Exam 4 part 1/5
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
community ecology and strucutre
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
ecology in simplist terms?
Multi-disciplinary science studying relationships between living organisms and their surrounds (both abiotic and biotic)
Scale of interaction
Refers to the different levels at which ecological interactions occur, ranging from individual organisms to populations, communities, and ecosystems, including global processes in the biosphere.
Biosphere does what in the scale of ecological interactions?
Its the whole global process
Ecosystems ecological interaction in the scale?
The flow of energy and matter
Communitys ecological interaction in the scale?
The interactions among different species within a community, including competition, predation, and symbiosis.
Population ecological interaction in the scale?
Population dynamics the unit of evolution
Individual ecological interaction in the scale?
Survival and reproduction the unit of natural selection
In the individual approach how do they adapt to the environment? Survival and reproduction?
Natrual selection is the process by which individuals better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring.
What is the Population approach?
The population approach examines how populations interact with their environment, focusing on factors like density, distribution, and the population dynamics of growth and decline from births and immigration(+) and deaths and emigration (-). This approach is limited by resources, diseases, and competition.
What is community approach?
All populations (of different species) together in one place ( may include plants, fungi, animals and etc;). Different species present, diversity of populations, this approach helps us understand how species interact with each other and compete for the same resources.
What is the ecosystem approach?
The community along with the non-living environment. considers organism and their environment , food webs, trophic levels, and energy flow.
Ecosystem was coined by who?
In 1935, British ecologist Arthur Tansley.
What is the biosphere approach?
The global environment , consists of living things on the planet. “the sum of all ecosystems’.
Community approach can be organized by either ___________ or __________.
Physical characteristics or biological characteristics.
Community approach physical characteristics are to
emphasize the environment, e.g., streams, sand dunes, deserts, grasslands, etc.
Community approach biological characteristics are to
emphasize the dominant species e.g. plants, bacteria, animals, etc.
Community structure what is it?
the types and numbers of species ( or subjects of species) present
Community change what is it?
the dynamic fluctuations of communities over time
what are early species?
annual plants that grow and are later succeeded by grasses and perennials.
what are intermediate species?
Shrubs, then pines, and young oak, and hickory begin to grow.
what are late species?
The mature oak and hickory forest remains stable until the next disturbance.
Communities groups are split up and characterized into 3 groups what are they?
Taxonomic affinity, guild, and fuctional group.
Taxonomic affinity means what?
all the bird species in a community
Guild means what?
A group of species that use the same resources, like bees, hummingbirds and bats, all sucking nectar plants.
Functional group means what?
The species that function in similar ways, but do not necessarily use the same resources.
When characterizing species types what are the big 3?
Foundation species, keystone species, and dominant.
Foundation species, what are they?
This species can causes physical or chemical changes in the environment that affects other species.
keystone species, can be described as what?
The ones that control the distribution or abundance of other species, but not necessarily the most abundant specie.
An example of keystone species.
the star fish is great example
Some examples of foundation species.
beavers, worms, buffalo
Dominant species are best described as
having the most abundance in either numbers or biomass, overall this species out-competes others
an example of dominant species are
The Alder trees after the forest harvest in British Colombia and the Kelp forest off the coast of California
How do we measure community structure?
In terms of species richness, evenness, and diversirty.
Species Richness is
the number of different species in a community
Species evennesss is
relative abundances compared with one another.
Species Diversity is
the combination of species richness and species evenness this measures the communities complexity
Species richness is highest where globally?
In the Equatorial regions (Northern part of South America)
Higher species evenness
means there is a more of an even spread of the same species in a given community
Lower species evenness
means the species in the given community are not even might be 15 of one specie and 2 or 3 of some other species
There is higher specie evenness when the relative abundance
is equally spread out
what method is used to find the species diversity?
The most common method is an index called the Shannon-Weiner index aka “Shannon index”
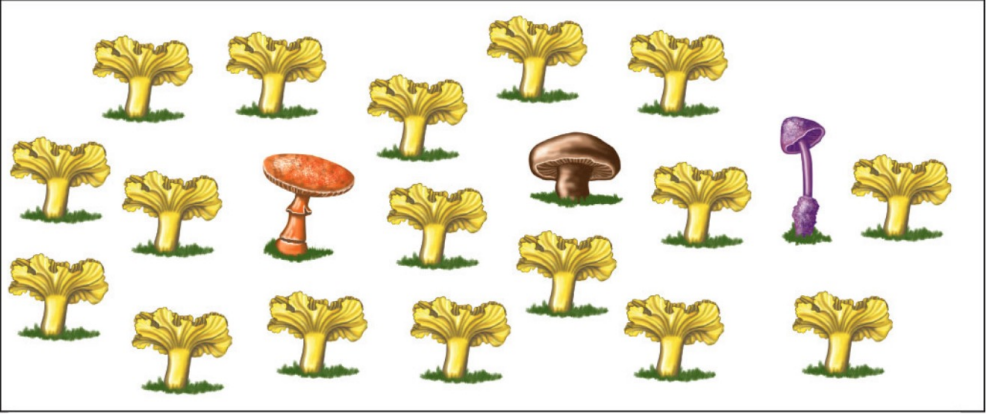

In the mushroom example find the abundance total
20, mushrooms in community A
In the mushroom example find the richness total
4, this is the number of different species
Find the proportion by dividing the abundance from the total, and do it for each species.
yellow mushrooms 17/20 = 0.85 , orange mushroom 1/20 = 0.05, purple mushroom 1/20 = 0.05, and the brown mushrroom 1/20 = 0.05.
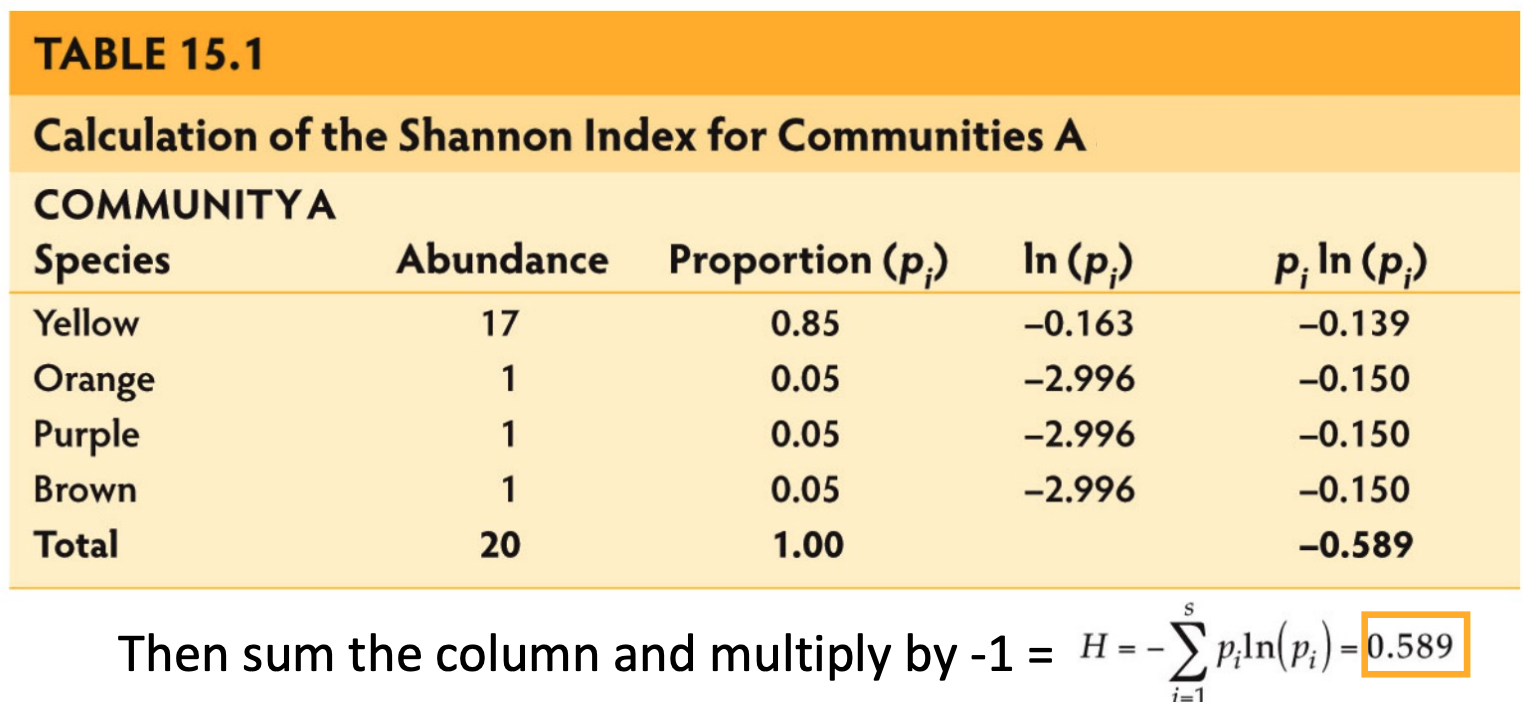
when measuring communities after finding the pi ln (pi) you must multiple the columns sum by -1.
in our mushroom community A we get 0.589
From the Shannon index a lower value indicates
the communties diversity is low
From the Shannon index a higher value indicates
the communities diversity is higher
what is species accumulation curve and how do we use it?
This curve helps determine when most or enough species in a community have been observed.
What does the function represent in a species accumulation curve
Species richness is plotted as a function of the total number of the individuals that have been counted
Community structure is made up 5 parts what are they?
Climate patterns, Geography, heterogeneity, disturbances, and interactions
Climate patterns influence the community how?
The communities location, wether it be global, local, and unpredictable/variable climate patterns (temperatures, solar radiation, perception, etc.)
From certain climate patterns we can identify significant changes as they can: (warming temperatures example)
alter species survival rates, shift species distributions, disrupt and destabilize food webs, sporadic events (like droughts, freezes, and heat waves), and “Mismatches” in warming environments
What is a temporal mistmatch in warming climates
Shifts in the phenology induce temporal (mis)matches (because of warming temperatures the bees regular seasonal patterns happen at different times then they used to. this can be problem for example if a bee waits longer to go find flowers to pollinate it might wait to long and no longer will their be enough flowers because their seasonal period is ending.)
what is spatial mismatches under a warming climate
As temperatures rise we expect to see some species move, the species range shifts, a class example being the butterflies moving up higher in altitude from the lady bugs in the lower region, giving the species less overlap on each other.
Body size mismatches under warming climate
this is the changes in body size induce size (mis)matches, because of warming the body size will decrease
Geography as a community structure is the communities location
this being isolated, mainland, physical stress, etc
Heterogeneity or patchiness influences what in a community structure?
the patchiness of resources (moisture, nutrient availability, etc.) in a community, a wetter environment offers different levels of nutrients compared to a more dry and barren land.
How does frequency influence community strucutre?
The frequency of disturbances or disruptive events like fires, storms, landlslides, etc.
How do interactions influence community structures?
Interactions between organisms like predation, competition, symbiosis, etc. we can easily see some of these connections through a food web for example.