Chapter 17-18: Aversive Control
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Discriminative Stimulus
A stimulus/event preceding an operant and setting the occasion for its reinforcement
Punishment
Basically behavioural principle occurring when a behaviour is followed by a consequence that results in a decrease in future probability of the behaviour
Consequence following behaviour may involve presentation of an aversive stimulus/event (positive) OR removal of a reinforcing stimulus/event (negative)
Behaviour is weakened
Extinction Stimulus (S delta)
A stimulus/event preceding an operant and setting the occasion for its non-reinforcement
Conditioned Aversive Stimulus (S-ave)
A stimulus/event preceding an operant and setting the occasion for avoidance
Ex: a warning sign, buzzing of a bee
Unconditional (Primary) Aversive Stimulus
A stimulus/event that as a function of a species’ history, an organism escapes
Important for survival → impact fitness of an organism
Ex: dodo bird DYING
3 Types of Aversive Contingencies
DEFINED INI TERMS OF EFFECT ON BEHAVIOUR
Spanking is only a punisher if it results in decrease of behaviour
Positive Punishment: any event/stimulus added to decrease behaviour
Negative Punishment: any event/stimulus removed to decrease behaviour
Negative Reinforcement: any event/stimulus removed to increase behaviour
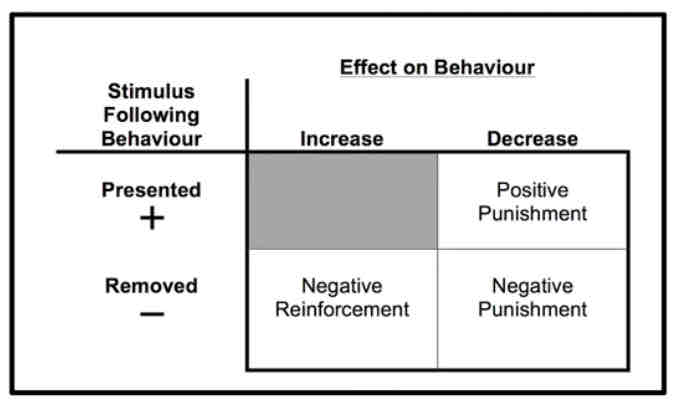
Types of Positive Punishment
Overcorrection
Restitution
Positive Practice
Guidance Compliance
Contingent Exercise
Physical Restraint
Response Blocking
Guided Compliance
Form of positive punishment contingent on problem behaviour following a request; individual is physically guided to comply with request
positively punishes non-compliance
Negatively reinforces compliance
Positive reinforcement of compliance easily incorporated
Overcorrection
Form of positive punishment where individual engages in effortful behaviour contingent on problem behaviour
Ex: making a mess and having to clean the entire room → requires compliance and monitoring → if not comply, have to punish non-compliance but may be met with defiance
Restitution
Contingent on problem behaviour; individual required to fix environment disrupted by problem behaviour
Positive Practice
Contingent on problem behaviour; individual engages in correct forms of relevant behaviour for a period of time
Physical Restraint
A form of positive punishment contingent on problem behaviour; body part involved in behaviour is held immobile for a specified period of time
Used with response blocking
Response Blocking
Physically stopping a behaviour from completing
Prevents problems generated by behaviour
Prevents behaviour from being reinforced
Contingent Exercise
Contingent on problem behaviour; individual engages in effortful behaviour for a specified period of time
Effortful behaviour is unrelated to problem behaviour
Types of Negative Punishment
Time Out from Positive Reinforcement
Response Cost
Time Out
Loss of access to positive reinforcers for a brief period contingent on the problem behaviours
Decreases occurrence of problem behaviours
Ex: removing a child from the room where positive reinforcers are available
Time-Out from Positive Reinforcement**** midterm types
Loss of access of positive reinforcement is contingent on a response
Must prevent access to reinforcer maintaining problem behaviour
Must be given immediately (physical guidance may be necessary)
There are no means of escaping time-out → other reinforcers should not be accessible
Often about getting rid of the child and their behaviour - escape behaviour for adult
Non-exclusionary Timeout
Remaining in the room of positive reinforcers but not in close proximity
Likely to be used when:
Person can be removed from reinforcing activities while remaining in the room
Presence of the person in the room is not disruptive to others
If criteria cannot be met, exclusionary timeout used instead
Exclusionary Timeout
Being physically removed from the room where positive reinforcers are unavailable
Removes the person from all sources of positive reinforcement
Time In Environment
Environment where problem behaviour occurs
When is Time Out Inappropriate to Use?
With problem behaviours maintained by negative reinforcement/sensory stimulation (automatic reinforcement)
Time out would negatively reinforce any behaviour maintained by escape
Response Cost
Removal of a specified amount of a reinforcer contingent on the occurrence of a problem behaviour
If reinforce loss delayed → conditioned punisher should be employed to bridge delay and provide immediate consequence
Consider what reinforcers to remove & magnitude of removal
Ex: removing 5 mins of recess when a behaviour occurs
Application of Aversive Activities
A method of reducing problem behaviours by the contingent application of aversive activities
Aversive Activity: low probability behaviour the person typically does not choose to engage in
A behaviour that can be a punisher for another behaviour
A form of positive punishment
Why Aversive Activities preferred over Aversive Stimulation?
Aversive/punishing stimulation is RARELY used in behaviour modification → more unethical
Ex: spanking, shouting/loud noise, ice
Premack Principle for Reinforcement
High probability behaviour reinforces low probability behaviour
Escape Learning
When an operant changes the environment from a situation where an unconditional negative reinforcer is present → to one where the unconditional negative reinforcer is absent
Escape responses learned faster than avoidance responses
Compatibility with reflexive unconditioned responses determines how quickly response occurs
Conditioning escape is easiest when…
Operant response is similar to reflexive unconditional response elicited by aversive stimulus
Rat escaping a shock by holding down a lever
Avoidance Learning
Response occurs before stimulus appears; when an operant prevents occurrence of an aversive stimulus
Discriminated Avoidance
A type of avoidance learning
When presence of S-ave controls probability of making avoidance response
Establishing S-ave is typically slower than establishing SD or S-delta because S-ave may become a CS eliciting other respondent behaviour that MAY interfere with operant behaviour
Ex: a warning signal
Nondiscriminated Avoidanced
A type of avoidance learning
Avoidance responding with NO S-ave to produce discrimination
Avoidance must be negatively reinforced occasionally to be maintained → poorly maintained when responses don’t reliably reduce frequency of aversive event
Operant-Respondent Interactions
Discriminated Avoidance: S-ave can function as CS for respondent behaviour which interrupts operant response
Respondent Extinction: avoidance behaviour maintained by operant conditioned can hinder respondent extinction
Ex: avoiding phobic stimuli is negatively reinforcing
Learned Helplessness
Seligman and Maier (1967)
Dogs exposed to predictable (signaled) but inescapable shock did not try to escape when allowed to → endured the pain
Actions have no effect on aversive outcome
Model for depression & anxiety
Experiment on Learned Helplessness
Master: received contingent shocks for leg extension
Yoked: received non-contingent shocks
Unshocked: received no shocks during pre-exposure
Following pre-exposure, extinction was implemented (shocks not administered)
In testing, task was re-learned except all groups were administered contingent shocks
Treating Learned Helplessness
Create a situation where failure to escape is not possible
Prevent learned helplessness in first place - pre-exposure to escape and avoidance contingencies can block learned helplessness brought on by inescapable aversive events
Overcorrection
Procedure use to decrease aggressive and disruptive behaviours exhibited by people with intellectual disabilities in institutional settings
Client required to engage in an effortful behaviour contingent on each instance of problem behaviour
2 forms:
Positive Practice
Restitution
Overcorrection: Positive Practice
Client must engage in correct forms of relevant behaviour contingent on an instance of the problem behaviour
Client does correct behaviour with guidance if necessary - done for a period of time
Must engage in correct behaviour many times in positive practice
Overcorrection: Restitution
Client must correct the environmental effects of problem behaviour and restore environment to a condition better than what existed before the problem behaviour; contingent on each instance of problem behaviour
Physical guidance used as needed
Client overcorrects the environmental effects of problem behaviour
Going beyond simply correcting the effect their behaviour had on the environment
Contingent Exercise
Client is instructed to engage in some form of physical exercise contingent on an instance of the problem behaviour → results in decrease in future probability of problem behaviour
A positive punishment procedure involving application of aversive activities
Aversive activity involves physical exercise unrelated to problem behaviour
Guided Compliance
Person is guided physically through the requested activity - contingent on occurrence of problem behaviour
Positive punishment of the problem behaviour because aversive stimulus (physical guidance) applied after problem behaviour, and it negatively reinforces compliance with the requested activity because aversive stimulus is removed after compliance begins
Physical Restraint
Punishment procedure where the change agent holds immobile the part of the client’s body involved in the behaviour - contingent on problem behaviour
Physical Restraint: Response Blocking
The change agent prevents the occurrence of a problem behaviour by physically blocking the response
Can also be used with brief restraint
Considerations before Using Positive Punishment
Use functional interventions first
Implement differential reinforcement with punishment
Consider the function of the problem behaviour
Choose the aversive stimulus with care
Collect data to make treatment decisions
Address the ethical considerations in the use of punishment
Ethics of Punishment
Informed consent
Alternative treatments
Recipient safety
Problem severity
Implementation guidelines
Training and supervision
Peer review
Accountability: preventing misuse and overuse