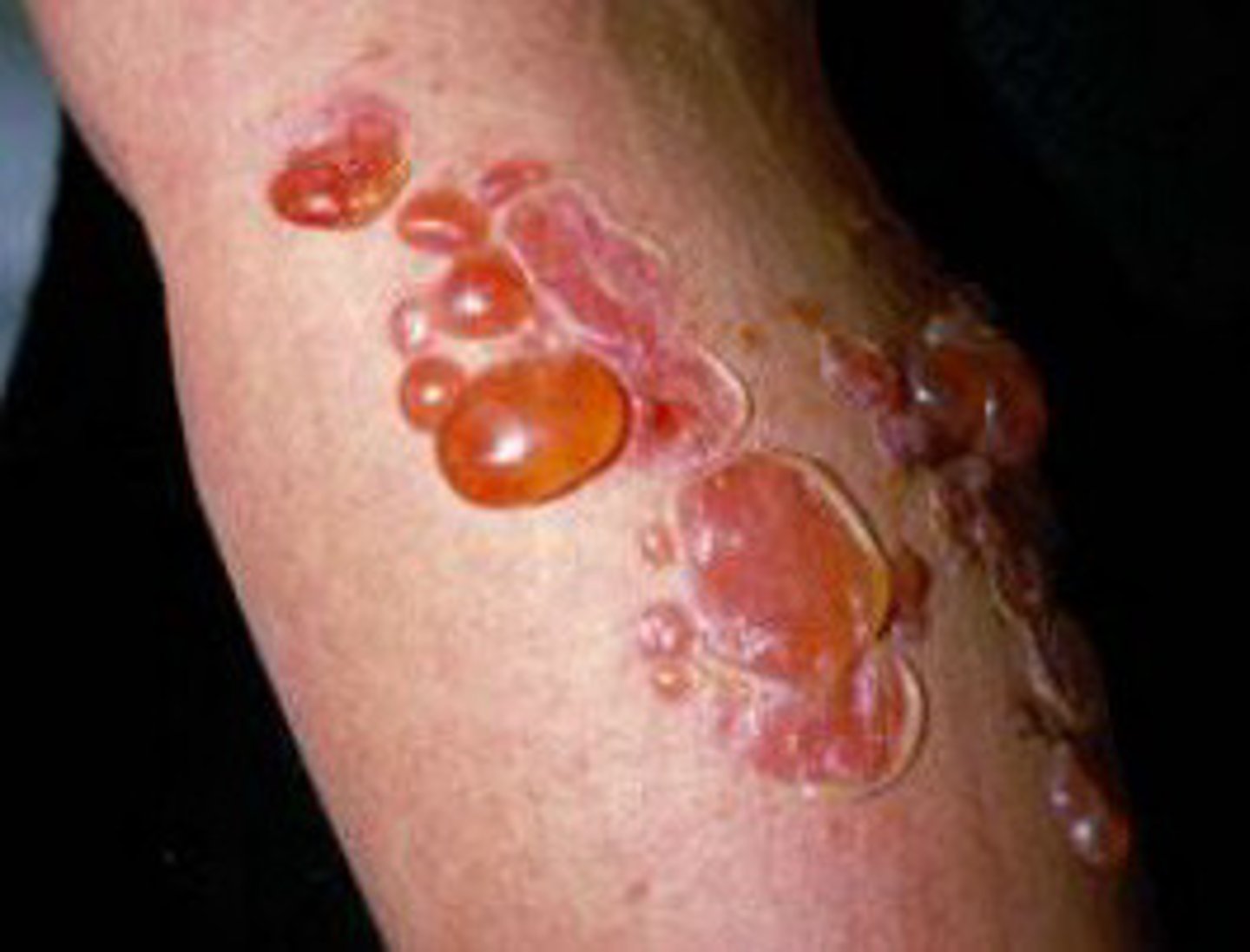
Studies show that _____ is just as effective/safe as _____ in the treatment of impetigo
Mupirocin is just as effective/safe as PO erythromycin
What are two common causative agents of impetigo?
1. S. aureus (MC)
2. Group A beta-hemolytic strep
Superficial infection or inflammation of the hair follicle that cause perifollicular papules and pustules with erythema
Folliculitis
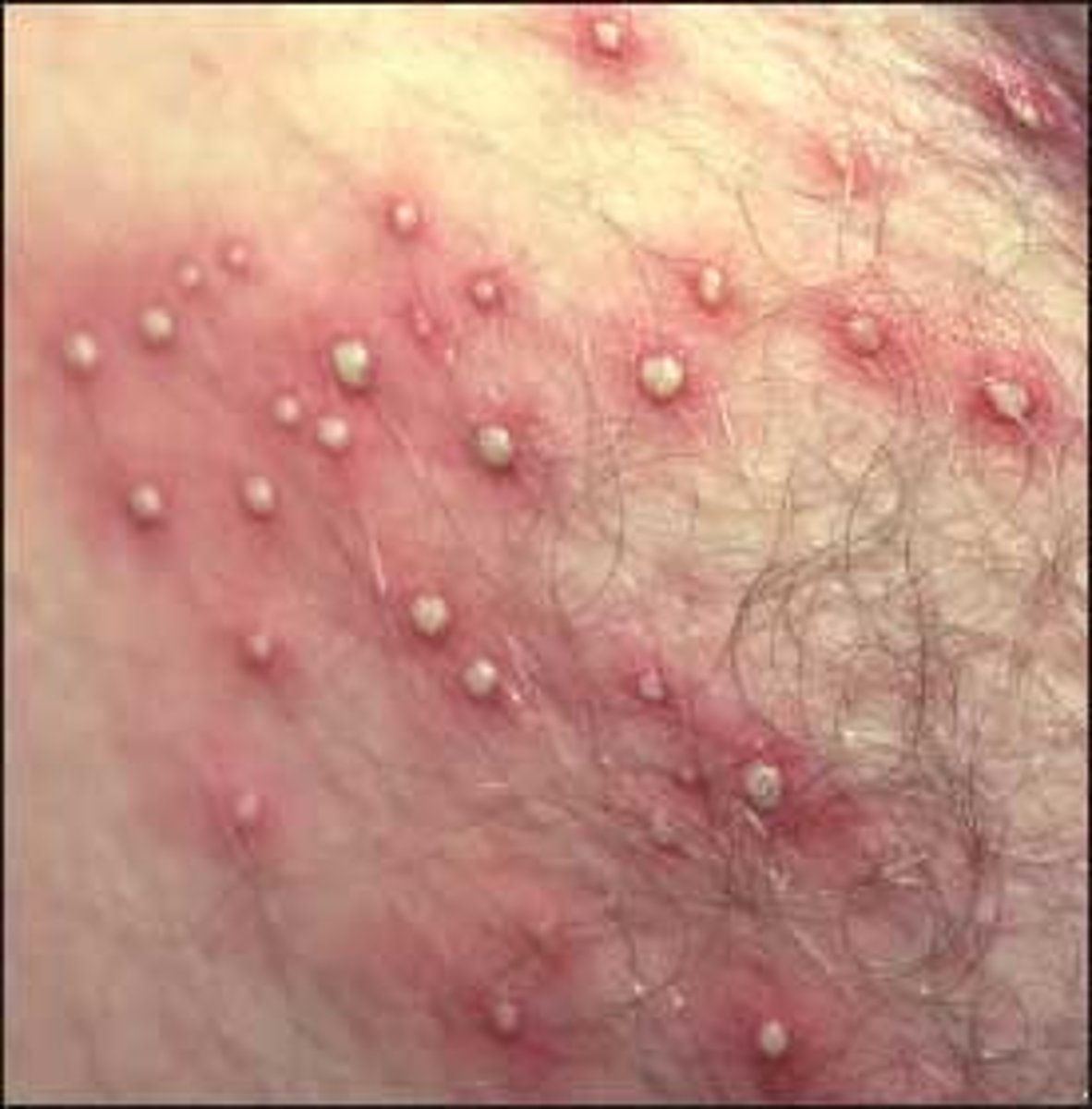
What is the MC causative agent for folliculitis?
Staph aureus
What is the MCC/risk factor of developing folliculitis?
Shaving/plucking
1. What is the tx for mild folliculitis ?
2. Moderate?
1. Mupirocin TID (topical abx)
2. Cephalexin or Dicloxacillin
Infection of the hair follicle after hot tub use causes edematous perifollicular papules and pustules that are typically seen on trunk
Hot Tub Folliculitis
Causative agent of hot tub folliculitis
Pseudomonas aeroginosa
What is the tx for Hot Tub Folliculitis?
1. Self limiting
2. Severe-> cipro
Infection of the hair follicle in the beard region that causes perifollicular pustules with erythema
Folliculitis barbae
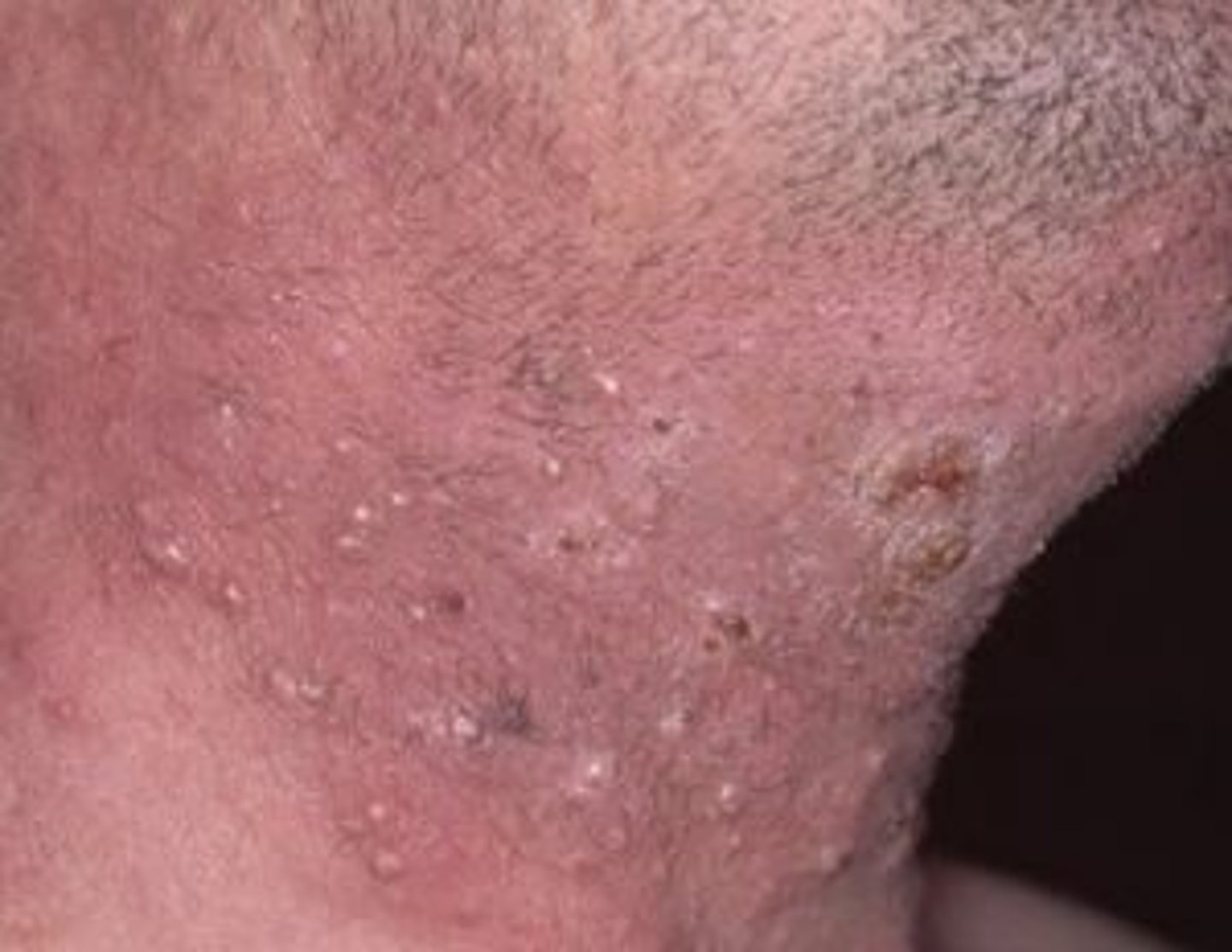
What is the MC cause of Folliculitis barbae?
Staph aureus in men who shave
Severe, deep-seated, recalcitrant folliculitis causing erythematous papules and nodules with central pustule, extends down entire hair shaft. Can lead to hair loss and scarring. Almost always related to shaving/haircutting.
Sycosis
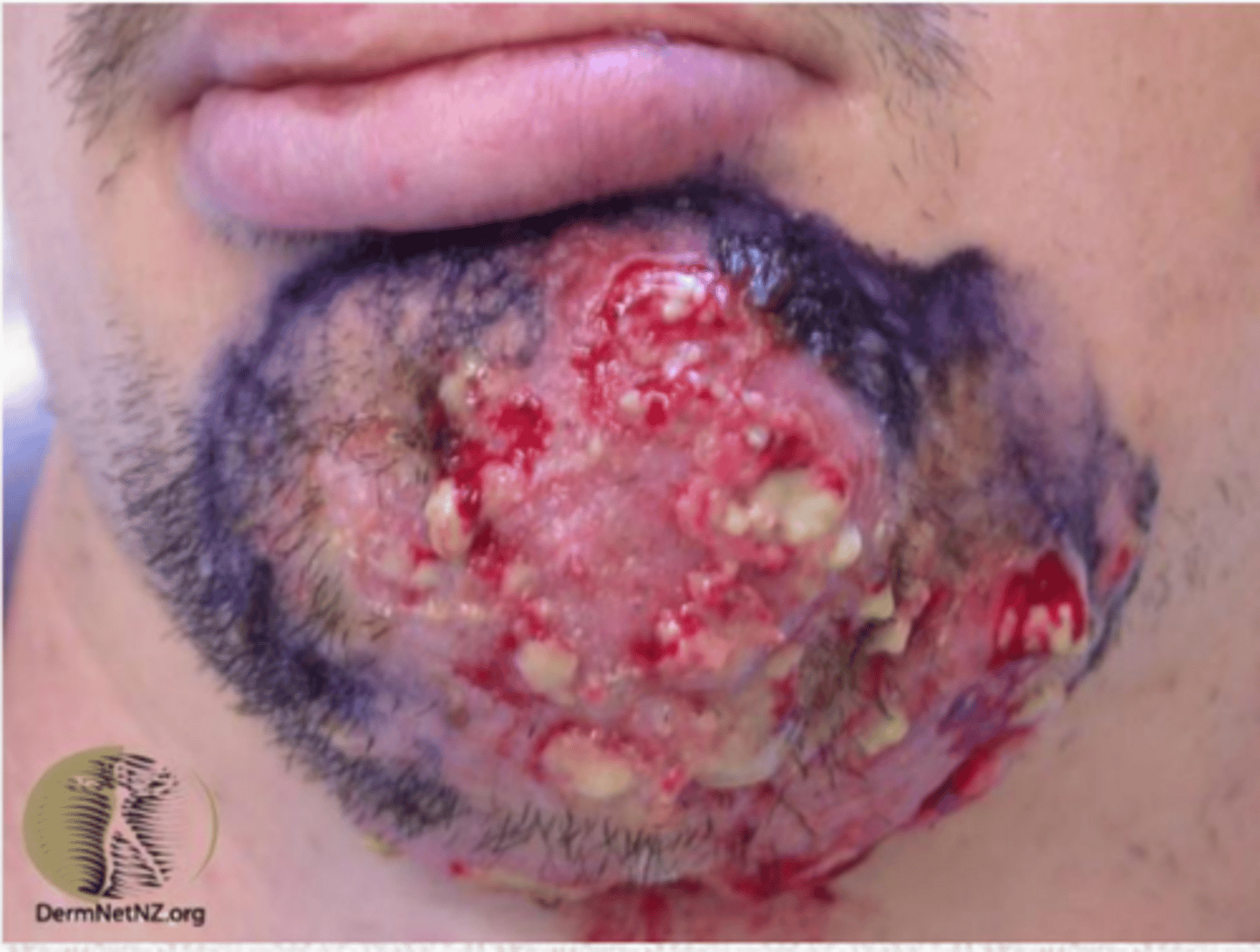
What causes Sycosis?
Tinea
Patients with Sycosis, we must culture ______ for fungus not just the lesion
hair
What is the tx for Folliculitus Barbae and Sycosis?
1. Barbae-> same tx as general folliculitus
2. Sycosis- For extensive disease tx with PO antibiotics for >/= 2
weeks
A chronic inflammatory condition in the beard region common in men that shave. It's known as "razor bumps" that resemble folliculitis generally due to ingrown hairs. It ranges from inflammatory papules and pustules to firm papules & keloidal scars.
Pseudofolliculitis barbae
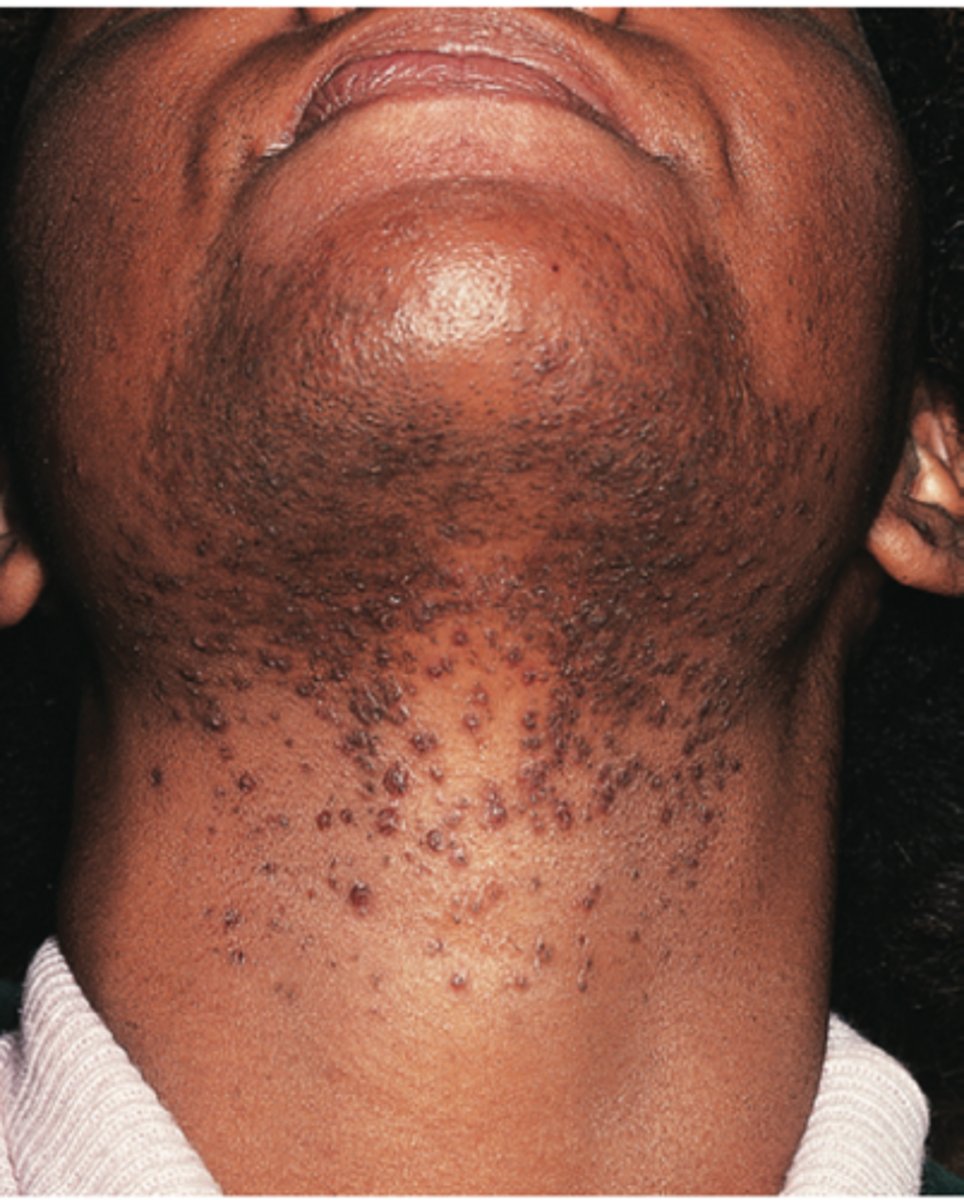
Pseudofolliculitis barbae MC affects?
African American men
What is the Tx for Pseudofolliculitis barbae?
1. Stop shaving**
2. Laser hair removal
3. Moisturize. Consider lotion with glycolic acid
4. Topical antibiotics- clindamycin gel, lotion, solution
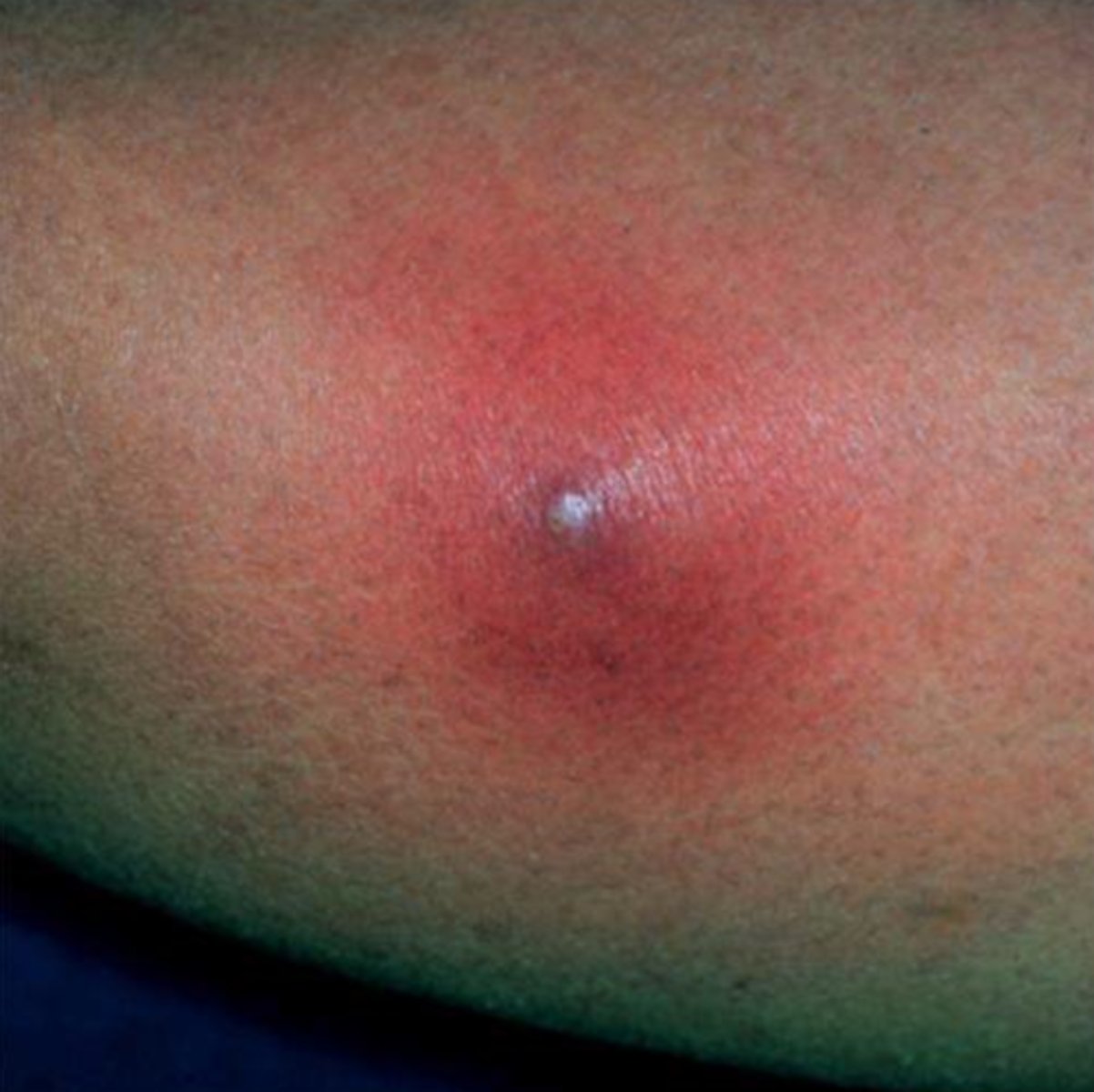
Deep-seated folliculitis with a single head, 1-2 cm, red warm, tender nodule initially. Progresses to become fluctuant with abscess formation
Furuncle
(we only have 1 Fun Uncle= single head)
Deep-seated folliculitis with multiple heads of interconnecting abscesses
Carbuncle
(We can fit many people in a Car= multiple heads)
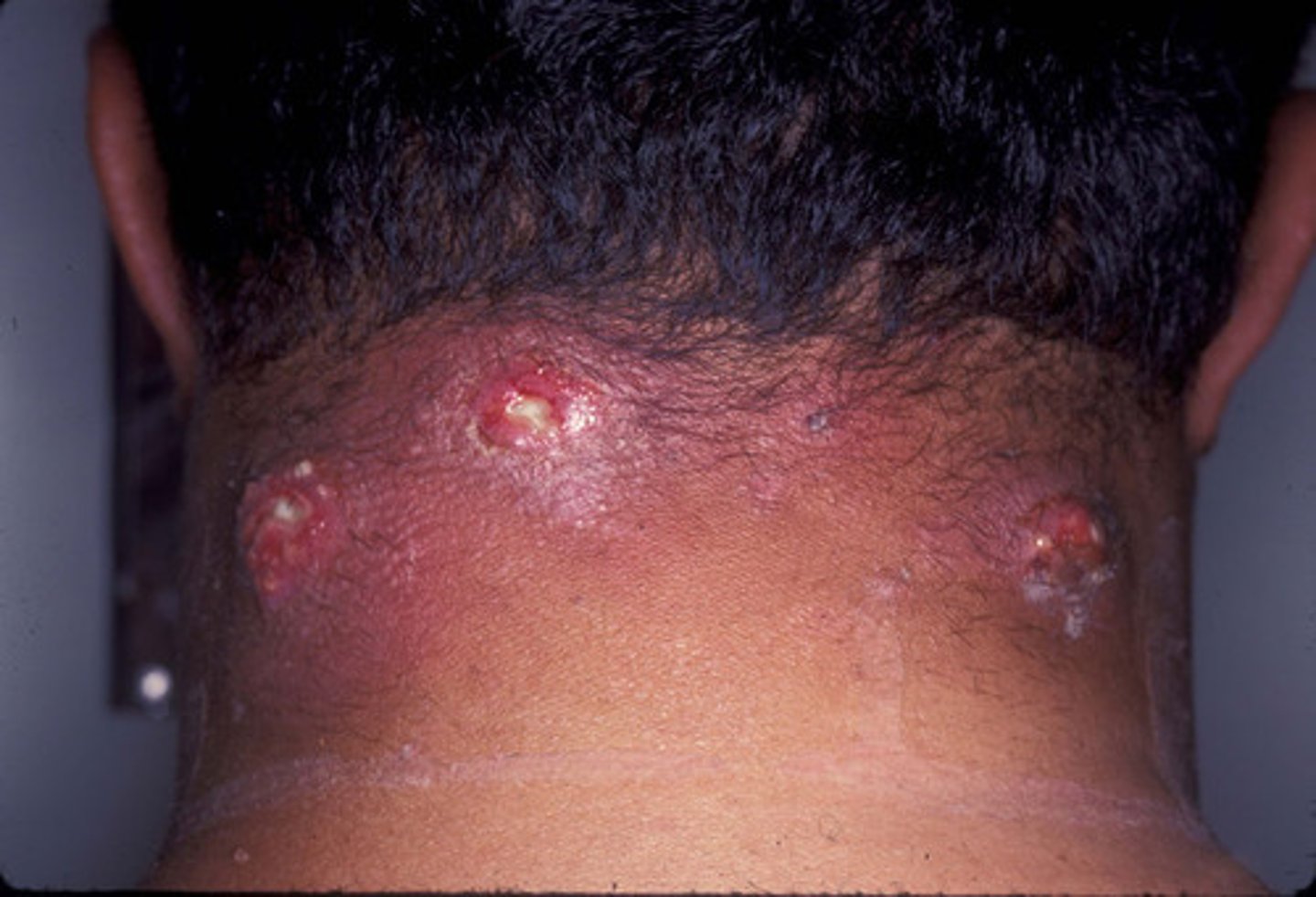
Where is the MC place for a Carbuncle?
1. nape of neck
2. head
3. any hair bearing areas
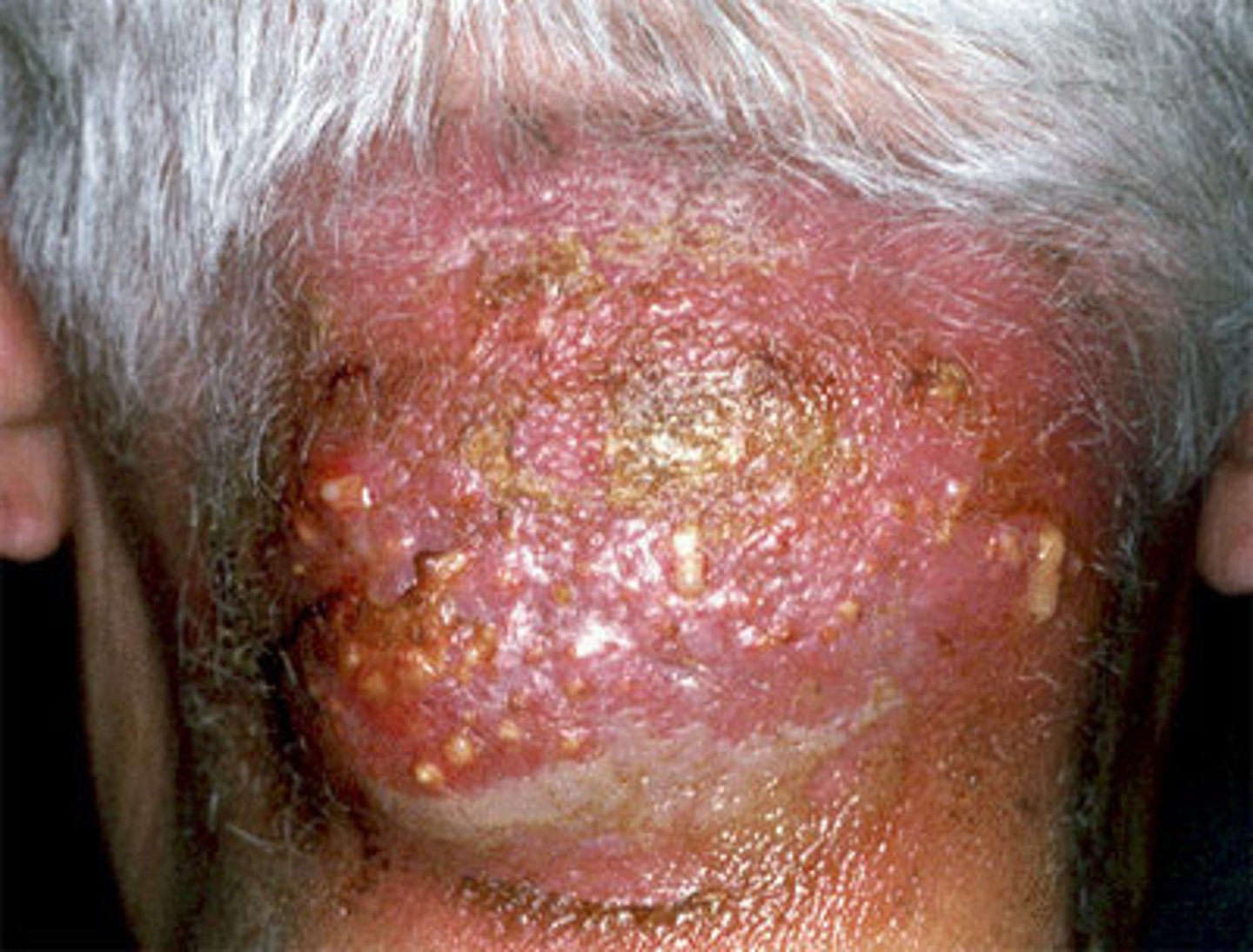
What is the MCC of Furuncles & Carbuncles?
Staph. Aureus folliculitis
What must be r/o in a pt with a fluctuant Furuncle or Carbuncle?
MRSA via bacterial culture
What is the tx for a Furuncle/Carbuncle?
1. I&D**
2. Topical and PO abx to cover MRSA ( Bactroban and Doxy, Bactrim, Clindamycin)
3. Place ¼ -½ inch packing and remove in 48-72 hours
4. Warm compresses
Acute or Chronic localized inflammation with purulent material in cavity due to infection or FB. Tender, erythematous, fluctuant mass. Most commonly found on axilla, perirectal, buttocks, head and neck
Abscess
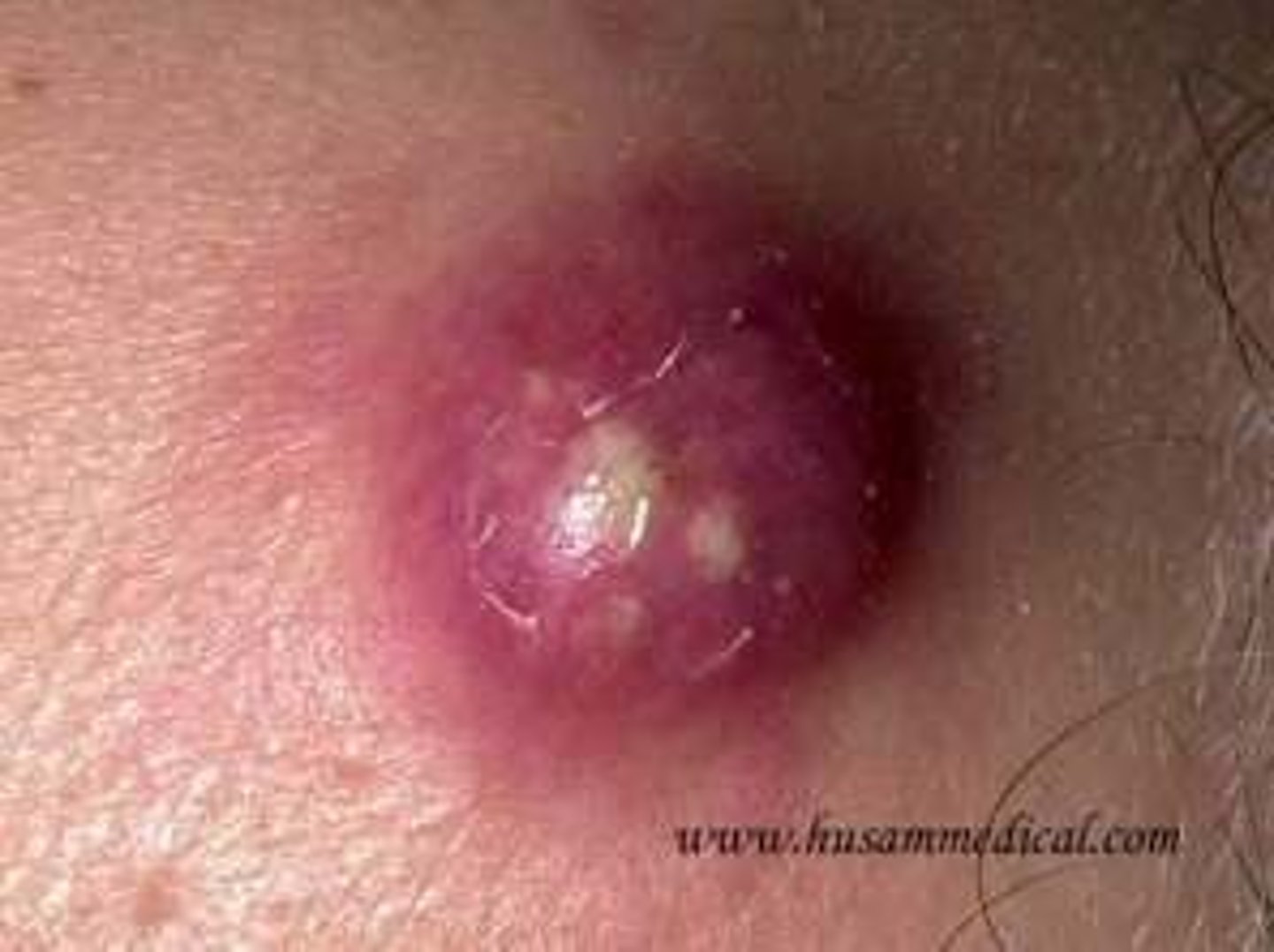
What is the tx for an abscess?
1. Warm compresses
2. possible I&D with culture (r/o MRSA)
3. PO abx
Acute spreading infection of dermal and subcutaneous tissue with slightly less well-defined edges. Erythematous, tender edematous area, warm to touch.
Cellulitis
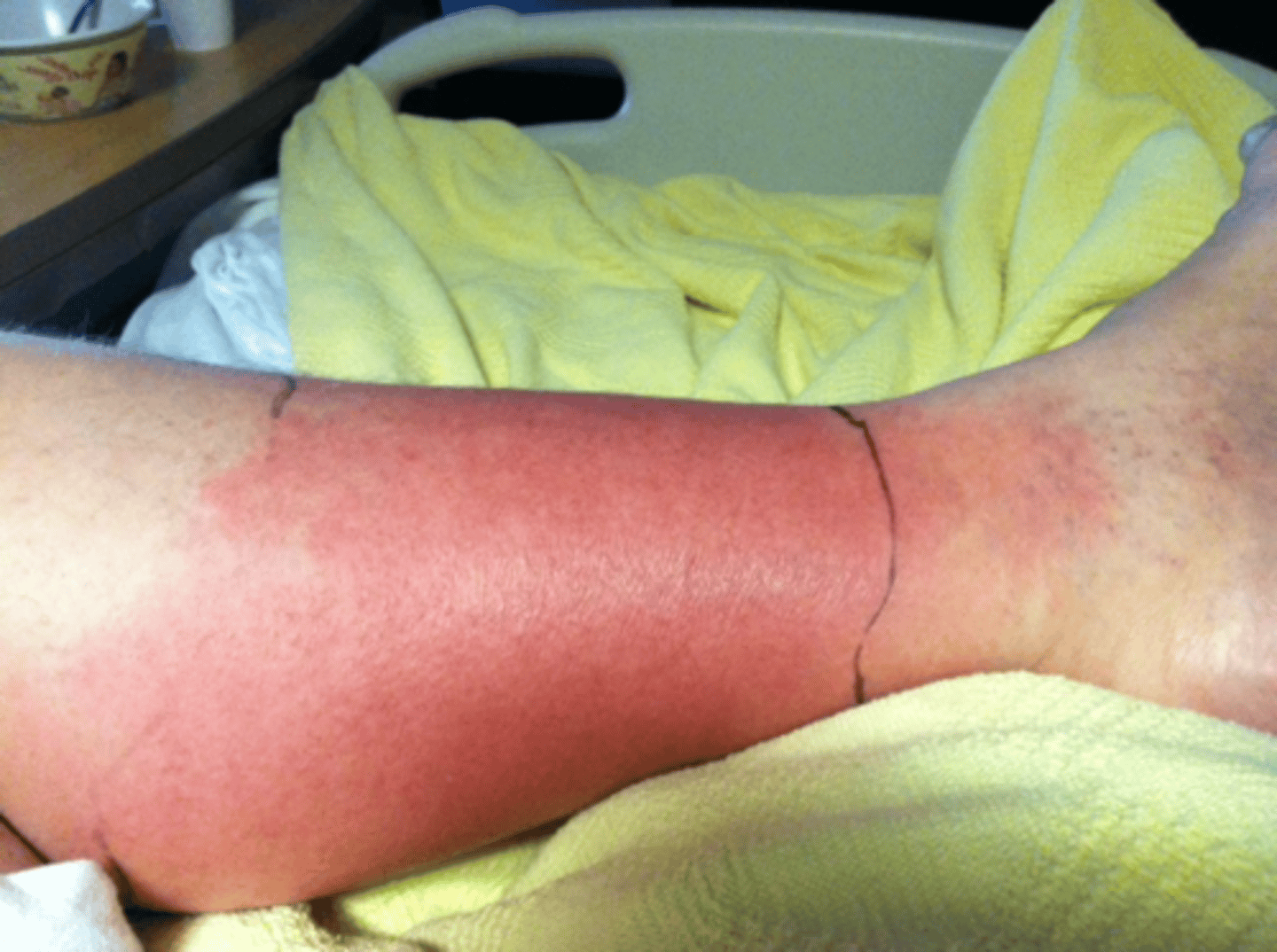
1. Where is cellulitis MC located in adults ?
2. Children?
1. Lower legs
2. Face/neck
What is the MCC of cellulitis?
Group A strep
True/False
Risk factors for cellulitis include ANY cause for break in skin, Immunosupression pt, Lymphadema, Stasis dermatitis, PVD
True
To tx Cellulitis you can tx the suspected organism ________ until culture comes back
empirically
How do you tx cellulitis if it's nonpurulent or suspect Beta-hemolytic strep or MSSA with no systemic symptoms?
PO Keflex or Dicloxacillin
How do you tx cellulitis if it's nonpurulent or suspect Beta-hemolytic strep or MSSA with systemic symptoms?
IV: Cefazolin, Ampicillin-sulbactam, nafcillin, or Clindamycin
How do you tx cellulitis if purulent or suspect MRSA with no systemic symptoms?
Oral: Clinda, Doxy, or Bactrim
How do you tx cellulitis if purulent or suspect MRSA with systemic symptoms?
IV vancomycin (or linezolid)
What could you use if pt has PCN allergy when treating cellulitis ?
Erythromycin or Clindamycin
True/False
You must outline the erythema to monitor if the cellulitis is progressive
True
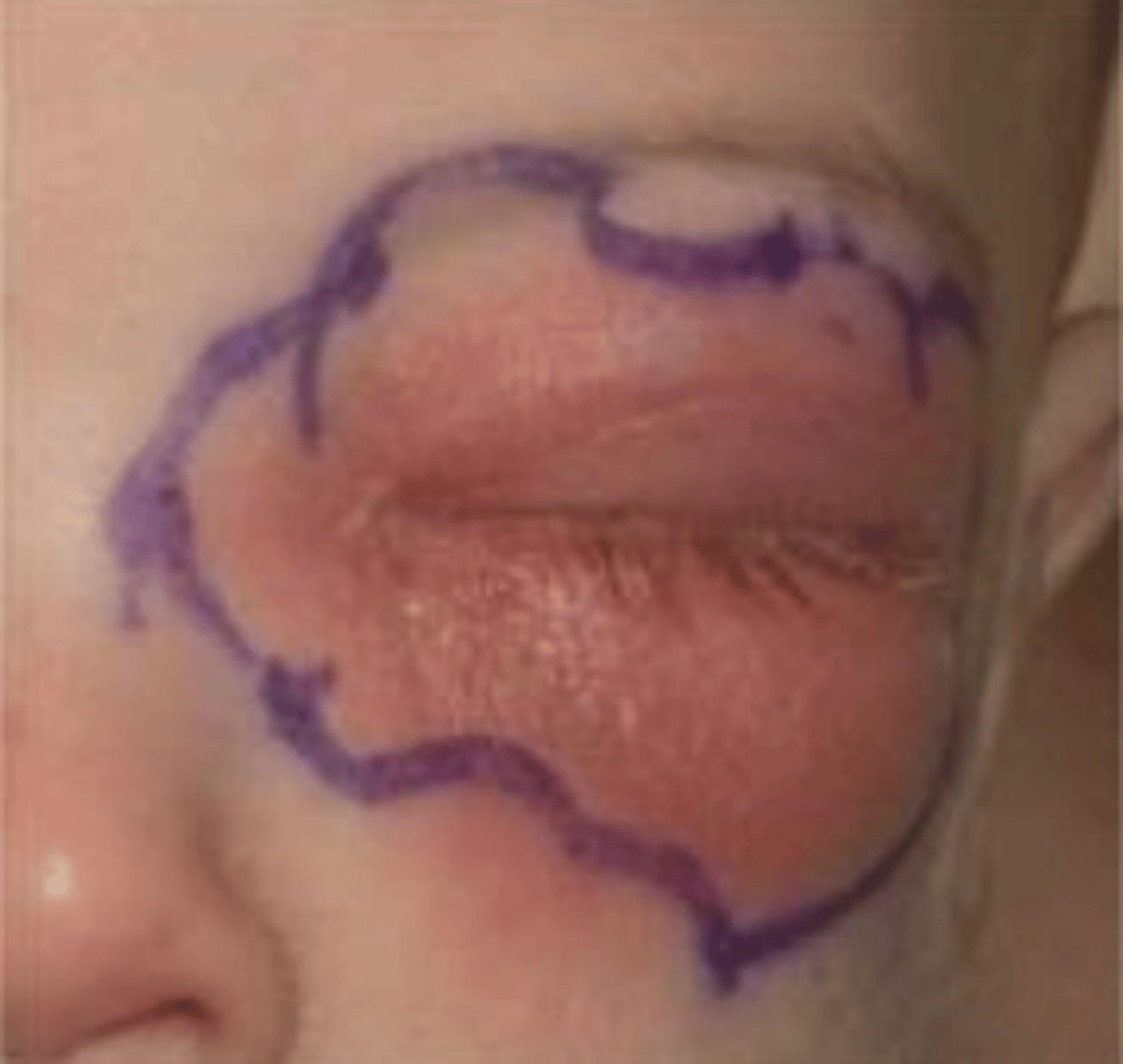
If you suspect the cellulitis is caused by necrotizing fasciitis you must?
Send to ER
IV Abx & surgical evaluation
Variant of cellulitis affecting the upper dermis and cutaneous lymphatics that causes intensely erythematous, edematous, tender, warm area. Well defined raised and indurated borders.
Erysipelas
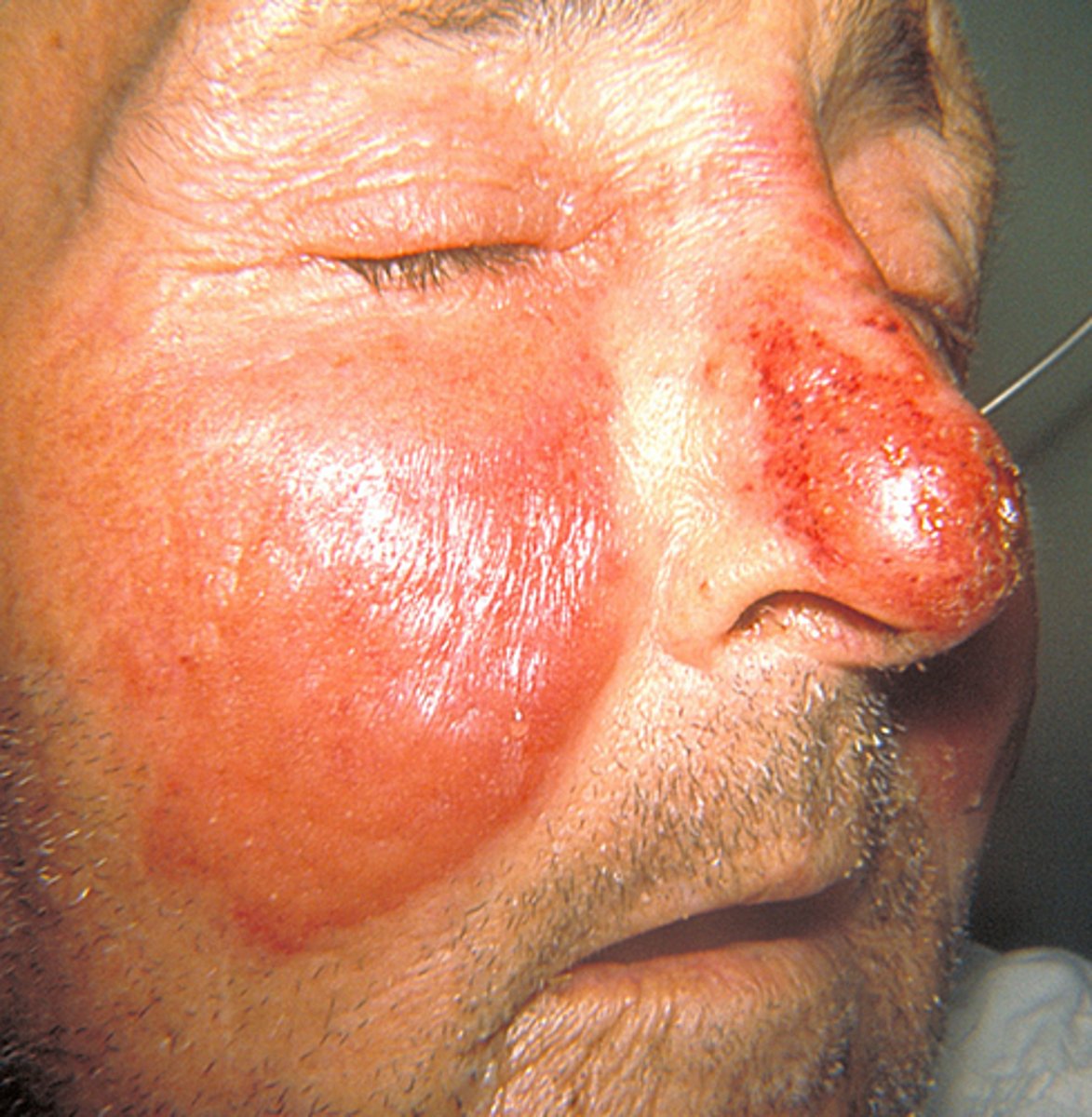
Where is Erysipelas MC located?
M/C face
(ears, lower legs but can be anywhere)
What is the MCC of Erysipelas?
GAS Beta-hemolytic strep
True/False
Pt with Erysipelas can present with systemic symptoms as well as prodromal symptoms.
True
What is the tx for Erysipelas?
1. No systemic symptoms= Cephalexin, Penicillin, Amoxicillin (against strep)
2. Systemic symptoms= IV cefazolin or ceftriazone
Ecthyma gangrenosum is a rare, cutaneous manifestation of MCC by ________
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Rare, cutaneous manifestation of pseudomonas septicemia. Begins as an erythematous macule to pustule/vesicle and proceeds to a necrotic erosion with infarcted center with rapidly expanding erythematous halo within 12-18 hours. Most commonly located on axilla, groin and perineum.
Ecthyma gangrenosum
What labs do we need to do order to dx Ecthyma gangrenosum?
1. Blood cultures
2. Bacterial skin culture
3. Take skin biopsy for culture with 4-5 mm punch, with special stain (Needle aspiration for gram stain and rapid dx)
How do we tx Ecthyma gangrenosum?
IV Piperacillin-tazobactam or ticarcillin-clavulanate
Rare inflammatory ulcerative skin lesion due to immunedysregulation with an unknown etiology. The acute onset begins as hemorrhagic pustule or nodule with erythematous halo the progress to necrotic ulcer with borders that are dusky-red or purple, irregular, raised, undermined, boggy with perforations that drain pus and purulent base. Pustules at the advancing border as well.
Pyoderma Gangrenosum
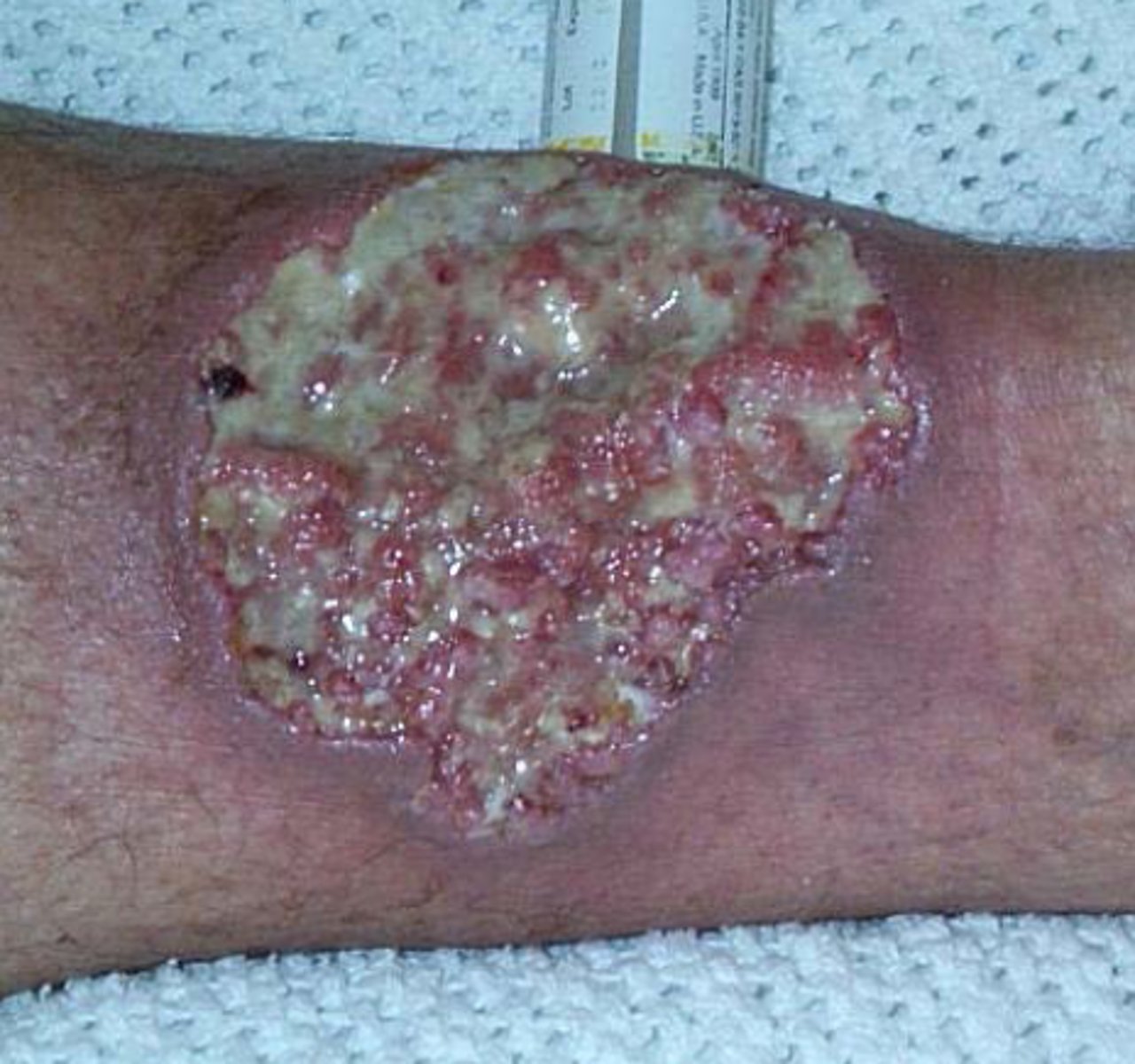
The Phenomenon of pathergy is seen in _________
Pyoderma Gangrenosum
What are the risk factors for Pyoderma Gangrenosum?
1. IBD (Crohns, UC)
2. Rheumatoid arthritis
3. Spondyloarthropathies
4. Leukemia, etc
Who gets Pyoderma Gangrenosum?
All ages, peak 40-60 years
F>M
How do we dx Pyoderma Gangrenosum?
1. Clinical Diagnosis of exclusion
2. Biopsy of ulcer edge (neutrophilic infiltrates)
How do we tx localized Pyoderma Gangrenosum?
1. high potency topical steroids or tacrolimus. Wound care
How do we tx extensive/rapid growing Pyoderma Gangrenosum?
Systemic steroids or immunomodulators (Cyclosporine)
45 YO female c/o increasing rash on left cheek and left ear. Patient states 3 days ago it began as a small red "spot" that has increased in size. She states the spot on her left cheek it is very tender. She also admits to fever, chills, malaise. She notes that she previously excoriated her left ear due to a patch of pruritic eczema. Physical exam shows an erythematous area with sharply demarcated raised border. What the dx and tx?
Erysipelas
Cephalexin
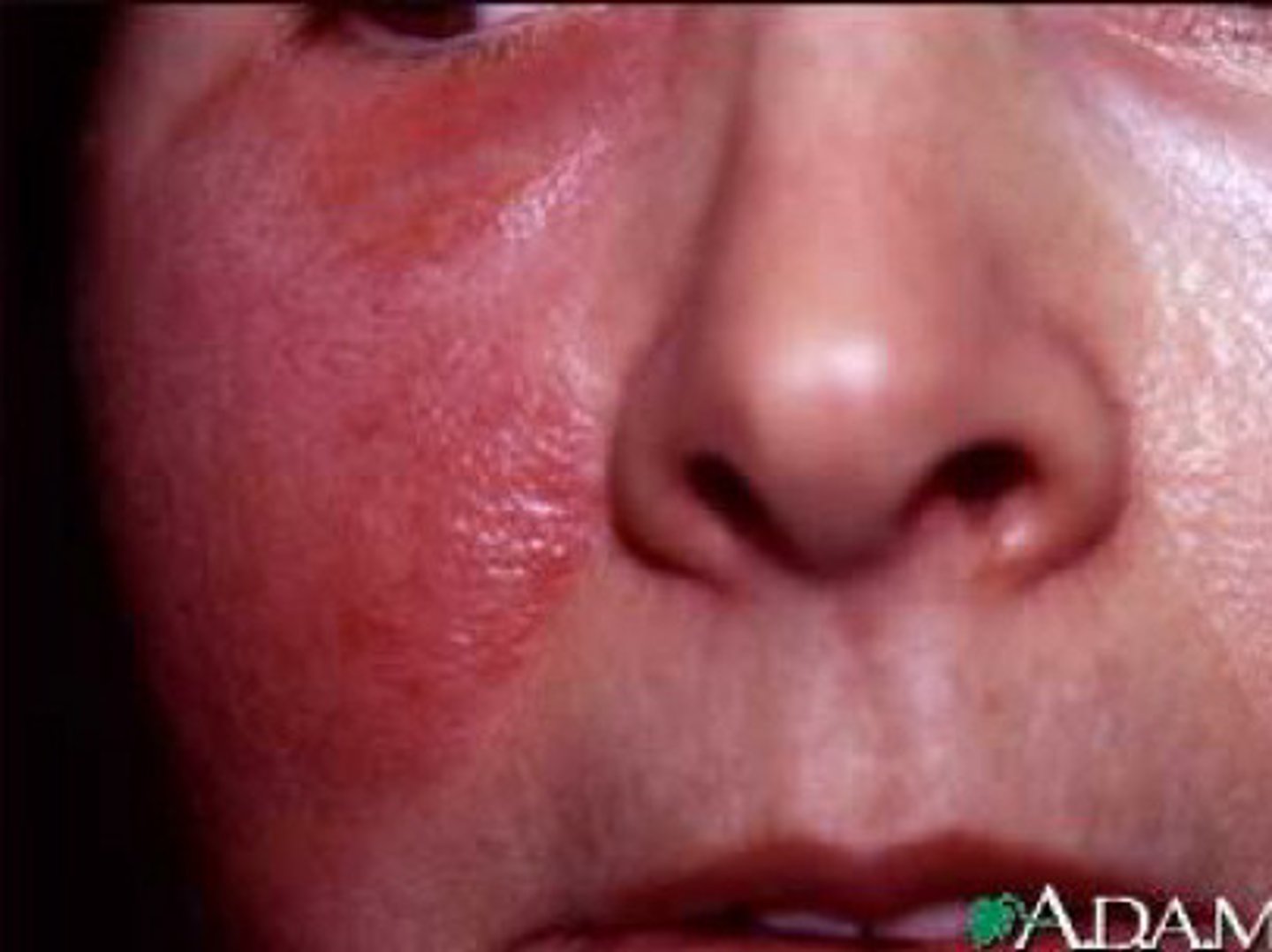
27 yo man who presents to the office c/o rash to right nostril x 4 days. Patient s/p URI and frequent cleaning of nose leading to tenderness. Patient also admits to frequent rubbing and no relief with topical OTC therapies such as Aquaphor. Rash began with small "bumps" that leaked clear fluid and now he is noticing scabs and pruritis. What is the diagnosis and tx ?
Impetigo
Mupirocin
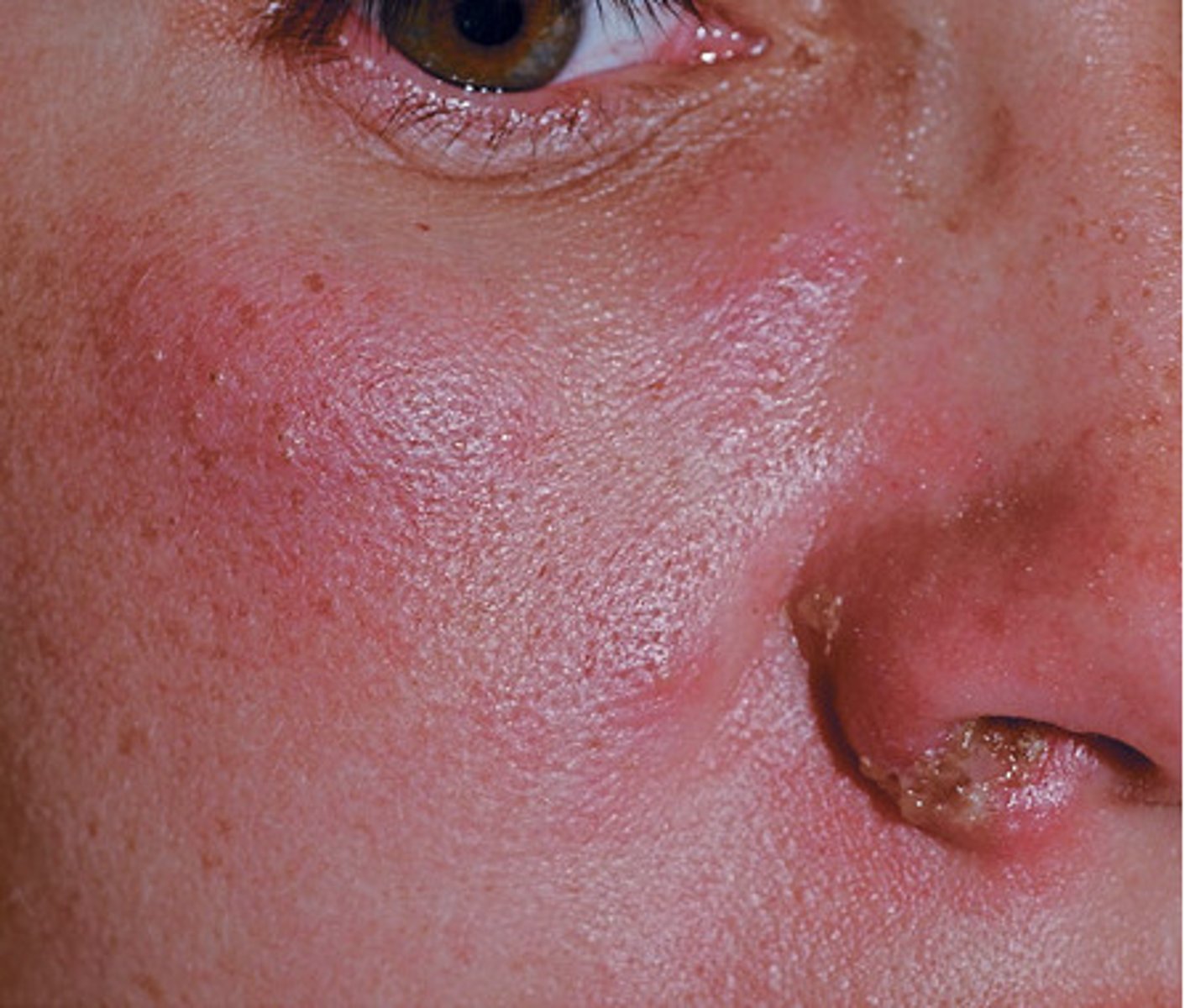
32 yo woman presents c/o an itchy rash that started 4 days ago on her trunk. She stated that the rash began as “bumps” that were pink and now look like pimples. Patient states her husband has a similar rash in a similar distribution. Both recently traveled to the Caribbean and deny any use of new lotions, soaps or meds. They frequented the ocean, pool and hot tub almost daily. What is the diagnosis and tx?
Hot tub folliculitis
Self-limiting
56 y/o man presents to the office complaining of a rash noted to
his nasolabial folds. On physical exam you note erythematous patches
with white and yellow greasy scales. What is the treatment of choice
for this patient?
A. Topical Steroid
B. Topical Antifungal
C. Topical Vitamin
D Analog
D. Topical Tar
B. Topical Antifungal
(seb derm)
Comedonal acne is best treated with?
A. Benzoyl Peroxide
B. Topical Clindamycin
C. Oral Doxycycline
D. Topical Tretinoin
D. Topical Tretinoin (retinoid)
A 30 y/o woman presents to the office complaining of a rash on herface for 6 months. Patient notes that she has multiple pimples and that her face tends to flush when she eats spicy food and when she drinks her morning coffee. What is the treatment of choice for this patient?
A. Topical Metronidazole
B. Topical Tretinoin
C. Topical Dapsone
D. Topical Erythromycin
A. Topical Metronidazole
(Rosacea)
35 y/o woman presents to your office c/o a rash to her shins x 1
month. Patient stated that the areas of rash are red and tender. She
admits she was newly diagnosed with sarcoidosis. On physical exam there are painful, erythematous, indurated nodules on the patient's anterior shins. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. erythema nodosum
B. erythema multiforme
C. stevens-johnson syndrome
D. pityriasis rosaea
A. erythema nodosum
A 27 y/o female presents to the office complaining of a rash near her mouth x 4 weeks. Patient stated that she had been using a heavy moisturizer and over the counter hydrocortisone for treatment without relief. On physical exam there are multiple 1-2mm papules
with fine scaling noted. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Acne
B. Rosacea
C. Perioral Dermatitis
D. Contact Dermatitis
C. Perioral Dermatitis
Swollen or inflamed lymphnode in groin or axilla.
Buboe
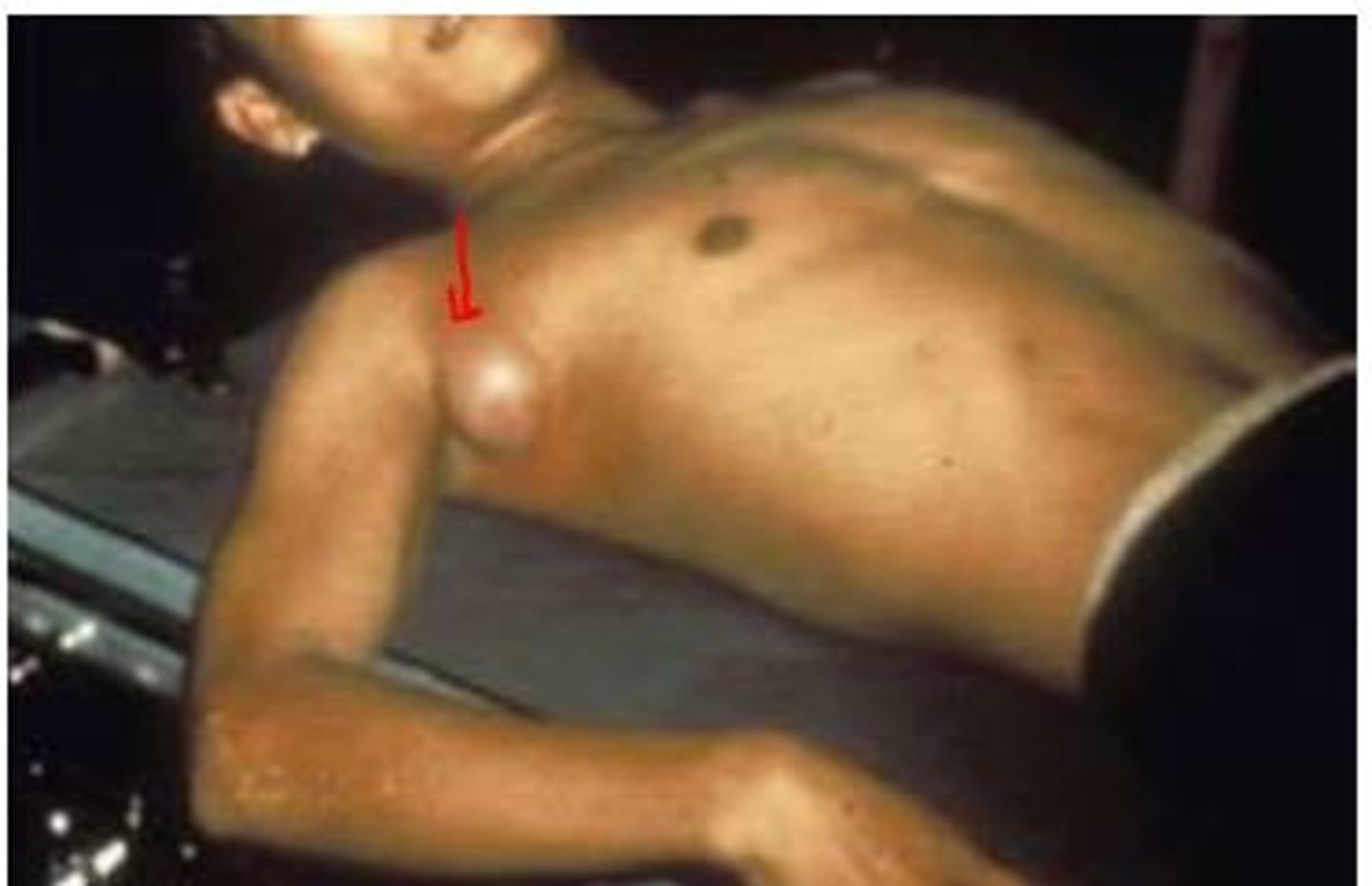
Solitary granulomatous lesion with central necrosis.
Gumma
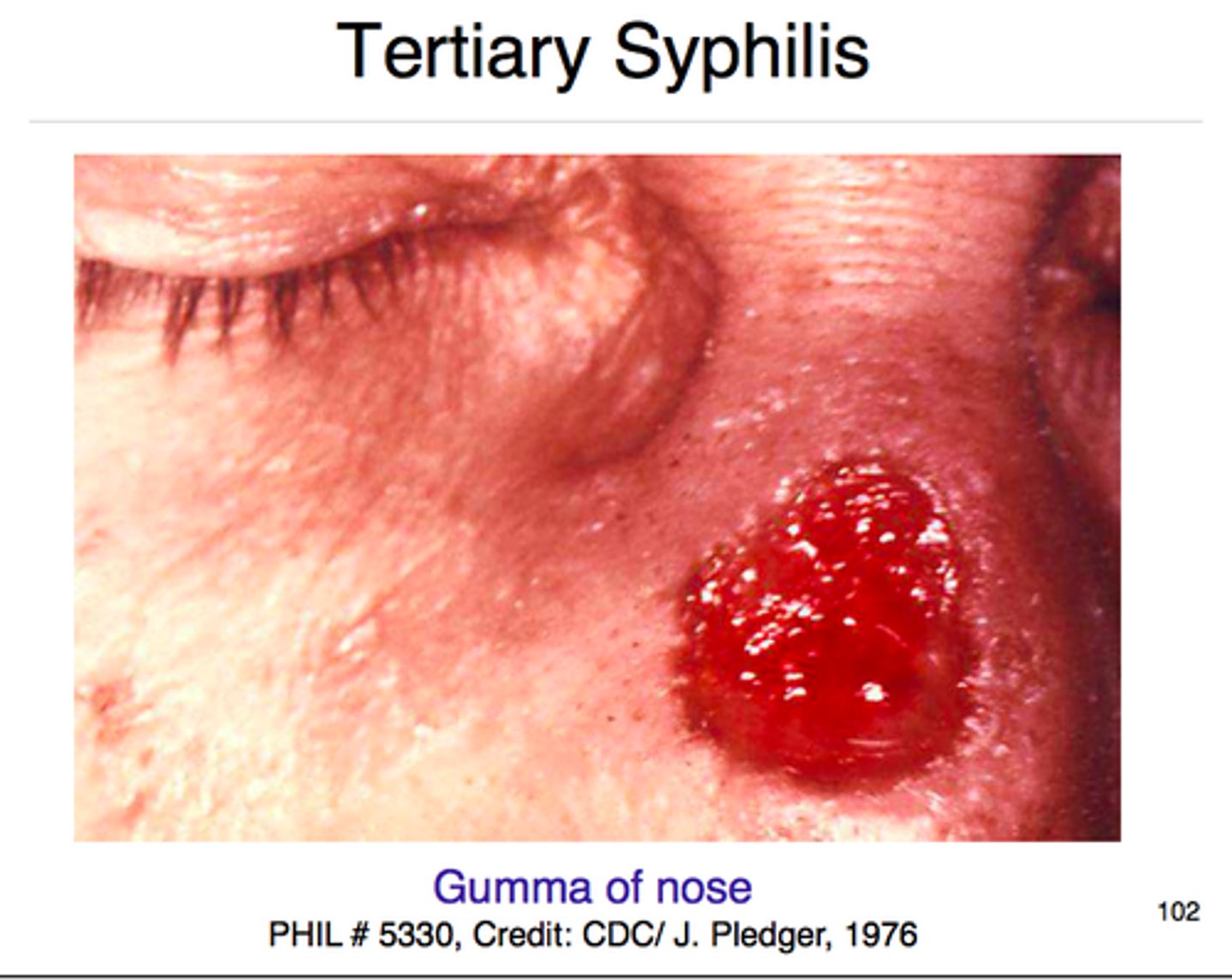
Term for lesion that resembling psoriasis
Psoriasiform