APP Unit 3
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
sensation and perception
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Sensation
bringing in sensory stimuli from the environment to the brain
Perception
Organizing & interpreting sensory info
Transduction
Converting an environmental energy into a neural impulse
Absolute Threshold
the minimum amount of energy needed to detect the presence of a stimulus (50% of the time)
Just noticeable difference (JND)(AKA difference threshold)
the minimum amount of energy needed to detect a change in a stimulus or the difference between two stimuli (50% of the time)
Weber’s Law (related to JDN)
JND is a fixed proportion of the intesiry of the stimulus
The greater initial intensity of a stimulus the more it is going to take to notice
Sensory adaptation
decline in sensitivity to stimuli that are presented at a constant level (our sensory neurons become less responsive)
Sensory Interaction
Occurs when one sense impacts another (taste and smell)
Synesthesia
Cross-talk of the senses (KIKI- Sharp object)
Amplitude
Brightness/intensity
Wavelength
color/hue
Short Wavelengths
blues
Long Wavelengths
reds
Visual Process
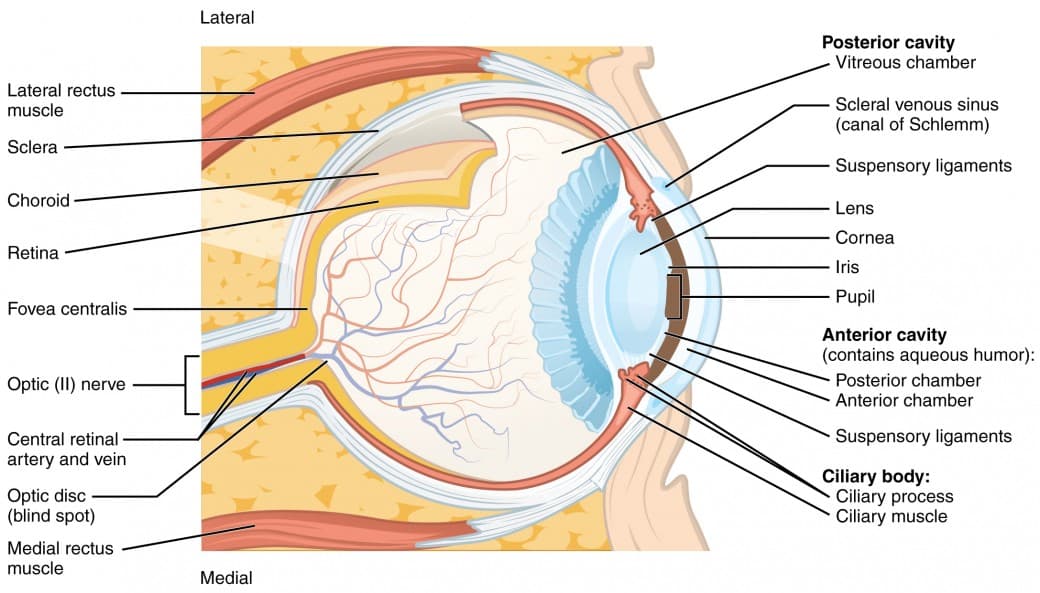
Light wave - cornea - iris + pupil - lens - retina - photoreceptors - bipolar cells - ganglion - forms the optic nerve - optic disk - thalamus - occipital lobe
Accomodation
the ability of the lens to bend light rays in order to focus the image (based on the objects location on the retina)
Nearsightedness
Occurs when the lens bends too much causes the image to fall in front of the retina
Farsightedness
occurs when the lens doesn’t bend enough causes the image to fall in behind the retina
Photoreceptors
Sensory receptors for vision ~ responsible for transduction
Cones
Color vision; helps us to see in the daytime/bright loghting; located in the center of the retina
Fovea
Center of the retina, highest concentration of cones; greatest visual activity (detail)
Rods
Detect black white and gray sensitive to movement more sensitive in dim lighting; located on the outher edge of the retina (peripheral vision)
Bipolar cells
Receive visual signals from photoreceptors (rods & cones) help to see contrast and edges
Ganglion Cells
Signals sent from bipolar cells; axons of ganglion cells bundle together to form the optic nerve
Optic nerve and Optic disk
The optic nerve leaves the eye at the optic disk
Blindspot
Where the optic nerve leaves the eye there are no rods and cones, which creates a blind spot
Feature detectors
Specialized cells that respond to specific features of more complex stimuli (edges, lines, angles)
Parallel Processing
Processing visual information is done simultaneously (as opposed to serial processing)
Blindsight
A condition in which a person can respon to a visual stimulus without consciously experiencing it
Prosopagnosia (face blindness)
the inability to recognize human faces
Visual agnosia
the inability to recognize objects
Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory
there are 3 types of receptors (cones) with different sensitivities to different wavelengths that can create all colors: red green blue
Color Blindness
Lack one of the three (or more in rare cases two) types of cones
(supports the Trichromatic theory of color vision)
Dichromatism
Only 2 cone types are functional
Monochromatism
Only one type of cone is functional
Opponent Process theory
Color perception is determined by the activity of 3 opponent systems: yellow-blue red-green black-white
Occurs in the ganglion cells
Afterimages
an image that continues to appear in the eyes after a period of exposure to the original image
Supports the opponent process theory of color vision
figure-ground
figure-the object
Ground- the background or surroundings in which the object occurs
Closure
filling in the gaps to perceive a completed image
Proximity
Objects close together are grouped together
Similarity
grouping based on shared characteristics
Perceptual constancies
Pereving object as unchanging (having consistent color,size, shaoe, brightness, ect.) even as illumination and retinal images change
Visual Cliff (what is it and what was learned)
Apparatus used to to test depth perception in infants
Depth perception is largely innate
Binocular depth cues
Retinal (binocular) disparity'
depth perception guided by the different images seen by each eye
Convergence
sensing the eyes converging (turning inward) as they focus on closer objects
Linear perspective (monocular depth cues)
parallel lines appear to converge in the distance
Relative Size
Closer objects appear larger that far away objects
Relative Clarity
Objects in the distance appear less clear/ more blurry; objects that are closer appear clear/sharp
Texture Gradient
Objects far away appear to have less detail than objects close up
Interposition
Objects that obstruct/block the view of of another object are perceived as closer
Phi Phenomenon/Stroboscopic motion
an illusion of a movement (as in a motion picture) experienced when viewing a rapid series of still images
Looming
As an image expands into our retina we perceive it as approaching us
Selective attention
the ability to focus your conscious awareness (attention) on a particular stimulus while ignoring others
Cocktail Party Effect
In a crowded environment, we can completely block out others and focus on 1 thing but when something relevant to you is said your attention shifts
Inattentional blindness & change blindness
Failure to see visible objects or events (or a change in one’s environment) because one’s attention is focused elsewhere (or we’ve stopped processing due to top-down processing)
Ex. Folding laundry; Basketball Passes
Bottom-up processing
using details/features.characteristics of a stimulus to guide perception (understand our world) external focus
Ex. Istlef Awlyas
Top-down Processing
Using Schemas, prior experiences, expectations or context to guide perception (understand our world) (internal focus) we make a quick assumptions using little evidence
Ex.

Schemas
Mental represensations of people, objects, events, ideas, etc.
created by experience (visual, auditory, emotion etc)*
Ex. Boo calls Sully Kitty because that's how she has pictured a cat
Perceptual set & Priming
The tendency to perceive a stimulus in a particular way (guided by prior experiences, expectations, surroundings/context, current mood, etc.)
Ex. Scary Mary
Amplitude
Loudness/ Intensity
Frequency
Pitch
Timbre
Purity
Auditory Process
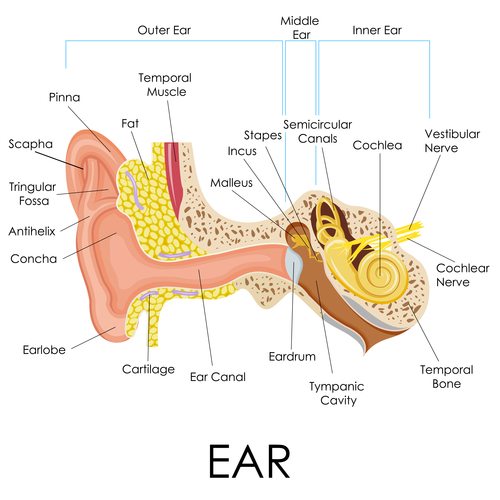
Perceiving loudness
The brain interprets loudness from the number of activate hair cells
Perceiving Location
Based on differences in the timing & intensity each sound wave enters the ear
Place theory
Perception of pitch corresponds to the vibration of different portions, or locations/ places along the basilar membrane
Best explains the High frequency sounds
Frequency Theory
perception of pitch corresponds to the firing rate, or frequency, at which the auditory nerve vibrates
best explains low frequency sounds
Volley Theory
Groups of neurons fire slightly out of phase with one another
So that when combined a particular pitch is perceived
Conduction Deafness
problems/damage to the three little bones tympanic membrane
(may be corrected with hearing aid)
Sensorineural deafness
problems/damge to the cilia (hair cells) or auditory nerve
(maay be corrected with a cochlear or auditory nerve implant)
Taste Buds (papillae)
papillae/taste buds contain sensory receptors for taste
6 taste: sweet sour bitter salty umami (savory meaty taste) & oleogustus (unique taste of fat
taste buds are most sensitive to 1 or 2 taste and weak to others
Flavor
flavor is a combination of what two senses
taste & smell (sensory interaction)
Supertasters. Medium tasters & nontasters
Supertasters have more buds than others
Olfaction (+sensory receptors)
Cilia (hair cells) in the nose
Olfactory blub
cilia in the nose sends signals to the olfactory bulb in the brain
*doesn’t go through thalamus first
(part of the limbic system)
Pheromones
Odor chemicals that shape the behavior/physiology of animals
Somatosensory system (touch)
4 types of touch receptors? Pain, Pressure, Warm. Cold
Hot= warm + cold wetness= cold+pressure
Understanding Pain
It’s important to feel pain so the body gets the sensation it needs for the body to develop and so the brain can be stimulated
Gate Control Theory
Pain can be blocked at the spinal cord Other sensory information aside from the pain signals can take over the pain pathway
Phantom Limb Sensations
When lacking the normal sensory imput from a missing limb, the brain misinterprets and amplifies spontaneous but irrelevant CNS activity
Vestibular sense (balance)
Sensory System providing information about spatial prientation (position of head & body in space) as well as our sense of balance
Ex. Visual system & inner ear semicircular canals & vestibular sacs play large role
Kinesthesia
Sensory system providing information about where parts of your body are in relationship to each other, providing us with out sense of coordination
Ex. Ability to sense the movement of muscles tendons and joints