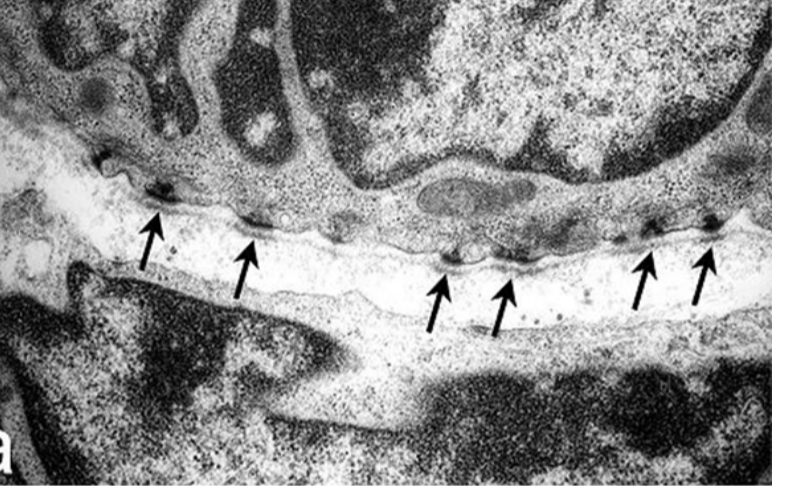
Cell junctions
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Tight junctions
Found in barrier tissues where it is important to prevent leakage - stomach, bladder, intestines
Individual sealing strands (transmembrane)
Hold together adjacent cells - to make them electrically tight - no ions or molecules can pass
P=occludins and Claudine
Adherens junction
Like a belt
Are for flexible support so are found in places such as the skin, heart muscle and intestinal lining
P=cadherin - spans gap + links to Catenin-binds to actin
Protein plaque like structure, creates a bridge between two cell membranes
Prevents cell seperation from tension such as contraction
Desmosomes
Heavy duty anchors - (spot welds/button structure) found in skin, cervix, heart
P:cadherin (spans gap) links to desmoplakin - links to keratin
Protein plaque - Gap is mainted but more subtle due to isolated points of contact between cells
Gap junction
Made up of 2 hemichannels
A hemichannel/connexon is made up of 6 connexion proteins
These migrate and dock together at a chemical level. The opening is the cell has special molecules that control what goes in and out
Found: cardiac muscle, smooth muscle
Allows rapid communication through electrical impulse, ions etc
Hemidesmosomes
Connect epithelium to basement membrane
P=integrin proteins (span gap) Link to laminin in BM and keratin in cytoplasm
*prevents sliding and migration
What forms a junctional complex?
TAD
Tight, adherens, desmosome
Which junction is not lateral but instead basal?
Hemidesmosome
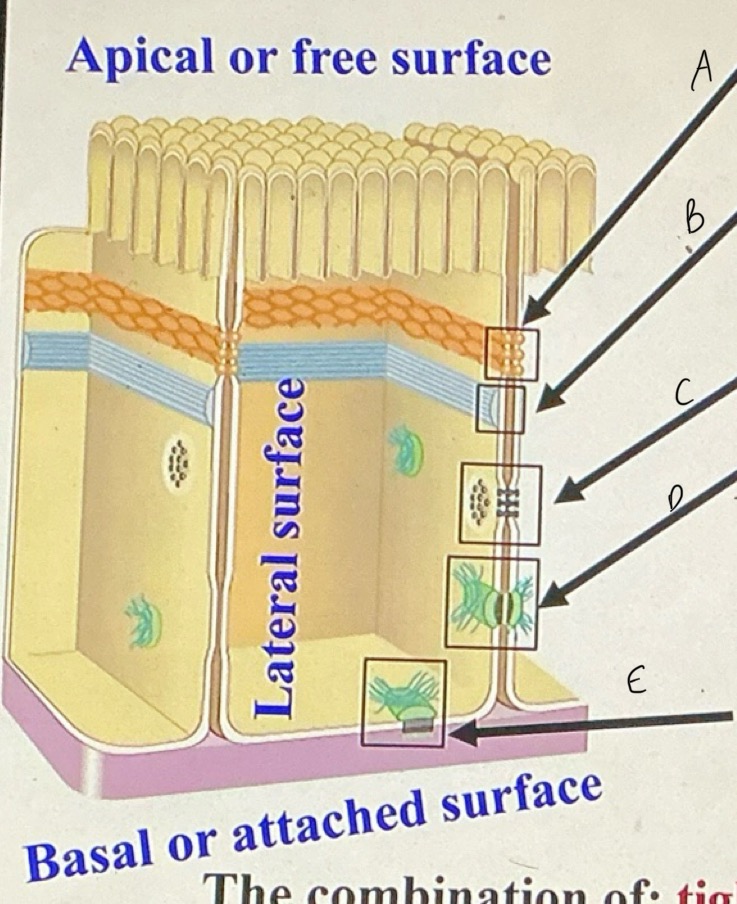
Label A,B,C,D and E
A=tight junction
B=adherens
C=gap
D=desmosome
E=hemidesmosome
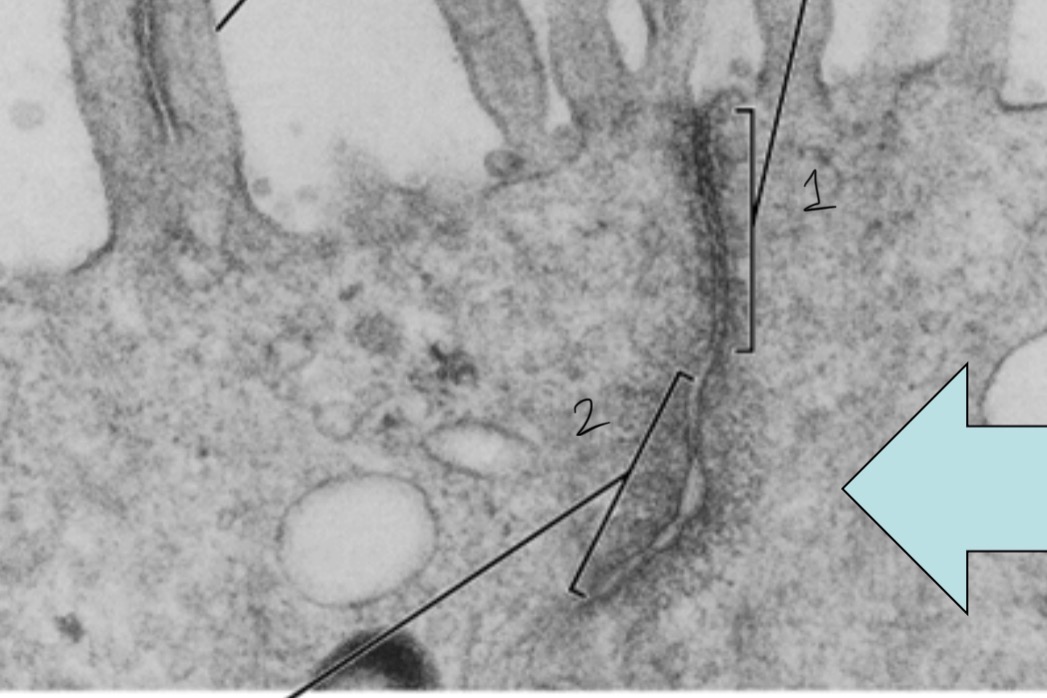
What is 1 and 2?
1=tight 2=adherens