Chapter 75: Skin Disorders
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Chapter 75: Skin Disorders
Psoriasis: Chronic inflammatory skin disorder caused by overproduction of keratin leading to rapid epidermal turnover
Cell turnover rate increases up to 7 times normal
Autoimmune component with exacerbations and remissions
Common locations: elbows, knees, trunk, scalp, sacrum, lateral extremities
Can involve joints causing psoriatic arthritis (joint pain and stiffness)
Related Skin Condition
Dermatitis: Inflammatory skin reaction due to allergen exposure (internal or external)
Lesions vary in borders and distribution
Can progress from acute to chronic
Increased risk of secondary bacterial infection due to scratching
Types: nonspecific eczematous, contact, atopic
Infection Prevention
Skin infections may be bacterial, viral, or fungal
Emphasize daily bathing or showering and hand hygiene
Psoriasis
Infections: Severe streptococcal throat infection, Candida, upper respiratory infection
Skin trauma: Surgery, sunburn (Koebner phenomenon)
Genetics
Stress (immune overstimulation)
Seasonal variation: Warm weather improves symptoms
Hormonal changes: Puberty, menopause
Medications: Lithium, beta-blockers, indomethacin
Obesity
Psoriasis (image)
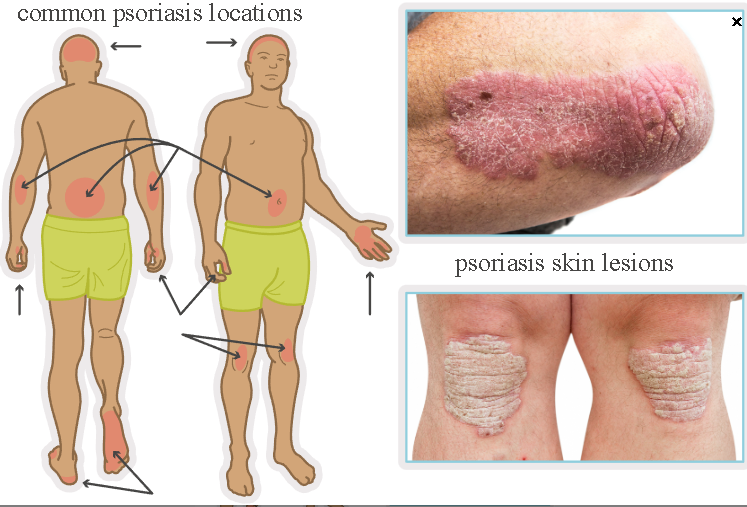
Psoriasis
Psoriasis vulgaris: Reddened, thickened skin with silvery-white scales, bilateral distribution
Exfoliative psoriasis: Diffuse erythema and scaling without clear lesions
Risk for dehydration and hypothermia or hyperthermia
Palmoplantar pustulosis: Hyperkeratotic plaques and pustules on palms and soles
Pustules darken, peel, crust
Disease course: Cyclic
Pruritus with periods of exacerbation and remission
Classification by Body Surface Area
Mild: Less than 5 percent BSA
Moderate: 5 to 10 percent BSA
Severe: Greater than 10 percent BSA
Physical Assessment Findings
Scaly plaques
Bleeding with removal of scales (Auspitz sign)
Pruritic lesions on scalp, elbows, knees, sacrum, lateral extremities
Nail pitting
Psoriasis Care
Treatment Goal
No cure
Reduce symptom severity and epidermal cell turnover
Tar Preparations (coal tar, tar blends)
Suppress keratinocyte proliferation and inflammation
Nursing Actions
Monitor for irritation
Teach proper application
Client Education
Burning or stinging may occur
Causes skin and clothing staining
Apply at night and cover with old clothing
Vitamin D Analogs (calcipotriene, calcitriol)
Regulate cell division and reduce proliferation
Nursing Actions
Monitor for itching, erythema, irritation
Monitor for hypercalcemia (muscle weakness, fatigue, anorexia)
Client Education
Limit sun exposure
Do not apply to face
Monitor for skin cancer changes
Vitamin A Derivative (tazarotene)
Slows epidermal cell growth and reduces inflammation
Nursing Actions
Contraindicated in pregnancy
Monitor for burning, irritation, desquamation
Client Education
Avoid sun and artificial UV light
Use reliable contraception (teratogenic)
Discontinue and notify provider if pregnancy occurs
A nurse is reviewing information about a new prescription for corticosteroid cream with a client who has mild psoriasis. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
Select all that apply.
a
Apply an occlusive dressing after application.
b
Apply three to four times per day.
c
Wear gloves after application to lesions on the hands.
d
Avoid applying in skin folds.
e
Use medication continuously over a period of several months.
a
Apply an occlusive dressing after application.
c
Wear gloves after application to lesions on the hands.
d
Avoid applying in skin folds.
The client should avoid applying to skin folds because this increases the risk for fungal infections.
The nurse should instruct the client to apply the corticosteroid cream 1-4 times daily.
Psoriasis Meds
Corticosteroids (triamcinolone, betamethasone)
Decrease inflammation and suppress cell proliferation
Nursing Actions
Monitor for skin thinning, striae, hypopigmentation
Reinforce correct application
Client Education
Use high-potency steroids only as prescribed
Periodic medication breaks recommended
Occlusive dressings may enhance absorption
Avoid face and skin folds
Can be applied to scalp
Report signs of skin atrophy
Systemic Medications
Cytotoxic Agents (methotrexate, acitretin)
Used for severe or refractory psoriasis
Nursing Actions
Monitor liver and renal function
Monitor for bone marrow suppression (leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia)
Contraindicated in pregnancy
Client Education
Avoid alcohol
Use effective contraception
Biologic Agents (adalimumab, etanercept, ustekinumab, alefacept, infliximab)
Suppress immune response and keratinocyte activity
Nursing Actions
Screen for tuberculosis and hepatitis
Inspect injection sites
Rotate injection sites
Use infection control precautions
Client Education
Do not use if pregnant or breastfeeding
Administer subcutaneous injections correctly
Report signs of infection
Increased cancer risk
No live vaccines
Immunosuppressants (cyclosporine, azathioprine)
Used when other therapies fail
Key Points
Increased risk for infection and nephrotoxicity
Short-term use recommended (less than 6 months)
Client Education
Monitor blood pressure (risk of hypertension)
Psoriasis Procedures
Photochemotherapy (PUVA)
Methoxsalen given orally followed by UVA exposure
Decreases epidermal proliferation
Given 2 to 3 times weekly on nonconsecutive days
Nursing Actions
Monitor response
Ensure eye protection during treatment and for 24 hours after
Client Education
Report erythema, swelling, discomfort
Long-term risks: premature aging, cataracts, skin cancer
Obtain regular eye exams
Use sunscreen
Narrow-Band UVB Therapy
No photosensitizing medication
Fewer treatments required
Laser Therapy
Used for mild to moderate psoriasis
Targets lesions and limits damage to surrounding skin
Nursing Interventions
Teach lifestyle modifications and coping strategies
Collaborate on individualized treatment plan
Client Education
Use comfort measures: emollient creams, oatmeal baths
Do not scratch or pick lesions
Dermatitis
Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
Avoid exposure to harsh chemicals
Dermatitis Risk Factors
External exposure to allergens
Internal exposure to allergens or irritants
Stress (eczema-related)
Genetic predisposition (eczematous dermatitis)
Cause may be unknown
Dermatitis Findings
Nonspecific Eczematous
Thickened areas of skin (lichenification)
Dry or moist, crusted lesions
Pruritus
Symmetrical involvement anywhere on the body
Contact
Caused by direct contact with allergen, chemical, or mechanical irritant
Rash is well-demarcated and localized
Distribution depends on exposure pattern
Atopic
Chronic inflammatory rash
Triggered by allergens or chronic skin disease
Thickened skin with scaling and desquamation
Severe pruritus
Common locations: face, neck, upper torso, skin folds (antecubital, popliteal)
Dermatitis Care
Avoidance Therapy
Avoid known triggers if identified
Do not scratch lesions (prevents secondary infection)
Use fragrance-free soaps, detergents, cosmetics
Avoid fabric softener dryer sheets
Wash skin after irritant exposure
Apply cool, damp compresses to reduce inflammation
Use colloidal oatmeal baths for itching
Dermatitis Meds
Corticosteroids
Topical, intralesional, systemic (hydrocortisone, betamethasone, triamcinolone, prednisone)
Reduce inflammatory response
Nursing Actions
Monitor for adrenal suppression with prolonged use
Teach correct application technique
Client Education
Taper doses if used long-term
Do not apply to infected lesions
Warm, moist dressings may increase absorption
Avoid occlusive dressings over steroid-treated rash
Antihistamines
Topical or systemic (diphenhydramine, cetirizine, fexofenadine)
Decrease redness, pruritus, edema
Nursing Actions
Monitor for urinary retention (systemic use)
Client Education
Can cause photosensitivity
Avoid driving or machinery with systemic use
Take systemic forms at bedtime (drowsiness)
Topical Immunosuppressants
Tacrolimus, pimecrolimus
Used for eczema unresponsive to steroids
Nursing Actions
Monitor for erythema and burning
Avoid occlusive dressings
Client Education
Do not use if infection present
Discontinue once rash clears
Avoid direct sunlight and tanning beds
Skin Infections
Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
Avoid exposure to infectious organisms
Maintain proper skin hygiene
Perform effective hand hygiene
Use isolation precautions when indicated (MRSA)
Bacterial Infections (Furuncles, carbuncles, cellulitis, MRSA) Findings
Expected Findings
Fever, malaise, chills, pain (variable)
Single or multiple lesions (pustules, papules, nodules)
Skin may be erythematous, edematous, painful, warm
Medication Management
Mild infections: topical antibiotics
Cellulitis or extensive infection: systemic antibiotics (penicillin or cephalosporin)
Penicillin or cephalosporin allergy: tetracycline, erythromycin, azithromycin, tobramycin
MRSA: vancomycin IV or oral linezolid or clindamycin
Nursing Actions and Client Education
Bathe daily with antibacterial soap
Do not squeeze lesions
Remove crusts so medication penetrates
Apply warm compresses for comfort
Do not share personal items
Keep area exposed to air when possible
Avoid occlusive dressings
Viral Infections (Herpes simplex, herpes zoster) Findings
Expected Findings
Itching, pain, or tingling
Vesicular lesions that may ulcerate and crust
Common locations: face, oral mucosa, genitals, trunk
Medication Management
Antivirals: acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir
Burrow solution compresses (aluminum acetate) 20 minutes, three times daily
Nursing Actions and Client Education
Avoid close contact during active lesions
Avoid triggers (stress, UV light)
Use soothing measures (calamine, warm compresses)
Avoid tight clothing
Allow lesions to air dry
Practice strict hand hygiene
Do not share personal items
Fungal Infections (Tinea, mycosis, candidiasis) Findings
Expected Findings
Itching or burning
Single or multiple lesions
Oral candidiasis: white plaques
Body folds: erythematous, moist lesions
Medication Management
Antifungals: nystatin, clotrimazole, miconazole
Nursing Actions and Client Education
Apply medication as prescribed
Clean and dry skin before application
Avoid sharing footwear and clothing
Reposition frequently to increase airflow to skin
A nurse is providing teaching with a client who has a history of psoriasis about photochemotherapy and ultraviolet light (PUVA) treatments. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
a
Apply vitamin A cream before each treatment.
b
Administer a psoralen medication before the treatment.
c
Use this treatment every evening.
d
Remove the scales gently following each treatment.
b
Administer a psoralen medication before the treatment.
PUVA treatments involve the administration of psoralen because this would enhance photosensitivity.
PUVA treatment does not involve the use of vitamin A cream and is two to three times per week on non-consecutive days.
A nurse is providing teaching with the guardian of a child who has contact dermatitis. Which of the following information should the nurse include?
a
Use fabric softener dryer sheets when drying the child’s clothing.
b
Apply a warm, dry compress to the rash area.
c
Place the child in a bath with colloidal oatmeal.
d
Leave the child’s hands uncovered during the night.
c
Place the child in a bath with colloidal oatmeal.
A nurse is providing teaching with a client who has a new prescription for clotrimazole topical cream. Which of the following statements should the nurse include?
a
“This cream reduces the discomfort for viral lesions.”
b
“This cream to treat bacterial infections.”
c
“Apply the topical medication for up to 2 weeks after the lesions are gone.”
d
“Apply the cream to lesions while they are moist.”
c
“Apply the topical medication for up to 2 weeks after the lesions are gone.”
A nurse is providing discharge instructions with a client who has a bacterial infection of the skin. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include?
a
Bathe daily with moisturizing soap.
b
Apply antibacterial topical medication to the crusted exudate.
c
Apply warm compresses to the affected area.
d
Cover affected area with snug-fitting clothing.
C Apply warm compresses to the affected area.