MLT 111 Exam 1 (Ch. 1, 3, 4)
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
All of the following are endogenous clearance test substances EXCEPT:
Insulin Clearance
Beta2 microglobulin
Creatinine
Cystatin C
Inulin Clearance (an exogenous test)
What is the number of total of mL’s renal blood flow a minute
1,200 mL/min
What consists of urine (organic and inorganic)?
Chloride, Sodium, Creatinine, Urea & Water
What filters blood and restricts cells/larger molecules from the plasma filtrate, in the urinate system?
glomerulus
Calculate the creatinine clearance for a patient of average size from the following data:Urine volume: 720 mL for 12 hours; Urine creatinine: 120 mg/dL; Serum creatinine: 1.5 mg/dL
100 mL/min
60 mL/min
120 mL/min
80 mL/min
80 mL/min
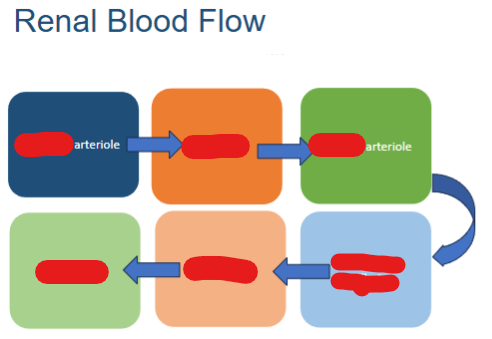
What is the order of RENAL BLOOD flow? (six terms)
Afferent arteriole, glomerulus, Efferent arteriole, peritubular capillaries, vasa recta and renal vein
For active transport to occur, a substance:
Must be in higher concentration in the filtrate than in the blood
Must combine with a carrier protein to create electrochemical energy
Must be filtered through the proximal convoluted tubule
Must be in higher concentration in the blood than in the filtrate
Must combine with a carrier protein to create electrochemical energy
In the measurement of osmolality, a solute that is dissolved in solvent will:
Decrease the freezing point
Decrease the boiling point
Raise the vapor pressure
Raise the dew point
Decrease the freezing point
John White donates one of his two healthy kidneys to his twin brother. His glomerular filtration rate can be expected to:
Decrease gradually over 1 year
Decrease by 50%
Increase by 50%
Remain within a normal range
Remain within a normal range
Measurement of urine osmolality is a more accurate measure of renal concentrating ability than specific gravity because:
Osmolality is measured by instrumentation
Osmolality is influenced equally by small and large molecules
Specific gravity is not influenced by urea and glucose molecules
Specific gravity measures only urea and glucose molecules
Osmolality is influenced equally by small and large molecules
Normal functions of the kidney include all of the following EXCEPT:
Elimination of serum proteins
Regulating electrolyte balance
Elimination of nitrogenous wastes
Regulating body hydration
Elimination of serum proteins
Results for glomerular filtration tests are reported in:
Milliliters per 24 hours
Milliliters per minute
Milliequivalents per liter
Milligrams per deciliter
Milliliters per minute
Substances that can interfere with serum osmolality readings include all of the following EXCEPT:
Sodium
Lipids
Ethanol
Lactic acid
Sodium
The extent to which the kidney concentrates the glomerular filtrate can be determined by measuring:
Urine and serum osmolality
Serum osmolality
Urine creatinine
Serum creatinine
Urine and serum osmolality
What are functions of the kidneys?
to clear waste by blood filtration
maintain hydration (water & electrolytes)
maintain acid-base balance
How much urine does kidneys convert from plasma daily?
600-2000 mL
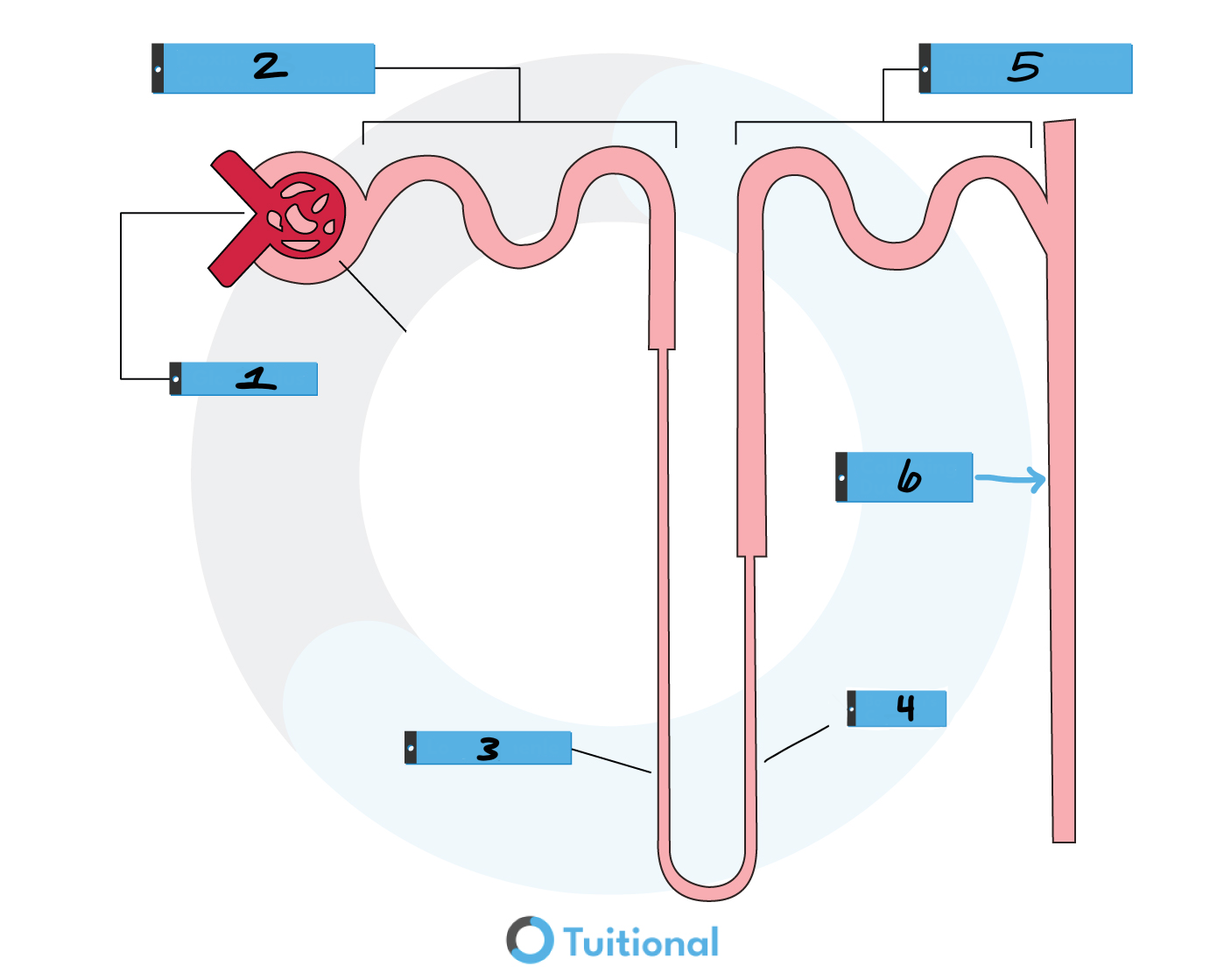
In what order does URINE FILTRATE flow?
Glomerulus(in Bowmans capsule)
proximal convoluted tubule
Loop of Henle (descending then ascending)
distal convoluted tubule
collecting duct
What and where controls water reabsorption by responding to ADH?
collecting duct
What does RAAS stand for?
Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System (RAAS)
What hormone system regulates blood pressure?
Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System (RAAS)
Which of the following are reasons to perform urinalysis testing?
A. Aid disease diagnosis
B. Monitor disease progress
C. A and B
D. A only
C. Both (Aid disease diagnosis and Monitor disease progress)
Which of the following is NOT a organic constituent of urine?
Urea, Uric Acid, Water, Potassium, Sodium, Creatinine, Chloride and Sodium
Chloride, Potassium & Sodium
What is the value of specific gravity of plasma filtrate?
1.010
The formula C= UV/ (X) 1.73/A is to calculate what?
creatinine clearance
What are the four types of infectious agents?
Bacteria, Fungi, Parasites and Viruses
What is a reservoir?
a location of potentially harmful microorganisms— like humans, animals and fomites.
What is a portal of entry?
Places microorganisms can enter a host— like open wounds, breaks in skin and mucous membranes(eyes, nose, mouth)
What procedure ensures that acceptable stands are met during the process of patient testing?
Quality Control
Chain of infection order: There are (6)
Infections agent
Reservoir
Portal of exit
Means of transmission
Portal of entry
Susceptible host
What does RACE stand for?
rescue, alarm, contain, extinguish
What does PASS stand for?
Pull, Aim, Squeeze, Sweep
The Center of Disease Control recommends that Standard PRECAUTIONS be followed when encountering…
All body fluid specimens
The ability to obtain the published result on control sample is referred to as…
accuracy
What’s the highest acceptable range for confidence limits in the clinical laboratory?
+3 SD
The most regulated level of the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendment categories is?
high-complexity
What’s the daily urine volume?
1,200 to 1,500 mL
What’s renal blood flow volume?
1,200 mL/min
The kidneys convert how much plasma to urine?
600- 2,000 mL
A first morning specimen is frequently requested to confirm:
Orthostatic proteinuria
Urination output decreases ; dehydration is..
Average of 200-500mL urine output
Oliguria
What condition related to painful urination (UTI or kidney stones)?
dysuria
A urine specimen containing a large amount of precipitated amorphous(or crystals) material may have been preserved using:
Refrigeration
What’s a good preservative of urinary cellular cultures?
boric acid, Formalin, Thymol
An alternative to the catheterized specimen is the; need to avoid risk of bacteria contamination…
Midstream clean-catch specimen (clean & pee a bit before collection)
An unpreserved urine specimen left at room temperature overnight will have decreased:
Glucose and ketones
Documentation of appropriate handling of specimens for drug analysis is provided by the:
Chain of custody form
Increased turbidity in urine stored at room temperature is usually caused by:
Bacterial Growth
Quantitation of a substance that varies with daily activities should be performed on a:
24-hour specimen
Sodium fluoride used as a preservative for urinalysis best protects:
Drugs
The first morning specimen from a patient with no history of symptoms for diabetes is positive for glucose. The patient should:
Be asked to collect the second morning specimen
The polyuria associated with diabetes mellitus is caused by increase in what:
The presence of excess glucose in the urine and increased urination
The recommended specimen for routine urinalysis or pregnancy testing is the:
First morning specimen
The specimen of choice for routine urinalysis is the first morning urine because it:
Is more concentrated to better detect abnormalities
Urea is a product of:
Protein and amino acid metabolism
What is the maximum length of time a urine specimen can remain unpreserved at room temperature before testing?
2 hours
When urine output decreases when the body is dehydrated is the condition of
oliguria
When the suspension of urination/decrease in flow of blood to the kidneys; (risks of kidney damage)
anuria
Increased urination at night is called…🌙
nocturia
A condition of excess thirst and urine production (caused by diabetes insipidus & mellitus)…
polyuria
Order urinary filtrate?
Glomerulus capsule
Proximal convoluted tubule
Loop of Henlee
Distal convoluted tubule
Collecting duct (to bladder)
What the number of specific gravity in urine filtrate?
1.010
A decrease in ADH causing decreased reabsorption of water and increased urine (fluid balance issue) is the condition of…
Diabetes insipidus
When there’s is increased urine volume caused by the need to excrete the excess glucose…also (frequent urination, excessive glucose)
Diabetes Mellitus
What decreases overtime in urine samples?
Glucose (ketones and bilirubin too)
What increases overtime in a urine sample?
Nitrite (pH too)
What’s your sample has the highest concentration of any analyte?
First morning
What urine sample are best used for monitoring diabetes mellitus?
Fasting sample
What procedure is important for drug of abuse urine testing?
Chain of custody