Human Geography Unit 2
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Population Distribution
The way people are spread across Earth's surface
Ecumene
Part of the Earth's surface that is occupied by permanent human settlements
Arithmetic Density
Total # of people divided by total # of area
Physiological Density
Total # of people people divided by farm land
Arable Land
Land Suitable for farming
Doubling Time
The time it takes for a population to double
One-Child Policy
Limited families to one child in China (now 3)
Special Economic Zones (SEZ’s)
Special low tax/tarrif laws than rest of the country
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
# Of people per 1,000’s born a year
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
#Of people per 1,000 dying each year
Natural Increase Rate (NIR)
Birthrate-DeathRate
Life expectancy
How long a person is expected to live in a country
Sex Ratio
Number of females compared to number of Males
Dependency Ratio
Ppl in the workforce : People not
Demographic Transition Model
Model with 5 stages that helps to explain the rise and fall of population growth rates over time.
Demographic Transition Model Stage 1
High CBR, High CDR, NIR is about even. No Country is in this stage.
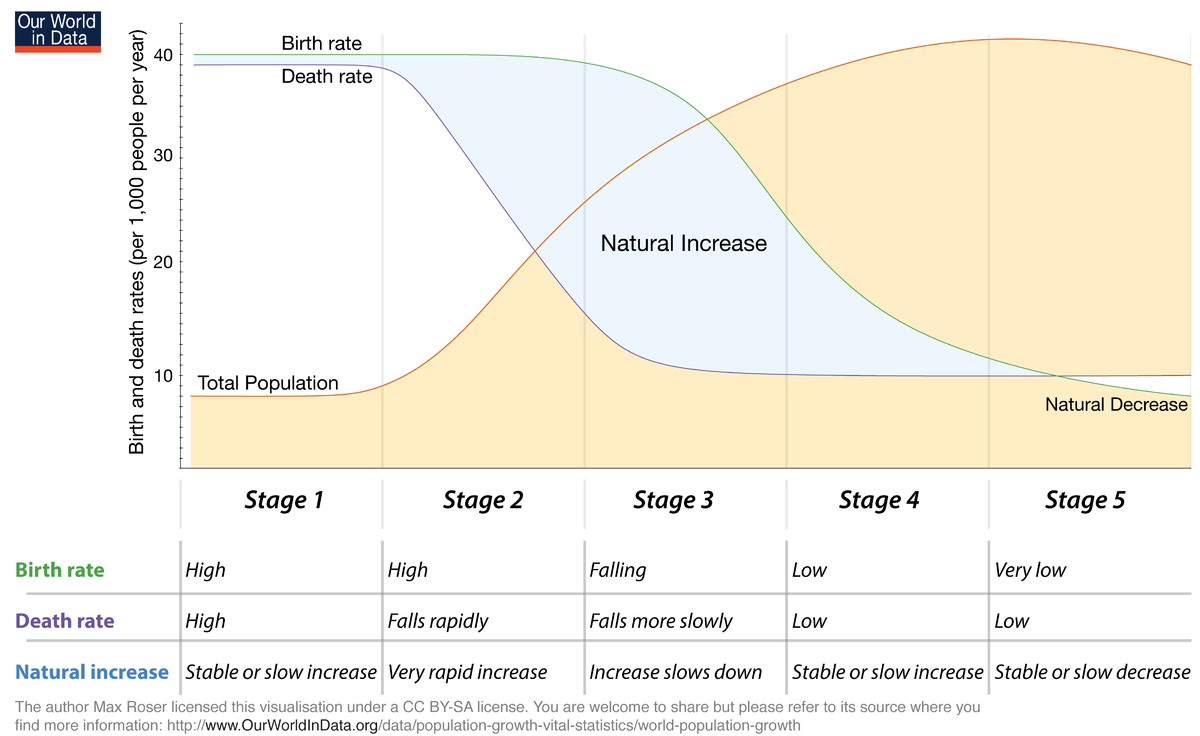
Demographic Transition Model Stage 2
CBR is high, CDR is falling rapidly, so the NIR will become very high. Death rates drop from immunization from factories. (THIS IS THE FASTEST POPULATION GROWS) This is seen in LDC’s.
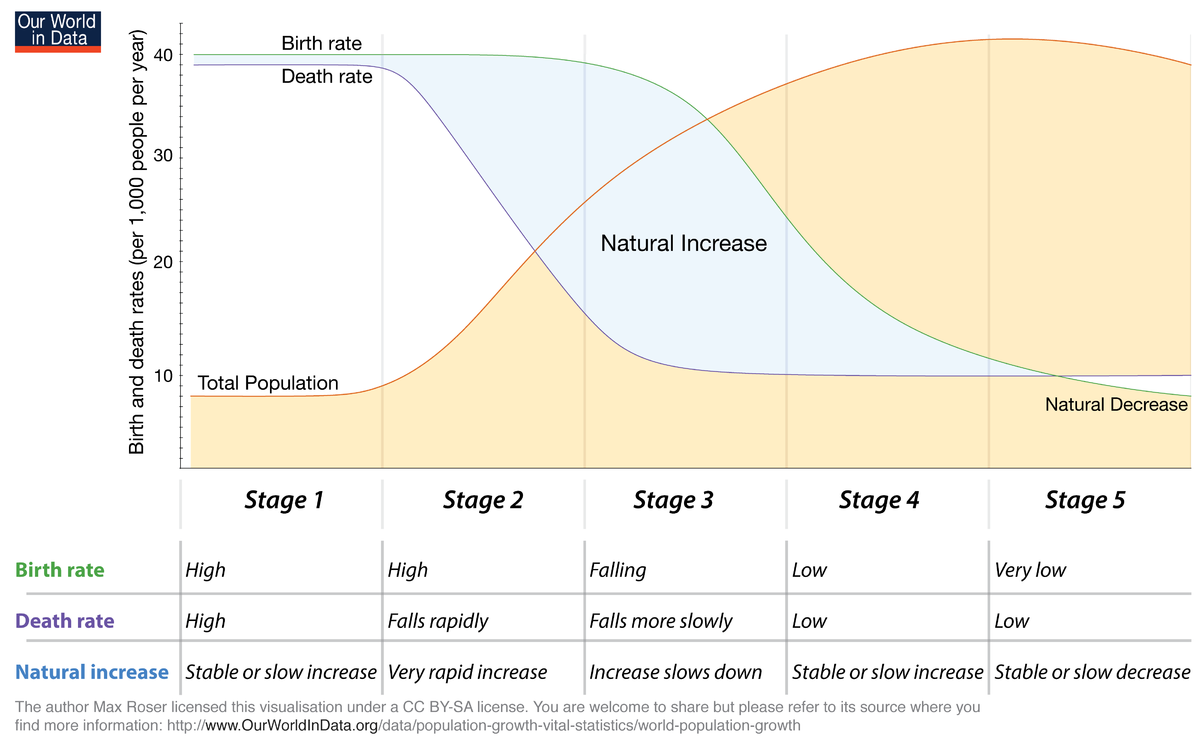
Demographic Transition Model Stage 3
CBR is falling but still high. CDR falls more slowly, but still low. NIR is increasing, but not as fast as stage 2. Big drop in the birth rate due to the advancement of education and equality. This is seen in Mid developed Countries Like Saudi.
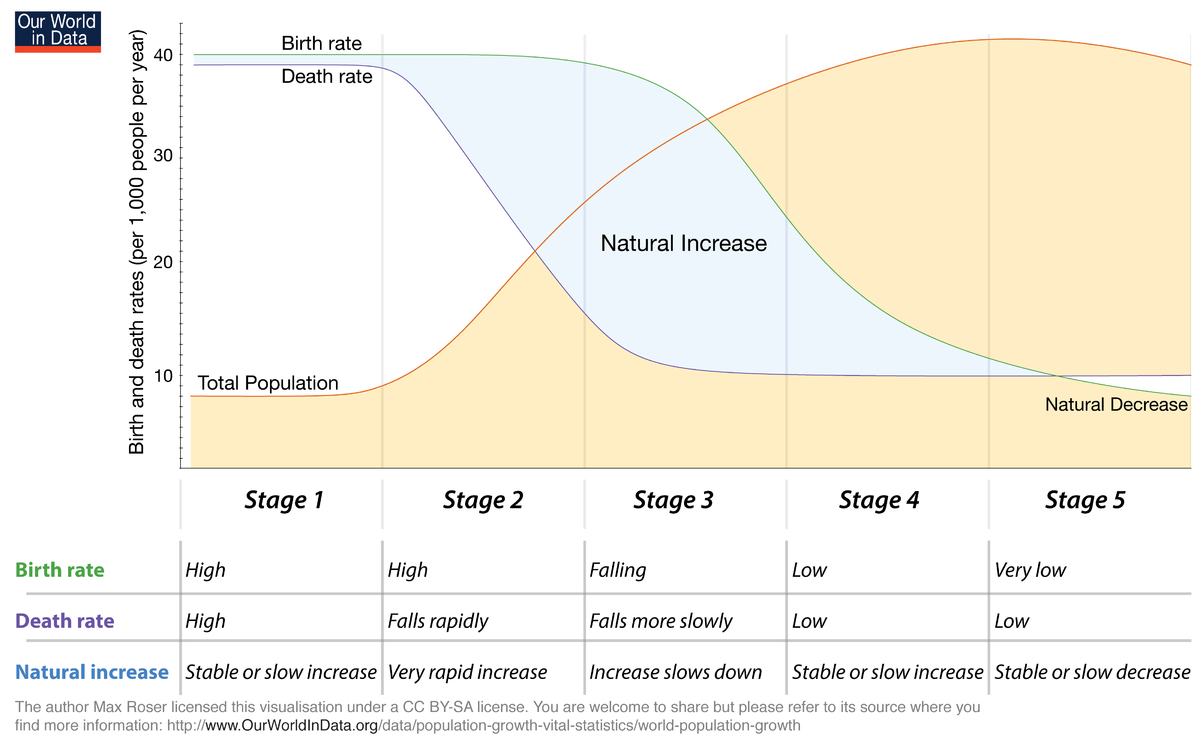
Demographic Transition Model Stage 4
CBR is low, CDR is low. NIR is very slow. At this stage, TOTAL POPULATION IS THE HIGHEST. US, etc.
Demographic Transition Model Stage 5
CBR is very low, CDR is low but starting to increase, and NIR is now negative. Extremely low birthrate and aging population. Japan, Germany,ETC.
In what Stage is there large amount of deaths, but zero/little growth.
Stage 1
(5 Short answer): Define Ecumene. Identify and explain one cultural reason why we people have decided to live in clusters. Identify one physical land type that many people to not live at and explain the reason why.
Ecumene is part of the earth surface that is occupied by permanent human settlements. When you surround yourself around people. you take cultural influence from them and are much happier. Climate and weather in that area must also be nice. People avoid living near deserts or mountains because of extreme climate and lack of resources.
(5 Short answer): Identify 2 specific strategies China implemented to help deal with a fast-growing population. Choose one of those strategies and explain 2 benefits or ways it might help meet the demand of the fast-growing population. Explain one negative impact of this strategy.
The one-child policy limited families to only 1 child in China. China also has replaced coal energy with Hydro electric power. 2 positives about the one-child policy is that there will be smaller families and there would be a lot of resources available. One negative is that families prefer men over women, therefore there will be a lot more men than women, meaning not enough women for the amount of men to create a family.
(5 Short answer): Be able to identify each population pyramid by stage. For each pyramid, be able to explain life expectancy, birth Rate, and death Rate. In addition, be able to explain the level of development and the rate of growth for each stage pyramid.
The first stage is” Primitive societies: Low growth.” The pyramid has a really wide base. CBR is high, and CDR is high. Life expectancy is low. The rate of growth is even. The second stage is “ Current least developed countries in the world.” The wide base means CBR is high, but CDR is lower. Life expectancy is a little better. The rate of growth is now higher. The third stage is “Current middle development countries.” Its edges start to become more rounded, and its CBR is lowering, and so is its CDR. The mid and upper ages become wider, so life expectancy is rising. The rate is still increasing, but not as much as in stage 2. Stage 4 is “More developed Countries today.” The pyramid starts to straighten out, and both CBR and CDR is low. Life expectancy is higher, but the rate of growth is slowing. And for the last stage #5, “Have been developed for a long time countries.” The CBR is low, and the CDR is rising. Life expectancy is the oldest, and the NIR is negative.
(5 Short answer): Name a specific European country that is in Stage 5 of the Demographic Model. Identify 2 strategies the country is using to battle their population issues and explain how each strategy will work.
Germany is in stage 5. Strategies they will use to increase population and occupying more jobs would be convincing women to work but still have kids, and making more comfortable working conditions for old people. By increasing gender equality and providing daycare, women might have more children. And jobs have been starting to give more flexible hours for old people.
(5 Short answer): Identify the significance of who Thomas Malthus is. Explain two governmental Anti-Natalism or two Pro-Natalist programs and how they have worked or would work. (Identify country)
Thomas Malthus is a person who thinks that eventually, population on earth will become so high, that there wouldn’t be enough resources for the population. However, he is proven wrong, because humans evolve and adapt new technological advancements and ways of multiplying or storing resources. 2 Pro-Natalist programs would be The Chinese government offering benefits like tax breaks, longer maternity leave, and better childcare support. And a law in Germany that guarantee day care for all children over 12 months. Tax breaks and child support in China makes it cheaper and less expensive and easier to have kids. The Daycare Law in Germany helps families keep their Child busy while they go to work or do something else. Overall these two programs/laws encourage Natalism.
(5 Short answer): Explain and provide an example of an Internally Displaced Person/people. Explain how not all migrants would be considered refugees (Show the differences)
An internally displaced person is a person forced to move from one location, similar to a refugee, but still in the country. An example of this could be people who lived in villages in South Sudan, are now at POC camps, because the villages are too dangerous, and the people leaving the villages to the camps are Internally Displaced People.. Not all migrants are refugees. Some immigrate to a country for a better job, education, future, and/or an overall better standard of living. Some migrants are refugees. A refugee is someone who is forced to move to another country because if they stay, they will face persecution
(5 Short answer): Define “Brain Drain.” Explain the potential positive and negative effects that brain drain has on the source/home country and the country they are going to.
Brain Drain is when a high skilled-educated person leaves a LDC to a MDC. This is not good for the country they are leaving because if that country keeps losing doctors , lawerys, ETC, less people will be able to get healthcare and the country's overall development will decrease. However, for the country they are going to, they are helping that country by making it more developed, with more doctors, lawyers, the economy goes up, people have better healthcare , and there are more workers. How ever, there is a negative to this. Immigrants who come into the country make it more difficult for the citizens of the country to be able to find a job.
(5 Short answer): Discuss an example of Environmental Migration. During your discussion, you must include where they migrated from and migrated to while also including the push and pull factors. Identify if migration is internal or international and identify the type within each.
In Tuvalu, there are storms and natural disasters happening. This classes a lack of water and supplies (Push factor). People are going to larger islands like Australia, Fiji, ETC because of better climate and less storms( Pull Factor) This is forced international Migration.
(5 Short answer): Discuss an example of Political Migration. During your discussion, you must include where they migrated from and migrated to while also including the push and pull factors. Identify if migration is internal or international and identify the type within each.
Refugees in Syria are fleeing due to a civil war (Push Factor) They are going to Europe, countries like Germany and Sweden so that they can live in peace away from war with a better economy (Pull Factor) This is international forced migration.
(5 Short answer): Discuss an example of Economic Migration. During your discussion, you must include where they migrated from and migrated to while also including the push and pull factors. Identify if migration is internal or international and identify the type within each.
People are moving from Indiana due to a lack of economic opportunities and jobs (Push factors)m They are going to Tampa Bay to enjoy the beach, and the new business and jobs (pull Factor). This is internal Migration Interregional.
Migration
Form of relocation involving the permanent relocation of people to a new location
Emigration
LEAVING a country
Immigration
GOING TO a country
Voluntary Migration
You choose to migrate
Forced Migration
something makes you migrate
Interregional Migration
One of the 2 types on Internal Migration. From one region to another.
Intraregional Migration
One of the 2 types of Internal Migration. Migration within one region
Rural to Urban
Country/Farm part region to the major cities. Stage 2
Urban to Suburban
Moving from inner cities to the smaller surrounding towns, Stage 4 or 5.
Counterurbanization
One of the 3 types of Intraregional Migration: Urban to rural. People wanting to move back to small-town life. (City to countryside)
Economic Migration
Migration due to jobs, payment, or good or bad economy.
Political Migration
Migration due to War, Freedom, Political persecution, ethnic or religion, refuge, ideology.
Environmental migration
Migration due to enviorment
Refugee
is someone who is forced to move to another country because if they stay, they will face persecution
International Migration
From one country to another
Internally displaced person
internally displaced person is a person forced to move from one location, similar to a refugee, but still in the country.
Asylum seeker
migrated to another country but wants to be seen as refugee (more rights)