sports science - option d(2)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
2.1: State the reasons why humans cannot live without water for a prolonged period of time
Water is the basic substance for all metabolic processes in the body.
Provides a medium which is essential for all metabolic processes/reactions in the body
Helps to regulate body temperature/homeostasis as water can absorb/release a relatively large amount of heat
Enables cell to cell communication
Helps give structure and form to the body
2.2: State where extracellular fluid can be located throughout the body
Blood plasma
Lymph
Saliva
Fluid in the eyes (aqueous humour and vitreous humour)
Fluid surrounding nerves/spinal cord/cerebrospinal fluid
Synovial fluid
2.3: Compare water distribution in trained and untrained individuals
Greater water content in their body both intra and extracellularly due to increased lean muscle mass compared to untrained who have more fat
Improved temperature regulatory process
Training increases blood plasma and extracellular fluid content
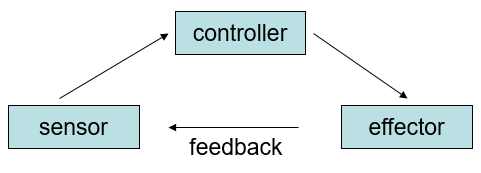
2.4: Explain that homeostasis involved monitoring levels of variables and correcting changes in levels by negative feedback mechanisms - Homeostasis & Feedback
Homeostasis is a state where the body’s internal environment remains relatively constant (within physiological limits)
Feedback systems are a cycle of events in which the status of a body condition is continually monitored, evaluated and changed.
2.4: Explain that homeostasis involved monitoring levels of variables and correcting changes in levels by negative feedback mechanisms - Negative Feedback
Negative feedback is a mechanism of response in which a stimulus initiates actions that reverse/reduce the stimulus.
Explanation: Receptors/Sensors in the feedback system detect the change and send input to the control centre. An effector then produces a physiological response that is able to return the controlled condition to its normal state.
e.g. Insulin and glucose
2.5: Explain the role of the loop of Henle, medulla, collecting duct and ADH in maintaining the water balance of the blood - Kidneys
Kidneys are the urinary organs
produce urine
dispose of metabolic waste
helps regulate the internal environment of the body
2.5: Explain the role of the loop of Henle, medulla, collecting duct and ADH in maintaining the water balance of the blood - Medulla
Inner part of the kidney
regulates concentration of urine by filtering water, salts and acid
2.5: Explain the role of the loop of Henle, medulla, collecting duct and ADH in maintaining the water balance of the blood - Loop of Henle
In the kidneys
main function is to reabsorb water and ions from the urine
2.5: Explain the role of the loop of Henle, medulla, collecting duct and ADH in maintaining the water balance of the blood - Collecting Duct
Collects all material that has not returned to the blood through the tubular membranes
This material exits the kidney as urine
2.5: Explain the role of the loop of Henle, medulla, collecting duct and ADH in maintaining the water balance of the blood - ADH
Anti-diuretic hormone
function is to hold water and increase water uptake
e.g. when body fluid levels are low, receptors in the hypothalamus are stimulated. Hypothalamus then stimulates the pituitary gland to release ADH, which acts on the kidney.
2.6: Describe how the hydration status of athletes can be monitored
Urine colour (volume)
Urine osmolarity
Body mass loss
Hydrometer
2.6: Describe how the hydration status of athletes can be monitored - Urine Colour
used as a subjective indicator of dehydration, the darker the colour suggests greater dehydration
2.6: Describe how the hydration status of athletes can be monitored - Urine Osmolarity
measure the freezing point in urine
2.6: Describe how the hydration status of athletes can be monitored - Hydrometer
measures the specific gravity of the urine and assesses its concentration
2.7: Explain why endurance athletes require a greater water intake
Water intake helps to maintain hydration/avoid dehydration, as well as maintaining thermoregulation
Water loss during prolonged exercise may lead to a decline in athletic performance or serious medical problems (heat exhaustion or heat stroke)
2.8: Discuss the regulation of electrolyte balance during acute and chronic exercise - During exercise
During exercise:
Osmotic pressure and blood pressure increase during exercise
Can be a large loss of sweat (water) which leads to a loss of electrolytes
Electrolyte loss depends on sweat rate, physical condition, training status and state of heat acclimitisation
2.8: Discuss the regulation of electrolyte balance during acute and chronic exercise - Body responds by
Body responds by:
The endocrine system monitoring fluid levels and electrolyte concentrations and corrects these imbalances
ADH causes the walls of DCT (distal convoluted tubule) and collecting dust to become permeable to water which then drastically increases the amount of water that is reabsorbed
ADH also has a vasoconstrictive response on the cardiovascular system