BU2 Module 3: ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT and ELECTRIC CURRENT
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
CIRCUIT
a complete path traversed by an electric current.
ELECTRICAL CIRCUIT
a path in which electrons flow from a current source.
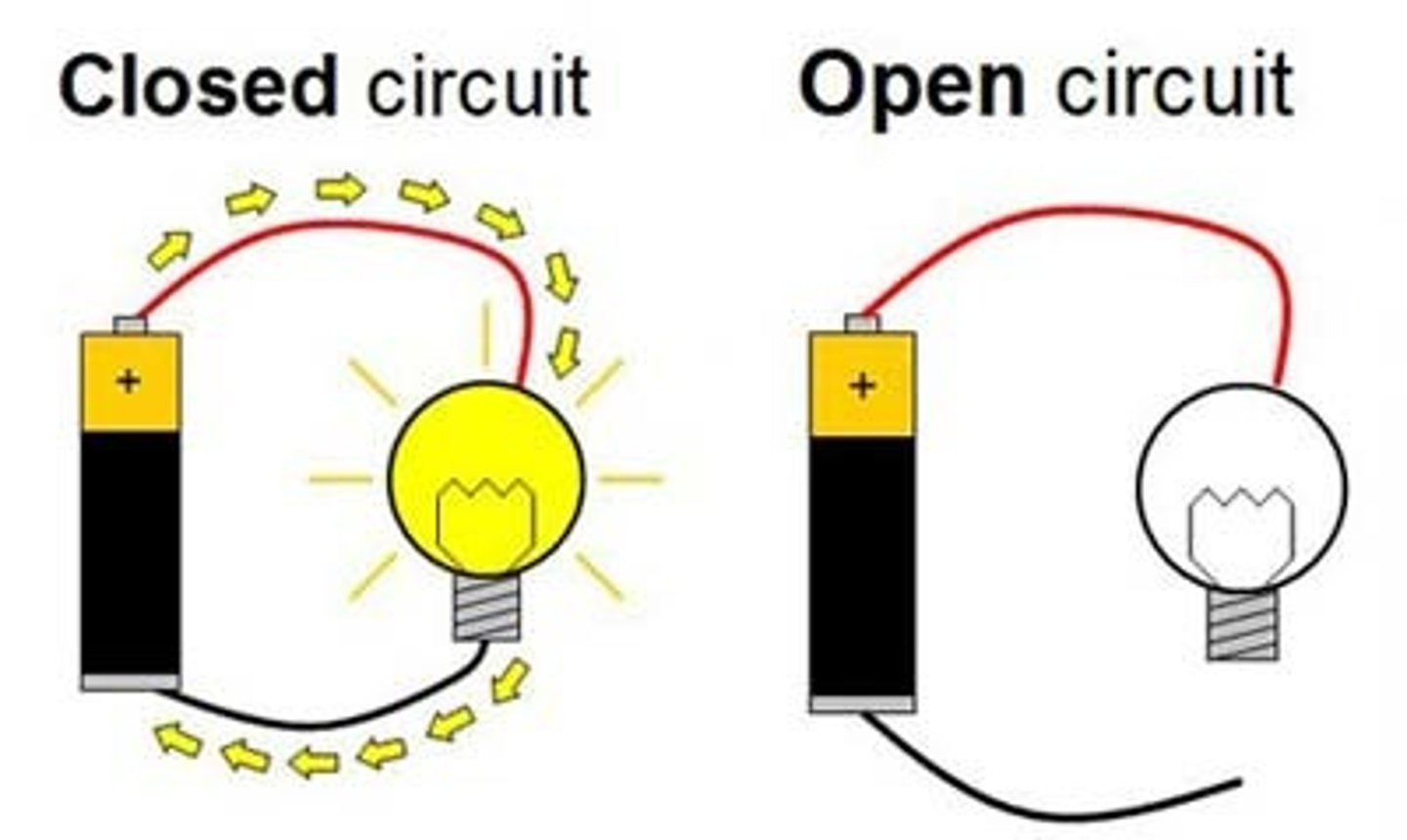
Closed Circuit
allows charge carriers to flow through continuously
Open Circuit
its conductive elements will no longer form a complete path, and unable to sustain continuous charge flow.
battery or generator
a device that gives energy to the charged particles of the current
lighting fixtures, electric motors, or computers, connecting wires or transmission lines
devices that use current
Ohm's Law and Kirchhoff's Rules
Two basic laws that mathematically describe electric circuits
Gustav Kirchhoff
a German Physicist who contributed to the fundamental understanding of electrical circuits, spectroscopy, and the emission of black-body radiation by heated objects.

Kirchhoff's rules
- multiloop electric circuits that embody the laws of conservation of electric charge and energy
- determine the value of the electric current in each branch of the circuit.
Junction Theorem
Current entering the Node/Junction = Current leaving the Node
Loop Equation
The sum of all the voltage drops around the loop is equal to zero
Short Circuit
A connection that allows current to take an unintended path.
Series Circuit
An electric circuit with a single path
voltage drop
a decrease in voltage (negative to positive)
Parallel Circuit
a separate path for the flow of current between the two points
Branch Circuit
The circuit conductors between the final overcurrent device protecting the circuit and the outlet
Appliance branch circuit
one or more appliance outlets, but no permanently connected lighting fixtures
General purpose branch circuit
supplies a number of outlets for lighting and appliances.
Individual branch circuit.
supplies only one utilization equipment.
ELECTRIC CURRENT
the flow or rate of flow of electric force in a conductor
coulombs per second (Amps)
The magnitude of the electric current is measured in
Conventional current flow
- the flow from the positive to the negative terminal
Electron flow
flow from negative to positive terminal.
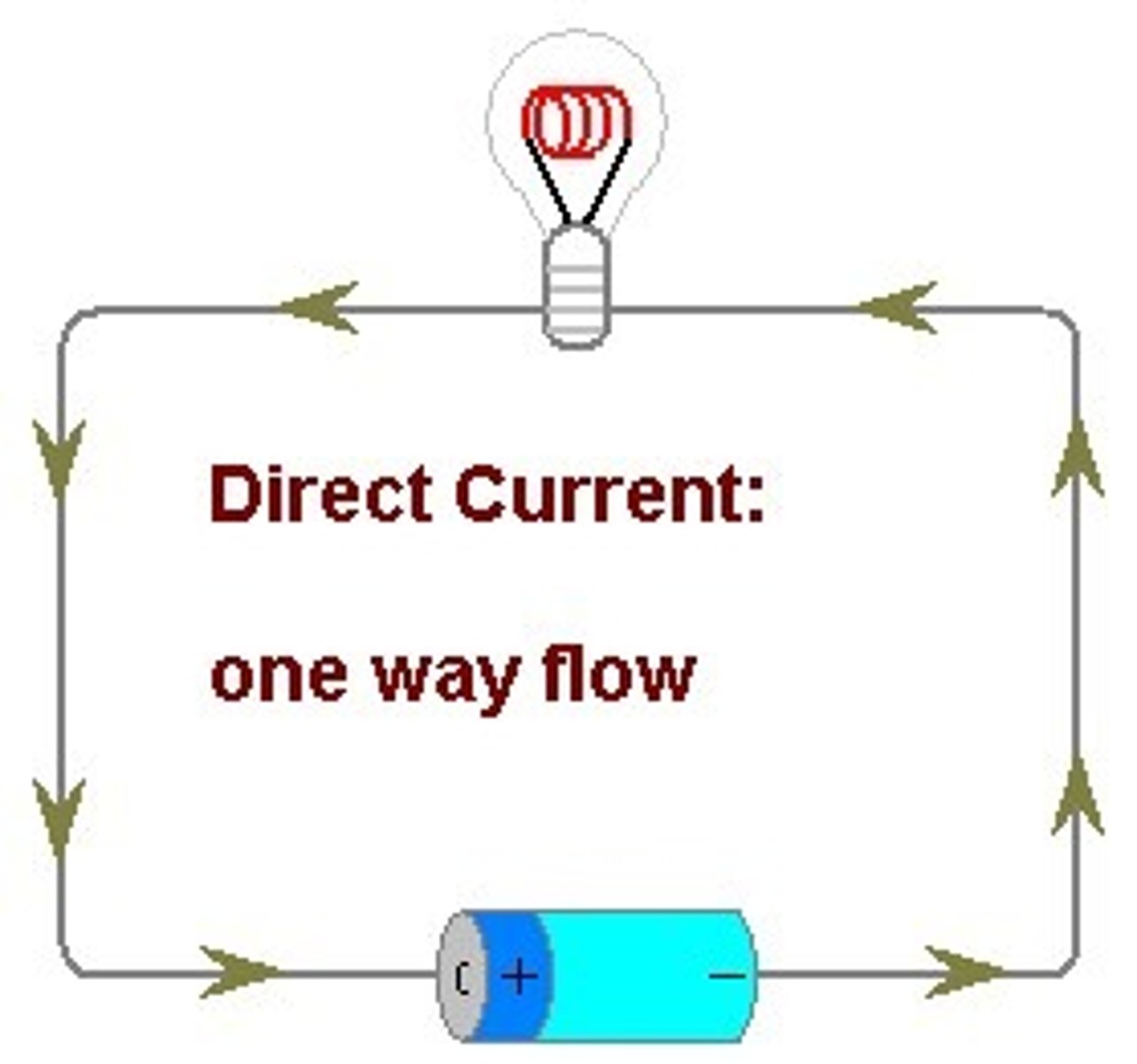
Direct Current
- flows in one direction steadily
- negative to positive
- dry cell or storage battery
- no frequency
Alternating Current
- reverses its direction
- generated by generator
- frequency is 50Hz or 60Hz