Surgical Nursing Exam 3
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Neurological Function Unit
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Olfactory Nerve I
You ask the patient to identify common scents, such as cinnamon and coffee
Optic Nerve II
Ask the patient to read something or tell how many fingers you are holding up
Oculomotor Nerve III
Controls eye movement and pupil constriction. Check for pupils reaction and accommodation.
Trigerminal Nerve V
Sesantion of face, scalp, and teeth. Contraction of chewing muscles. To test, you can ask the patient to identify touch on different parts of the face with their eyes closed.
Trochlear nerve IV and Abducens VI
Controls eye movement.Test by checking upward and lateral gaze of the eyes.
Facial nerve VII
Controls sense of taste, contraction of facial muscles, secretion of saliva. Ask the patient to smile, wrinkle forehead, check for symmetry.
Vestibulochochleat nerve VII
Sense of hearing, sense of equilibrium
Glossopharyngeal nerve IX
Sense of taste, secretion of saliva, sensory input for cardiac, respiratory, and blood pressure reflexes. Contraction of the pharynx, swallowing. Test by touching the back of the throat with an applicator to elicit gag reflex.
Vagus nerve X
Decreased HR, increased digestive reflexes, perilstasis.
Accessory nerve XI
Contracts shoulder and neck movements, important for head rotation and elevating shoulders.
Hypoglossal Nerve XII
Movement of tongue. Ask patient to stick out tongue and move it from side to side.
Myelogram
X-ray examination of the spinal canal and its contents after injecting of contrast material.
Electroenchephalogram
Electrodes are placed on the scalp to record brain activity. Analysis of the tracing can identify areas of abnormality, such as a seizure focus or areas of slowed activityin the brain.
CT scan
Used to diagnose neurological disorders in the brain or spine. Used when MRI is contraindicated because of metal in the body.
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging, a non-invasive imaging technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of organs and tissues in the body, particularly effective for visualizing soft tissue structures.
-Used to diagnose degenerative diseases
Angiogram
An xray following injection of dye that provides information about the structure of specific vessels as well as overall circulation of the area.
paresthesia
abnormal sensations, such as burning or tingling
Used to evaluate the level of consciousness in patients.What assessments are included in the FOUR score coma scale?
Eye response, motor response, brainstem reflexes, and respiration
What should be the first thing assessed when performing a neurological examination?
LOC
Level of consciousness
Patients response to verbal or tactile stimulation and orientation
Basic neurological assessment includes:
-History of neurologic problems
-LOC and orientation
-Vital signs
-Pupillary response to light
-Assess strength and equality of hand grip and movement of extremities
-Determine the ability to sense touch or pain in the extremities
Brainstem is evaluated using
pupillary and corneal reflexes
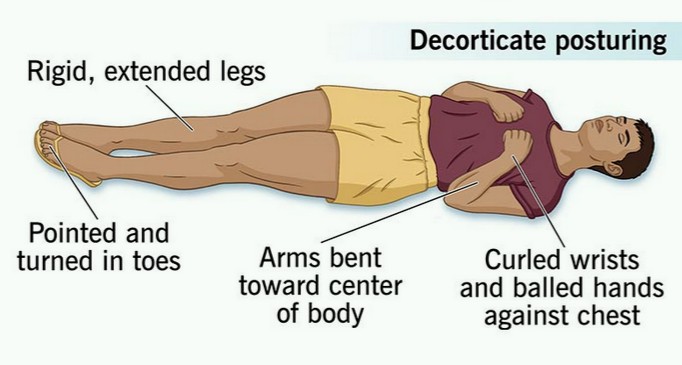
A decorticate posture indicates
damage to the nerve pathways in the midbrain,
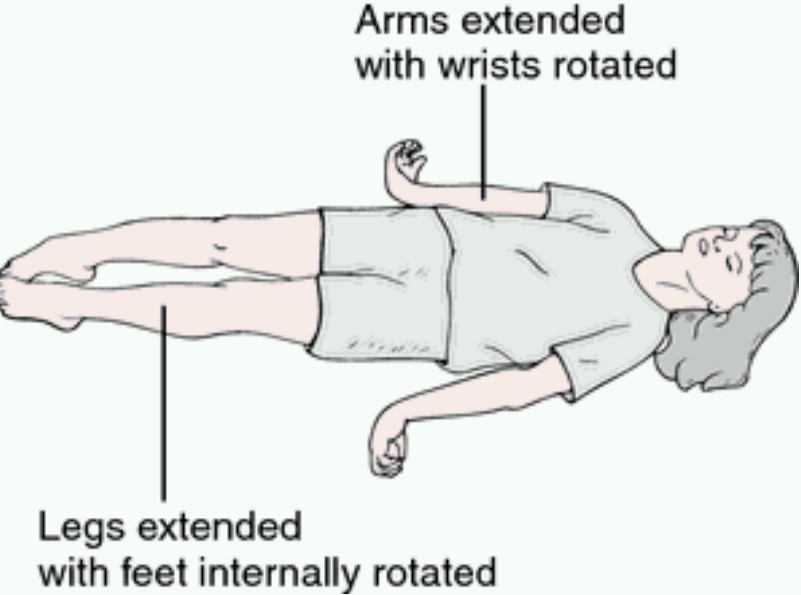
A decerebrate posture indicates
severe damage to your brain or major disruptions in brain function. Some conditions that cause it are treatable, but most people with this symptom don’t survive.
Indicating the patient to close their eyes and ask where the nurse is touching the face is testing the
trigerminal nerve
When performing a neurological assessment, which of the following is a symptom of increasing inter-cranial pressure?
Constricted pupils
Decreasing level of consciousness
narrowing blood pressure
Bradyapnea
Decreasing level of consciousness. As the brain is under increasing pressure, it can't function properly, leading to confusion, drowsiness, lethargy, and eventually coma.
Normal effects of aging on the CNS
reduced blood flow to the brain
impaired short-term memory
sleep disturbances
decrease of acetylcholine
After a patient comes back from a CT scan, what should be encouraged ?
Drinking fluids
Using high top tennis shoes helps with ________ and should be included in patients care plan
foot drop