Bed Mobility & Transfers
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
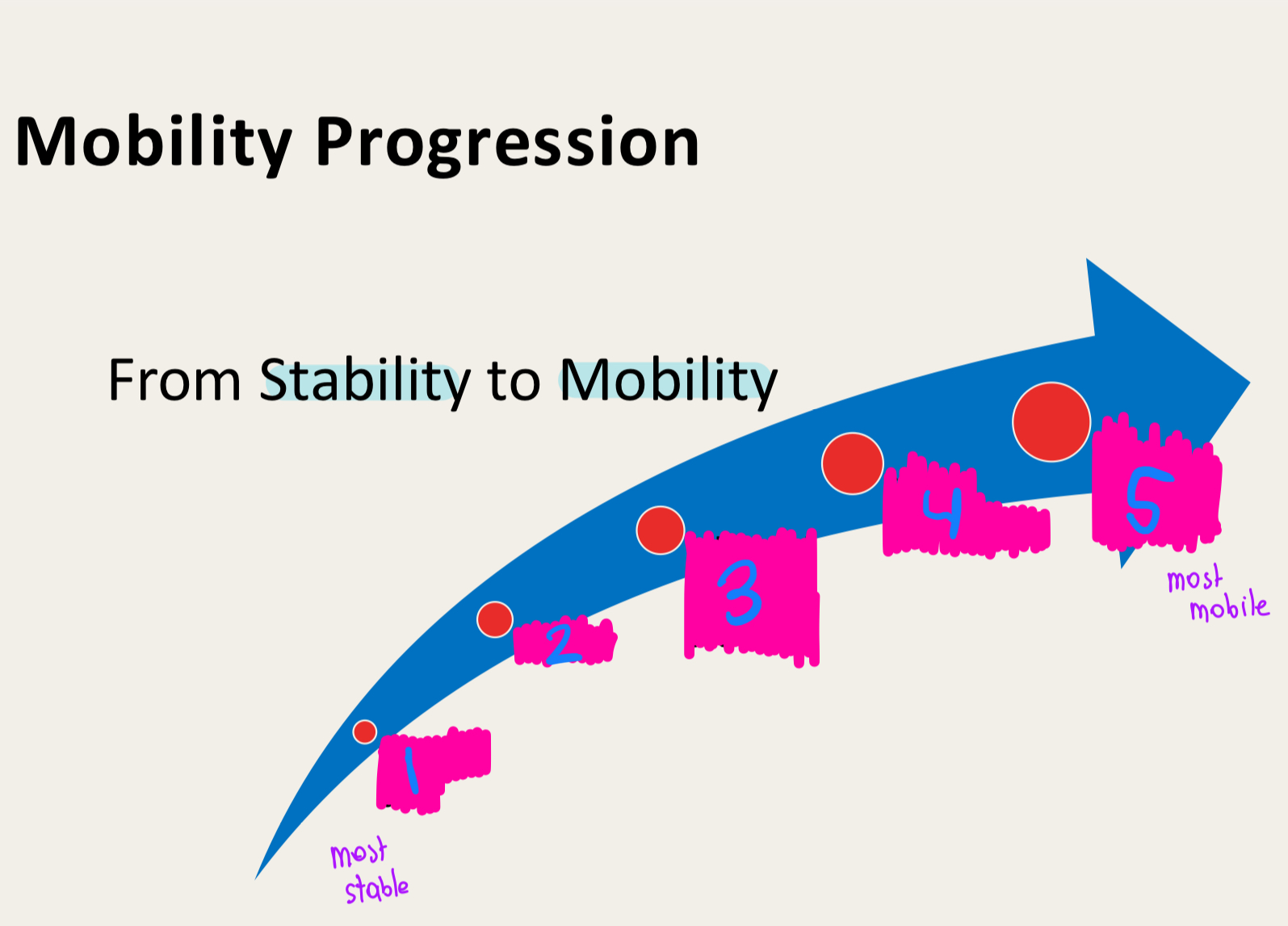
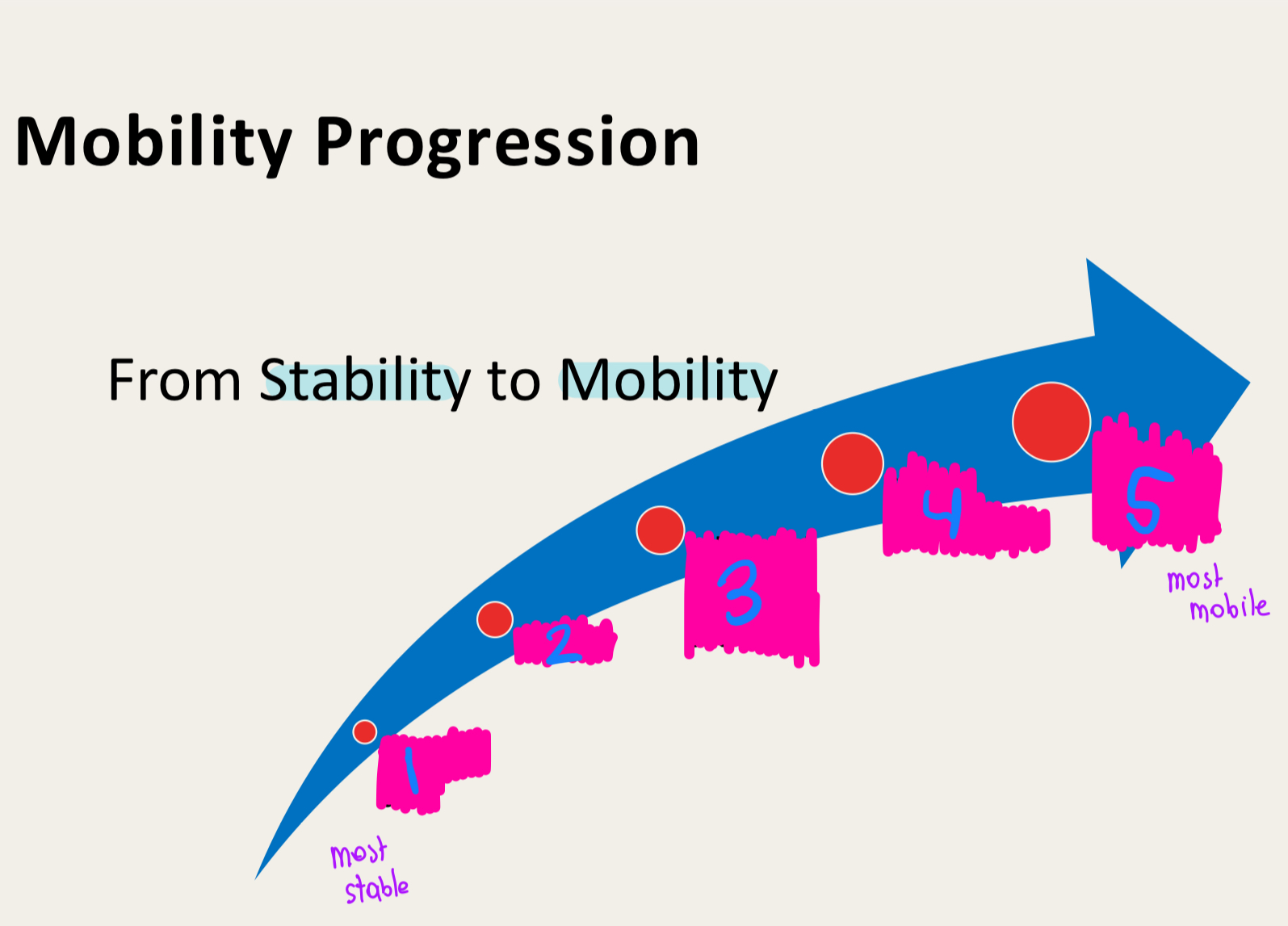
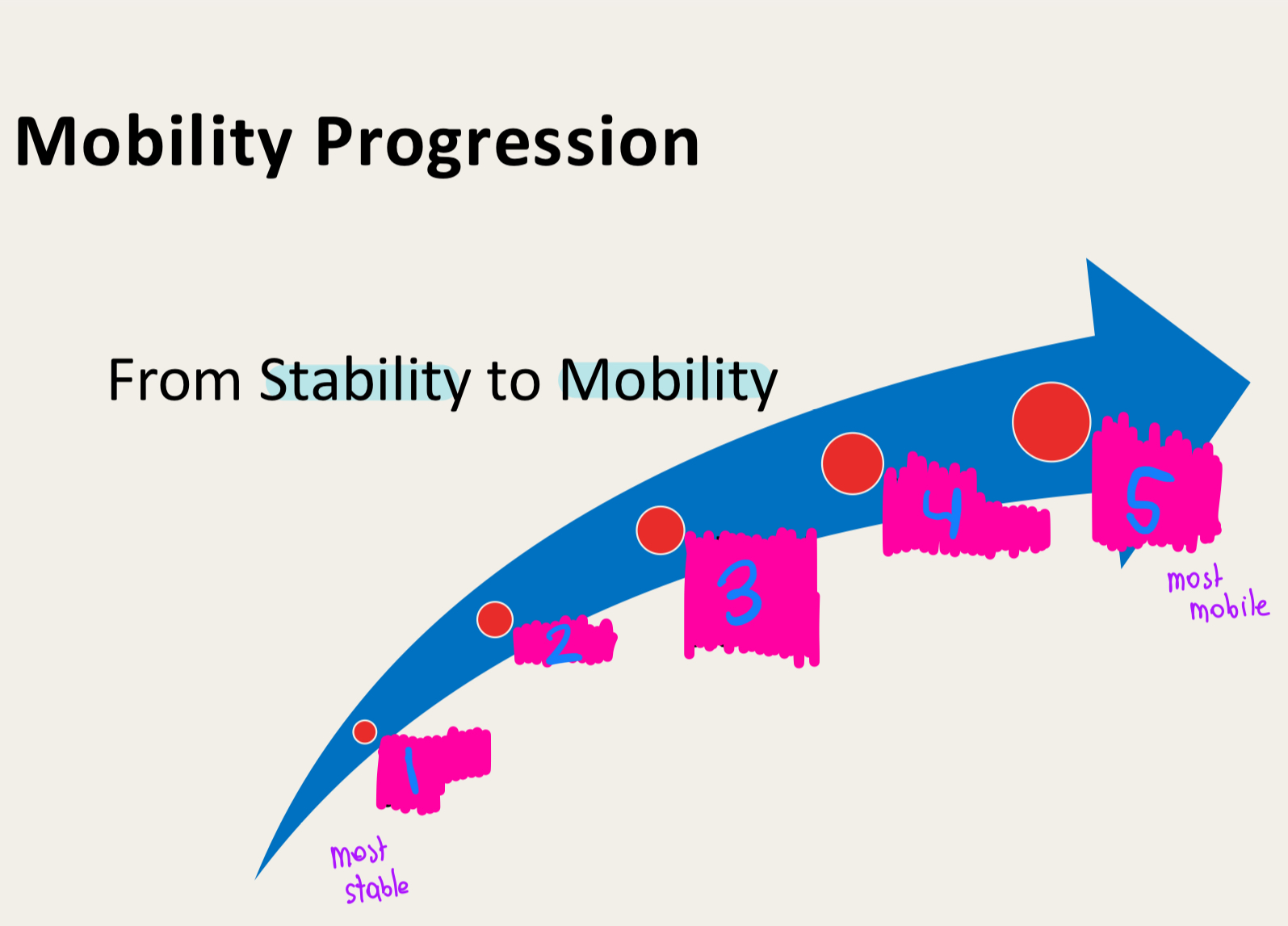
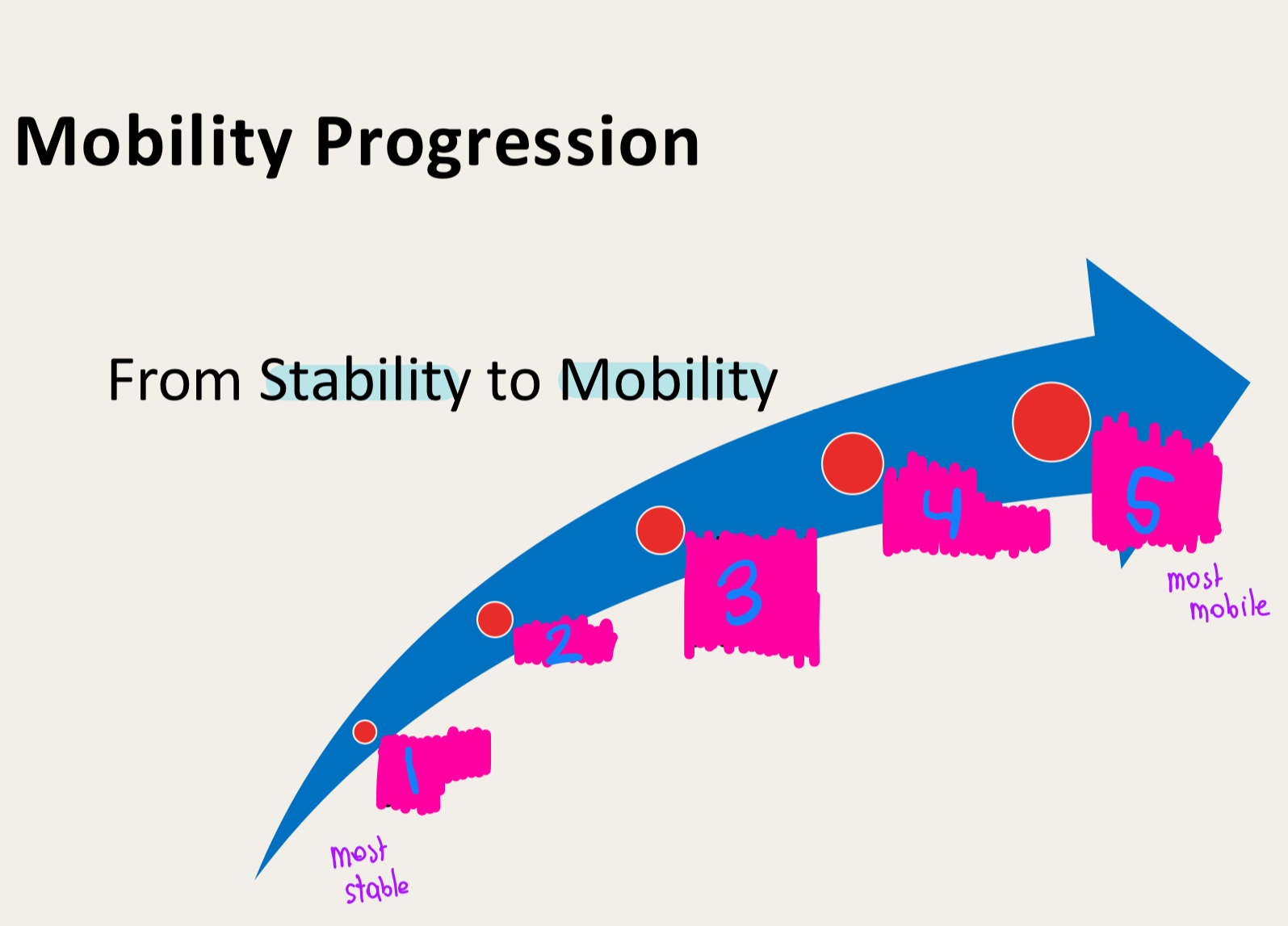
mobility
stability precedes..
attaining a position
maintaining a position precedes …
static and dynamic stability with a smaller base of support
static and dynamic stability with a large base of support precedes …
Attaining a position with a higher center of mass
attaining a position with a low center of mass precedes…
independence
autonomy
bed mobility with patients is usually taught when they have an ____ problem, and a loss of _____
rolling
scooting in supine
moving from supine to sit
sitting and scooting on the edge of bed
four types of bed mobility
if they have a lot of shearing/pain in the lower back
when should you not use the scooting up in the bed technique with a patient
good leg strength (strong hamstrings)
when can a patient use scooting in bed with bridging
Primary center of mass (greater trochanter of the shoulder)
when making a patient scoot with a draw sheet, the PT should be close to the patients ______ and make them tuck their chin to their neck if they are able to
weak legs can get stuck (ex. stroke patient)
one of the cons of bed mobility (supine to sit with log roll)
grabbing shoulder (greater trochanter) and legs if needed
how can i as the PT help facilitate a patient using the supine to sit with log roll
lumbar surgeries (no bending, lifting, or twisting needed with this)
when would you as the PT use the supine to sit with log roll with patients?
hip extensors
obliques
what muscles are used in the supine to sit with log roll?
squat pivot transfer
known as a lateral transfer
point A to point B
deconditioned
lateral transfer goals
move from ___ to ___
safety
maximize independence
use for _____ people
depends on my ability to contact the patient
close to center of mass as possible
when do we as PT’s use gait belts
stand
if the patient can ____, they can likely do a stand pivot transfer
adaptive and assistive
dependent vs independent
grading movements
____ and ____ equipment
___ vs ____
Normal rankings (assistance levels)
adaptive equipment and assistive devices
equipment utilized to provide accommodation to a physical or functional impairment
no
modified independent
would a person be considered independent if they use a walker or a cane?
independent
patient doesn't require physical assistance, adaptive equipment, or verbal cues to consistently perform the activity safely and in an acceptable timeframe
modified independent
can do the activity independently, but requires either equipment, time, or setup
contact guard assistance
Therapist is in contact with the patient. Tactile cues may be needed
minimal assistance
Patient performs 75% or more of the activity safely with or without adaptive or assistive equipment.
moderate assistance
Patient performs 50% to 75% of the activity the activity safely with or without adaptive or assistive equipment.
maximal assistance
Patient performs 25% to 49% of the activity the activity safely with or without adaptive or assistive equipment.
completely dependent
Patient performs 0 to 25% of the activity the activity safely with or without adaptive or assistive equipment.
assistance (functional level of patient)
time (time ADL’s as well)
safety (safe by themselves)?
Consistency
Adaptive/assistive
Unilateral weakness
Documentation of Transfer in the Medical Record
How much _____ the patient requires to perform the transfer and WHY (add to chart why)
Amount of ____ to complete it
Level of ____ demonstrated and verbalized
_____ of performance
Time of day
____ equipment utilized
Environment (closed environment, height of table, surface)
Direction of movement (left/right)… ( ex:______)
Bed to bed; bed to stretcher; bed to OR table transfer
indication for a supine transfer board
Assist patient to move up in bed
ALWAYS 2 PEOPLE
indication for a draw sheet or chuck
weird blood pressure changes
when is it good to use a tilt table
transfer board
can be used for spinal cord injuries, but when patients are independent with the car and bed transfers
chair to bed; bed to chair; chair to chair; wheelchair to car
indication for transfer board use
chair to bed; bed to chair; chair to chair
strength issues or larger in weight
indication for using a patient lift
dependent
a patient lift can lift a _____ person, protecting caregiver and patient from potential injury
fall prevention
anchor for PT
indications for using a gait belt with a patient
safe transfer up and down steps
patient has multiple floors in home
out of pocket with no insurance help
indication for using ramps and a stair glide
Provide assist to patient for bed mobility activities (strong upper body strength)
indication for using a overhead trapeze
Strong enough, rehab, caregiver training
Contraindications
person
assistive
verbally
Vital signs
Preparations for Transfer
What transfer am I asking the client to perform and why (__________)?
Are there _______ or precautions?
Based upon my assessment- do I need another _____?
Based upon my assessment- do I need _____ equipment?
____ discuss the transfer technique with the patient
Personal protective equipment (PPE)
Clear the area and prepare ALL equipment
Oxygen tubing, Foley catheter, IV tubing, bed controls, TV control, nursing call button, chest tubes, telemetry, etc.
8. _____ (pre and post transfer)
as much of the activity as he or she can
shoes or non-skid socks
squat-pivot
equal height
Basic Transfer Principles
Have the client perform ….
Always be aware of your body mechanics
Always have the client wear _____ prior to standing
Lock all wheels (bed and/or wheelchair)
Lower all side rails
Remove armrest of wheelchair for _____ transfers
Strive for _____ of transfer surfaces
Monitor equipment (catheter, IV's, CT's et al)
Be aware of hygiene and client modesty
parallel bars
1
walker
2
bilateral axillary crutches
3
single point cane
4
no assistance device
5