Topic 5 : Mendelian Genetics in Populations 1: Selection and mutation
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What can evolve and not
Only populations evolve, not individuals
What is population genetics?
Integrates theory of evolution wirth mendelian genetics
How do we determine genotypes?
By looking at the phenotype- Intestinal schistosomiasis example and examining the different proteins encoded by the alleles
How does protein help us look for genetic variation?
The different allels will make different versions of preoteins because theyèll have differences in amino acids which causes different folds and shapes to occur
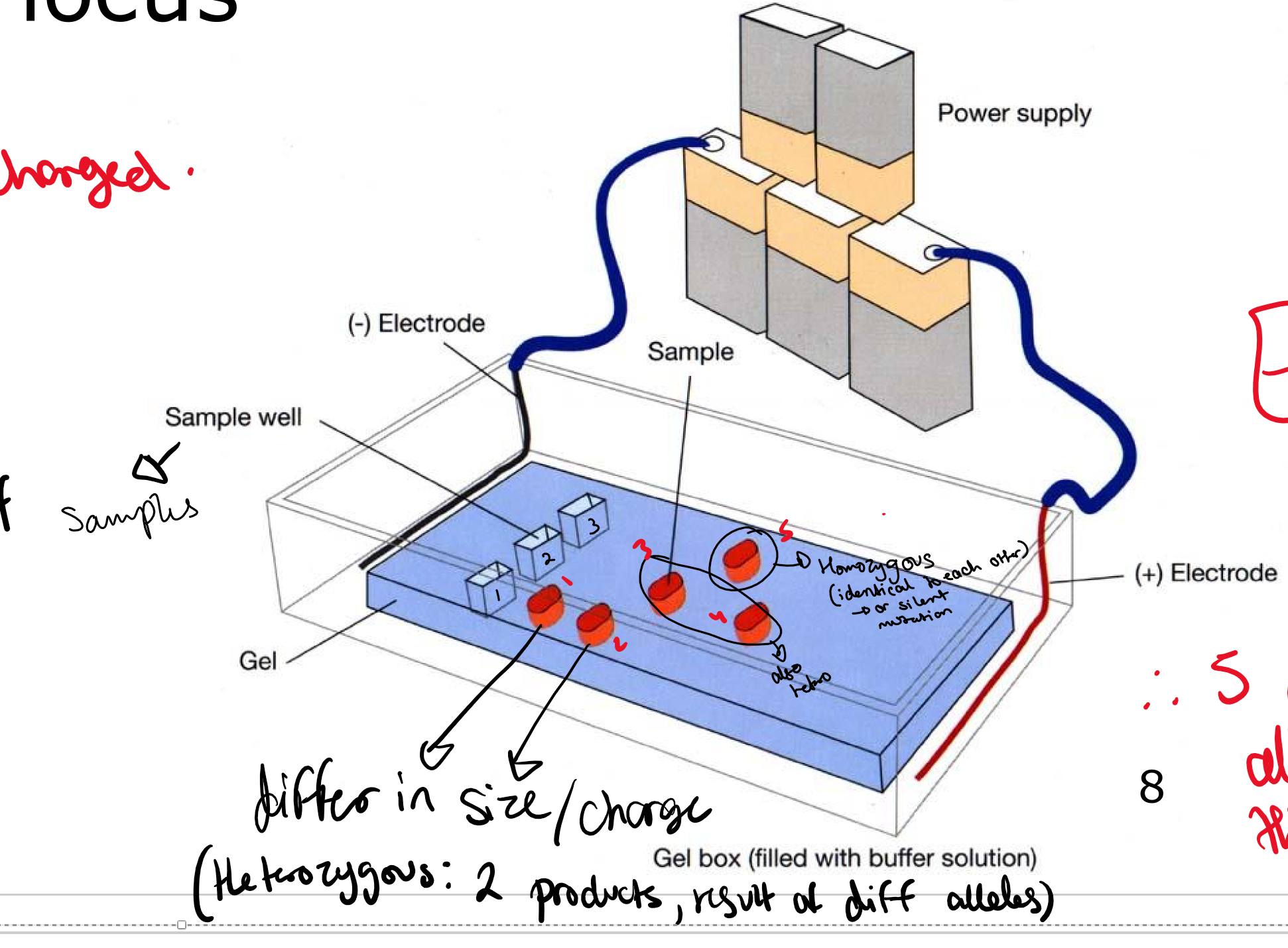
What was the first method to determine genotypes
Protein electrophoresis and measure the diversity in locus- because different alleles would give different shapes and they would all be placed at different spots due to their weight. If het then 2 is supposed to come out in one lane, if not then homo
How much is an individual heterozygous at their genes?
33-50%
How many of the genes that code for enzymes are polymorphic?
4-15%
What is polymorphic
-more than 1 allele in the POPULATION!!
How to measure genetic variation?
Find genotypic variation → Look at phenotypes
Look at proteins that are made from the different alleles
Use genetic techniques to find out the alleles: PCR, Microsatellite gel and electrophoresis
How to read microsatellite gel
each well should show two distinct bands or 1 thick band representing the alleles, can determine if homo or hetero
Genetic variation - Calculate allele frequencies
For allele frequencies, count the total popn and multiply it by two and homo x 2 and hetero x1 —> divide by popn x two
Hardy weinberg Assumptions
No mutation
No selection
Individuals mate at random
no genetic drift
no gene flow
What is hardy weinberg a model of?
Model of a population, not an individual
-only works for diploid organisms
What is panmictic
random mating
Genotype frequencies in panmictic populations
In panmictic populations —> Genotype frequencies DO NOT change because each male mates with a random female who likely has the same genotype frequencies —> because the whole population has the same frequency
gametes in panmictic population
Gametes are proportional to each other in the population and different alleles should equal to 1
Is evolution occuring under H-W? (2)
Genotype frequencies can be predicted from allele frequencies
Alleles frequencies are stable over a long period of time
—> If these two are true then evolution doesn’t occur
Under HW, what are the ratios of genotype frequencies for 2 alleles
homozygous are squared - p² and q²
Heterozygous - pq + pq = 2pq (heteros can happen 2 ways)
HW equation
p² +2pq +q²
What happens when actual vs expected values are similar or the same
Then assumption 1: Popn is not evolving is not violated and population is in hardy weinberg eqm
What is heterozygosity
heterozygous /sample pop
Heterozygote deficity
Actual heterozygote population is less than the expected
what does large population mean in HW
Genetic Drift —> when this assumption is violated then population is small and genetic drift occurs
What varies in fitness genotypes or phenotypes?
Genotypes: they give rise to phenotypes that allow individuals to be fit or not
Fruit flies selction example
Control group: Fruit flies-have genes to breakdown ethanol → ethanol breakdown fixation.
What happens when selection is symmetrical
genotype frequencies change but allele frequencies do not
When is selection rapid /slow
what is heterozygotes advantage
WHat are the patterns of selection (5)
Heterozygote advantage -: being het is more advantageous than being homo
Heterozygote inferiority: being homozygote is more advantageous than being het
Selection is rapid: recessive allele is lethal and common
Selection is slow: recessive alleles are lethal and rare
Frequency dependent selection
Elderflower orchids example
Bees will fly to rare flowers to search for nectar and go in a 1:1 ratio between diff coloured flowers. This is negative frequency dependent selection
What is the source of new alleles in a population?
Mutations
Imagine a mutation happens in a population wheere allele A turns into a at a rate of 1 in 1000. Initial frequncies of the alleles are : A: 0.9 and a : 0.1 . what is the new allele freqiencies
what can change allele frewucnies over a long period of time?
mutations
Drosophila and salt mutation experiment
inbred solution w same gene variations: Control group no salt: survived but also had mutation to be able to breakdown salt, group w stressed line: mutation to stop breakdown of salt increased a LOTTTTT due to environment and selection pressure
How can deleterious alleles persist (2)
mutation of the recessive allele
Heterozygote advantage
what is mutation selection balance
rate of mutation of recessive allele = rate of getting them out of the population