Questions I need to work for the macromolecules
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Describe the structure and function of the polysaccharides starch and glycogen, and identify where they are found within an organism
The polysaccharides have a long chain of sugars bonded together. Starch and Glycogen are synthesized and stored. For Plants, it is stored in the roots and seeds, and for glucose, it is in the liver and muscles.
List the two main biological functions of polysaccharides
Energy storage and Structural Support
steroids
makes cholesterol, Vitamin D, many hormones
List the components of a triglyceride (fat)
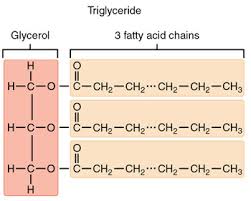
Provide at least 3 reasons why organisms store fat (AKA why is it important biologically!)
Energy Storage, Insulation, Protection and cushion of the organs
List two main roles of cholesterol in the body
Components for the cell membrane
Precursor for hormones
Describe the characteristic structure of a steroid
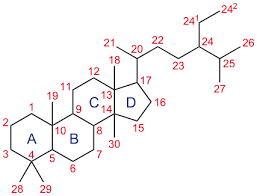
Two carbon rings, a carbon chain, and a purine
List the three main components of a nucleotide
Nitrogen base, Five-carbon sugar, Phosphate
Nucleic acid chains have polarity; given the structure of a nucleic acid, determine which end of the strand is the 5’ end and which is the 3’ end.
5’ end-free phosphate group
3’ end- free hydroxyl group (-OH)
List the components of an amino acid
Carboxyl group
Hydrogen
R-group
Amino group
Describe what type of bonds contribute to secondary structure of proteins. Then, specify whether these bonds take place within the “backbone” of the polypeptide, or between R-groups of amino acids in the polypeptide.
Hydrogen bonding found in the backbone of the polypeptide.
Describe the variety of bonds and interactions that contribute to tertiary structure of a protein. Then, specific whether these bonds take place within the “backbone” of the polypeptide, or between R-groups of amino acids in the polypeptide.
Hydrogen, Ionic, hydrophobic, Disulfide, Van der Waals force.
Describe quaternary structure of protein folding
Overall 3D arrangement of multiple polypeptide bonds to form a protein.
Define “denaturation” in the context of proteins
the process in which a protein loses its native 3D structure (secondary, tertiary, or quaternary) without breaking its primary sequence.
List conditions that can cause a protein to denature
Heat, pH changes, chemicals (like urea or detergents), or heavy metals can disrupt hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions, and hydrophobic interactions.
Identify which level of protein structure (1-4) remains when a protein is denatured
The primary structure
List the different functions that proteins have in the body and provide an example of each
Structural support, Enzymatic activity, transport, defense, movement, signaling, storage, regulation
Differentiate between dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis reactions
Define monomer and polymer
List the monomer and polymer for each of the macromolecule categories (remember, lipids do not have a true monomer)
Describe the general structure and function of carbohydrates
Determine whether simple sugars are soluble in water, and why? (hint: is a sugar a polar or non-polar molecule?)
Define “isomer” and provide an example
Distinguish between ribose and deoxyribose
Define “glycosidic linkage”
Describe the structure and function of the polysaccharides starch and glycogen, and identify where they are found within an organism
List the two main biological functions of polysaccharides
Identify the characteristics that all lipids have in common, despite having a diversity of structures and functions
State whether lipids tend to be hydrophobic or hydrophilic in nature and why
Differentiate between saturated fats and unsaturated fats
Provide an example of foods that contain saturated vs unsaturated fats
Describe how the degree of saturated of fatty acid tails affects the fluidity of fat (i.e. whether the fat will be semi-solid or liquid at room temperature
Define steroid
Describe the general structure of a phospholipid
Explain why phospholipids are referred to as “amphipathic”
Explain how the structure of a phospholipid relates to its function in the cell membrane
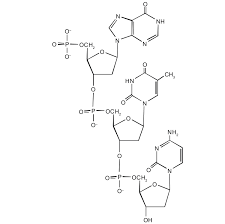
Identify the two main types of nucleic acids
Distinguish between the sugar is found in a nucleotide of RNA vs DNA
List the 5 options for nitrogenous bases, and understand which are found in DNA vs RNA
Describe “complementary pairing” and identify which nitrogenous bases pair with each other
Identify the type of bond that holds together two DNA polynucleotide strands
Nucleic acid chains have polarity; given the structure of a nucleic acid, determine which end of the strand is the 5’ end and which is the 3’ end
Recall the monomer of protein
Describe the difference between the term polypeptide and protein
Determine which component of the amino acid varies, making each amino acid distinct
Based on the chemical structure of a side chain (R-group), determine whether an amino acid is polar, non-polar, or ionized
Describe the primary structure of an amino acid
List the different functions that proteins have in the body and provide an example of each