Chapter 30: World War II and the Holocaust, 1939-1945 | Quizlet
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Demilitarized
elimination or prohibtion weapons, fortifications and other military installations

Appeasement
satisfying reasonable demands of dissatisfied powers in an effort to maintain peace and stability

Sanctions
restrictions intended to enforce international law

Blitzkrieg
German for "lightning war"; a swift and sudden military attack; used by the Germans during World War II

Isolationism
a policy of national isolation by abstention from alliances and other international political and economic relations

Neutrality
refusal to take sides or become involved in wars between other nations

Mobilization
the process of assembling troops and supplies and making them ready for war

Kamikaze
Japanese for "divine wind"; a suicide mission in which young Japanese pilots intentionally flew their airplanes into US fighting ships at sea

Blitz
the British term for the German air raids on British cities and towns during World War II

Ethnic
relating to people who have common racial, religious, or cultural origins

Genocide
the deliberate mass murder or physical extinction of a particular racial, political, or cultural group

Collaborator
a person who assists the enemy
Partisan
resistance fighter in World War II
Cold War
the period of political tension following World War II and ending with the fall of Communism in the Soviet Union at the end of the 1980s

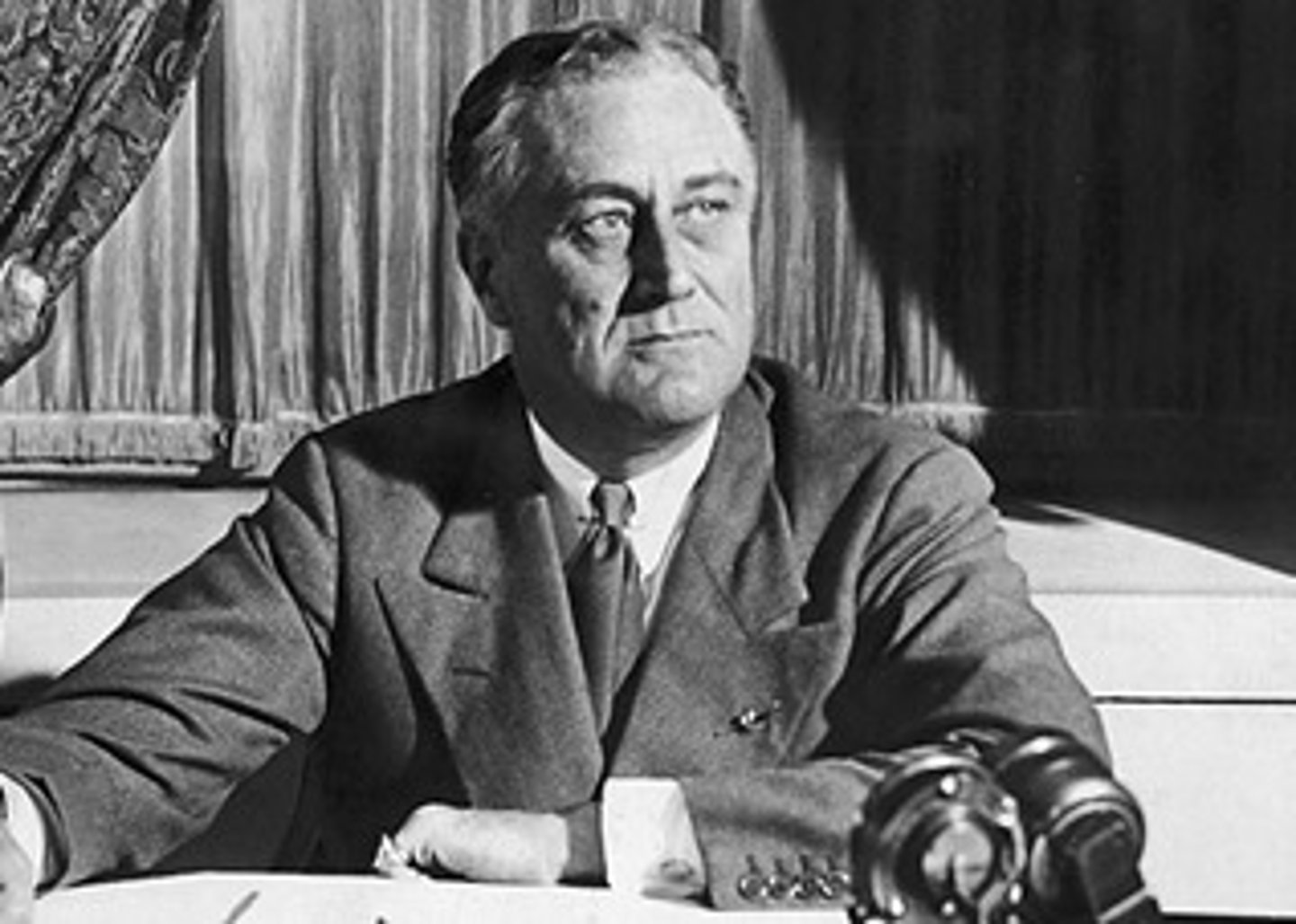
Franklin D Roosevelt
US President during the Great Depression and World War II

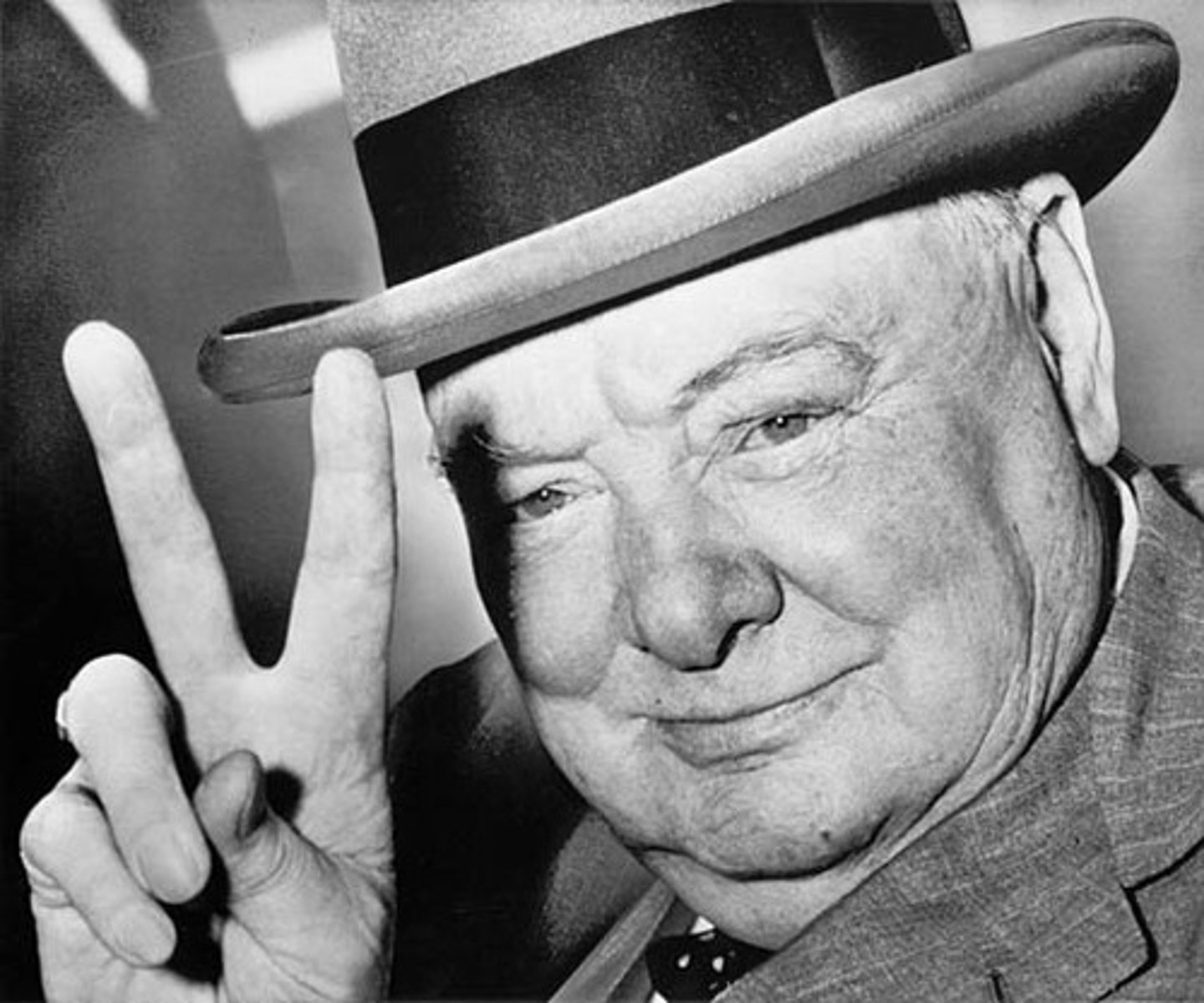
Winston Churchill
British Prime Minister during World War II

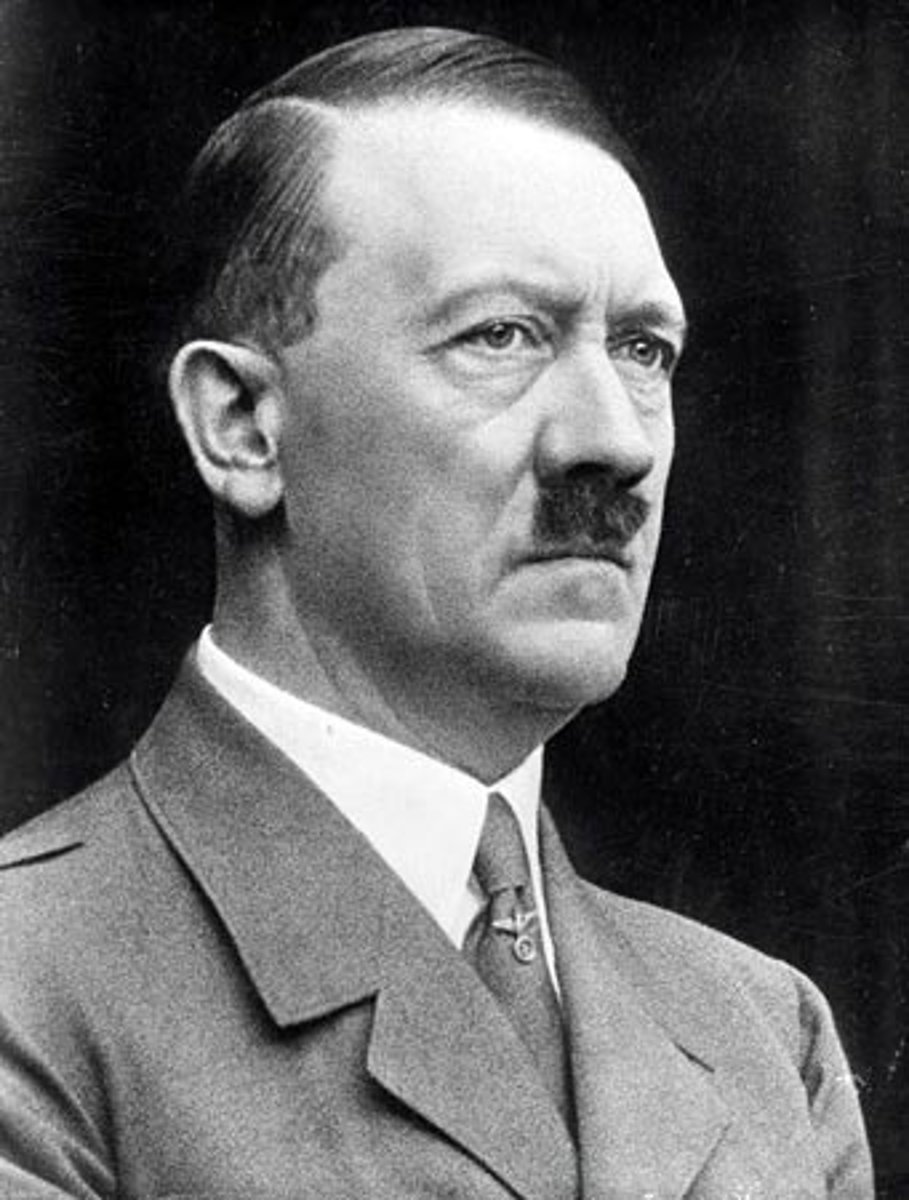
Adolf Hitler
Military Dictator and Chancellor of Germany during the 1930s and World War II, believed that the Aryan race was superior, implemented the Final Solution during the Holocaust, wrote Mein Kempf

Benito Mussolini
Military Dictator of Italy during World War II

Joseph Stalin
Russian leader who succeeded Lenin as head of the Communist Party (USSR) and created a totalitarian state by purging all opposition, leader of the Soviet Union during WWII

Allied Powers
during World War II, Great Britain (1939-1945), France (1939-1940), The United States (1941-1945), and The Soviet Union aka Russia (1941-1945)
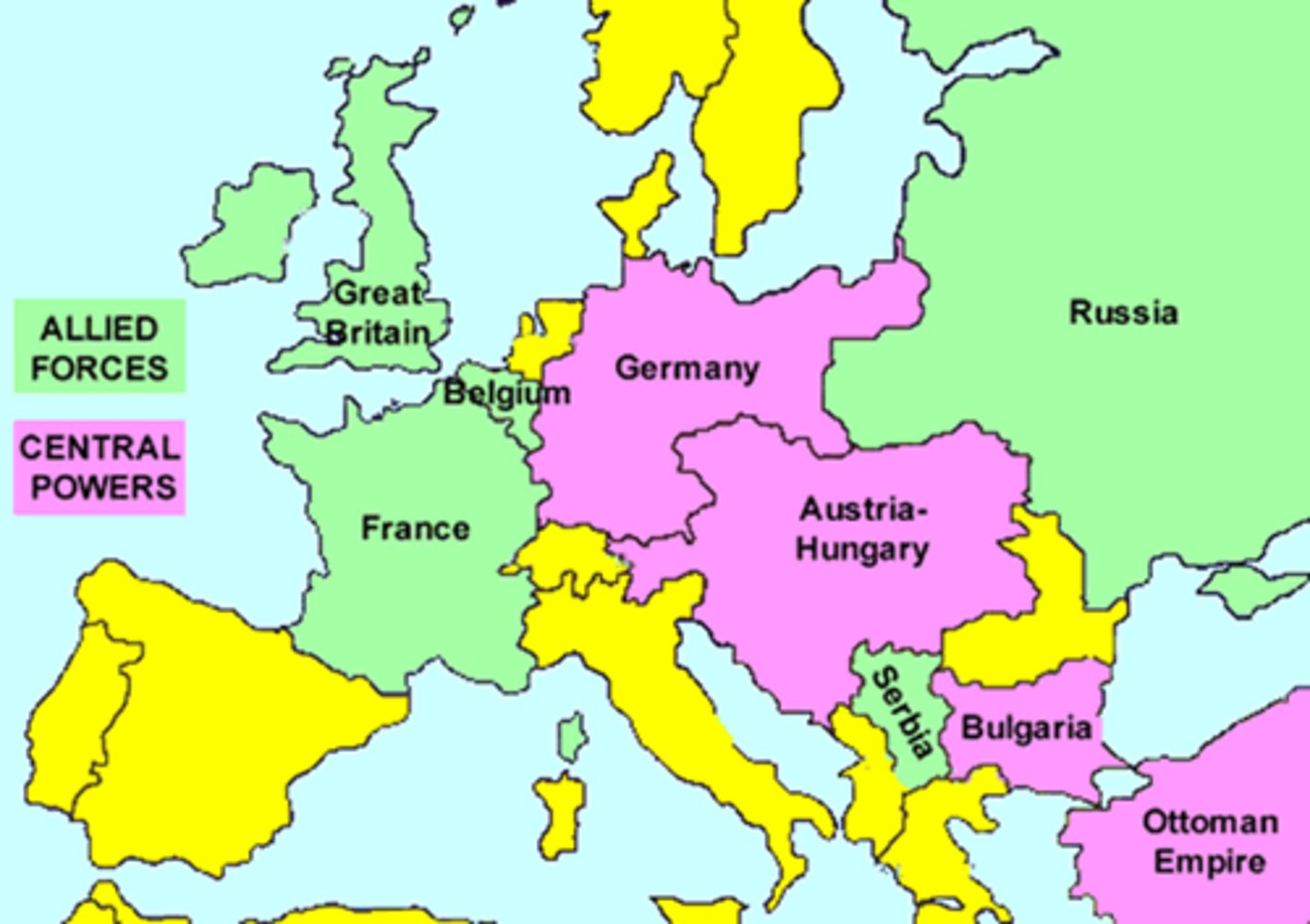
Axis Powers
during World War II, Germany, Japan, and Italy

Anti-Comintern Pact
alliance signed by Germany and Japan to fight communism
Sudetenland
territory located in Czechoslovakia that was given to Germany during the Munich Conference
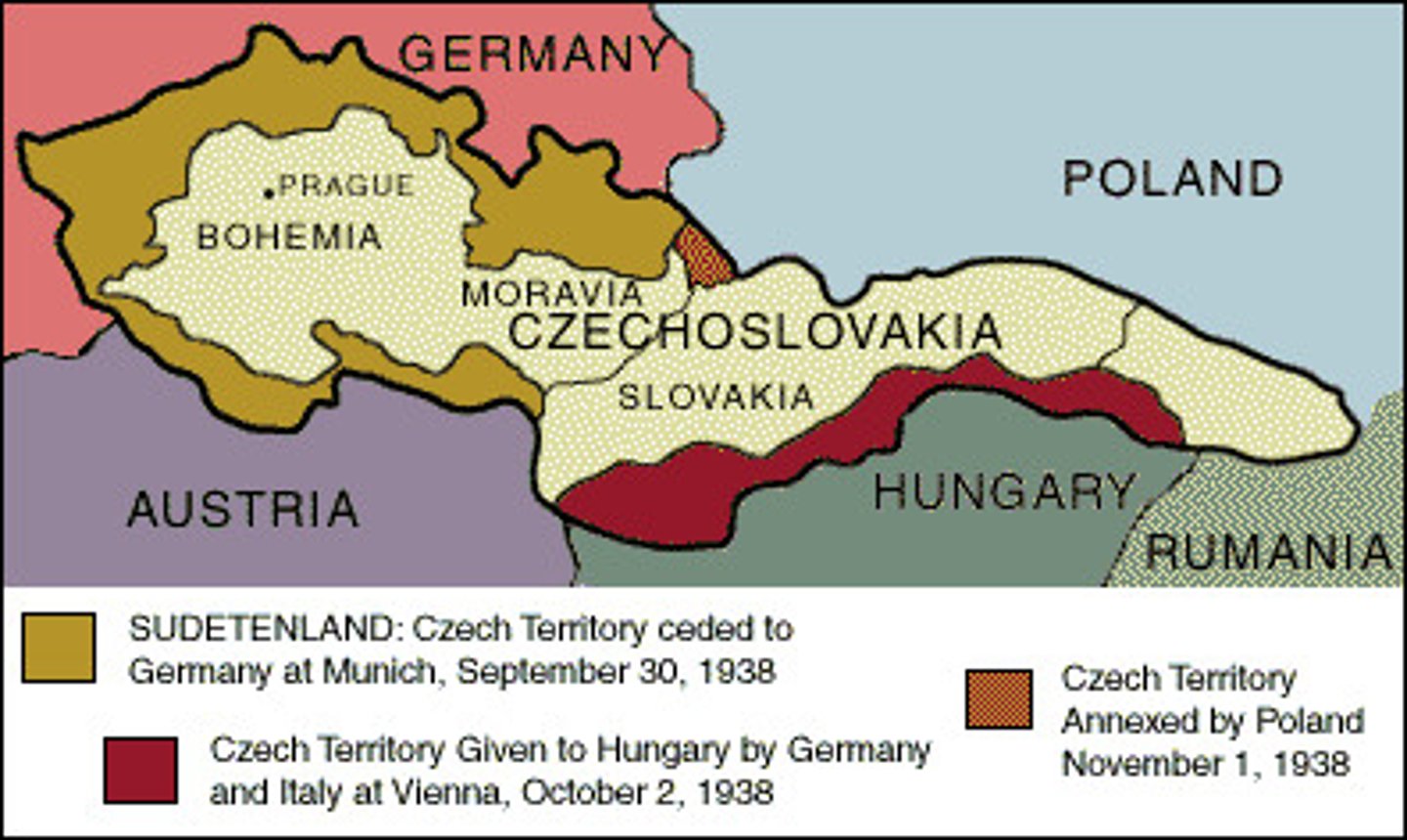
Munich Conference
European leaders met and agreed to let Germany take over the Sudetenland as long as Germany promised to stop expansion, considered the height of appeasement before WWII

Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression Pact
Germany and the Soviet Union agree to not attack each other, the Soviet Union gives up territory to Germany, signed 1939
Manchuria
Chinese territory that was invaded by Japan in 1931
"Raping of Nanjing"
Japan seized the Chinese capital of Nanjing, over 100,000 Chinese civilians and prisoners of war were massacred
Pearl Harbor
US Naval Base that was attacked by Japan on December 7, 1941,3,500 Americans were killed, the final blow that draws the US into World War II
Maginot Line
a line of fortresses and defenses built along the German border in France
Luftwaffe
German air force
RAF
Royal Air Force, in Britain
Balkans
the Greek Peninsula, during WWII it included the countries of Greece, Albania, Bulgaria, Serbia, Montenegro, Romania, Croatia, Slovakia, and Hungary
General Hideki Tojo
the Prime Minister of Japan during WWII
Battle of Stalingrad
considered the worst battle of WWII, German soldiers surrender to the Soviets in February 1943, pushing the German line back to where it was in 1942
Battle of the Coral Sea
American forces stop Japanese advancement in the Pacific in May of 1942
Battle of Midway
in June of 1942 US forces defeated the Japanese Navy, and established the US as the Naval authority in the Pacific
General Douglas MacArthur
U.S. General, Commander of U.S. (later Allied) forces in the southwestern Pacific during World War II, he accepted Japan's surrender in 1945 and administered the ensuing Allied occupation.
Japanese Internment Camps
110,000 Japanese Americans of which 65% were born in the US, were forcibly sent to to live in government-run camps on the west coast of the US,
Government officials were concerned that citizens of Japanese decent might help the Japanese invade the western coast of the US, they were forced to give up everything that they owned
Hitler Youth
a program created by Adolf Hitler to indoctrinate and later enlist soldiers into the military
Heinrich Himmler
German Nazi who was chief of the SS and the Gestapo and who oversaw the genocide of six million Jews
The Final Solution
Hitler's plan for the genocide of the Jewish people
Concentration Camp
prison camps used under the rule of Hitler in Nazi Germany. Conditions were inhuman, and prisoners, mostly Jewish people, were generally starved or worked to death, or killed immediately.
SS
A special police force in Nazi Germany founded as a personal bodyguard for Adolf Hitler in 1925, from the German word "Schutzstaffel, meaning protection squad.
Roma
Gypsie
D-Day
June 6, 1944, the Allied invasion of German-occupied France along beaches of Normandy, largest Naval Invasion in history
Battle of the Bulge
A 1944-1945 battle in which Allied forces turned back the last major German offensive of World War II.
Albert Einstein
German Jewish physicist who developed the theory of relativity, worked on the Manhattan Project
Hiroshima
US drops an atomic bomb on this city on August 6, 1945
Nagasaki
US drops an atomic bomb on this city on August 9, 1945
Charles de Gaulle
French general and statesman who became very popular during World War II as the leader of the Free French forces in exile
Dwight D. Eisenhower
American General who began in North Africa and became the Commander of Allied forces in Europe.
Eva Braun
Hitler's mistress and married him the day before they committed suicide in the underground bunker at the end of WWII.
Facsim
A political system headed by a dictator that calls for extreme nationalism and racism and no tolerance of opposition
George S Patton
American tank commander helped take North Africa, France, and the rest of Western Europe during WWII
Harry S. Truman
became the US President when FDR died; gave the order to drop the atomic bomb
Hirohito
Emperor of Japan during WWII
James Doolittle
A U.S. Army general best known for leading the famous "Doolittle Raid" on April 18th, 1942, in which B-25 bombers were launched from an aircraft carrier to bomb Japan and then crash-landed in China.
Soviet Union
formerly known as Russia
Kristallnacht
(Night of the Broken Glass) November 9, 1938, when mobs throughout Germany destroyed Jewish property and terrorized Jews.
Manhattan Project
secret plan to build the A-Bomb or the atomic bomb in the US
V-E Day
May 8, 1945 the day the war ended in the European Theater, Victory in Europe
Mein Kempf
'My Struggle' by hitler, later became the basic book of nazi goals and ideology, reflected obsession
Operation Overlord
the code name for the Allied invasion of Europe at Normandy on June 6, 1944; also known as D-Day
Operation Torch
Code name for allied invasion of North Africa from Nonmember 1942 to September 1943
Propaganda
Ideas spread to influence public opinion for or against a cause, widely used by both the Allies and Axis Powers during WWII
V-J Day
the day that the war ended in Japan or the Pacific Theater, Sept. 2, 1945, Victory in Japan
Yamamoto
Commander in Chief of the combined Japanese fleet, planned the attack of Pearl Harbor and Battle of Midway
Third Reich
German empire hitler created
Rome-Berlin Axis
Hitler and Mussolini signed treaty for alliance
Anschluss
Union between Germany and Austria. After awhile the Austrian chancellor opposed it, so Hitler took over Austria.
Battle of Britain
the period of Germany's air raids on Britain. focused on military and civilian targets.
Lend-Lease act
authorized the US President to supply war materials to Great Britain on credit
Revised Neutrality Act of 1939
allowed american firms to sell items to warring nations on cash and carry basis, was mostly to Britain
Potsdam Conference
The Big Three—Soviet leader Joseph Stalin, British Prime Minister Winston Churchill (replaced on July 26 by Prime Minister Clement Attlee), and U.S. President Harry Truman—met in Potsdam, Germany, from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to negotiate terms for the end of World War II.
Yalta Conference
was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union, represented by President Franklin D. Roosevelt, Prime Minister Winston Churchill and Premier Joseph Stalin, respectively, for the purpose of discussing Europe's post-war reorganization.
The Atlantic Charter
a joint declaration released by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill on August 14, 194, a broad statement about British and American war aims
Island Hopping
US strategy in the Pacific to take one island at a time that was controlled by Japan, as they worked their way towards Japan
Atomic Bomb
a nuclear weapon developed by the US during the Manhattan project, dropped by the US on Nagasaki and Hiroshima
Big Three
United States, Great Britain, France
Nuremberg Trails
a series of military tribunals conducted by the Allies after WWII, Nazi officials who has participated in the Holocaust and other war crimes were tried
United Nations
intergovernmental organization to promote international co-operation, created as a replacement of the League of Nations after WWII
Iron Curtain
Winston Churchill said in a speech that this had descended across the continent of Europe, dividing Europe into two hostile camps, essentially democracy verses communism