Full Bonding, structure and properties of matter set
1/68
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What is the range of the diameter for course particles (dust)?
2500nm-10 000nm
What is the range of the diameter for fine particles?
100nm-2500nm
What is the range of the diameter for Nanoparticles?
1nm-100nm
How does the SA:V ratio affect nanoparticles?
As particles decrease in size, the size of their surface area increases in relation to their volume, causing the surface area to volume ratio to increase
This can cause the properties of a material to be different depending on whether its a nanoparticles or a bulk
E.g: You’ll need less of a material that’s made up of nanoparticles to work as an effective catalyst compared to a material made up of nor al sized particles
What can nanoparticles be used for?
Catalysts: high Sa:V ratio
Nano-medicine: absorbed easily into the body and can be used to deliver drugs
Electrical circuits for computer chips: conduct electricity
Added to polymer fibres → surgical masks, wound dressings, deodorants: antimicrobial properties of silver nanoparticles
Cosmetics: used in moisturises to make them less oily
What are nano particles currently being used for?
Sun creams: better at protecting skin from UV rays and provided better skin coverage
What are the risks and controversies of using nanoparticles?
Affect of products on the human body hasn’t been tested long-term
Unknown if it causes any damage to cells
If washed away can be damaging to the environment
Why do metals bond metallically?
metallic bonding requires delocalised electrons
The electrons in the outer shells of metal atoms are delocalised
Strong electrostatic attraction between the positive ions and shared negative electrons
These forces of attraction hold atoms together in a regular structure
Metallic bonds are very strong
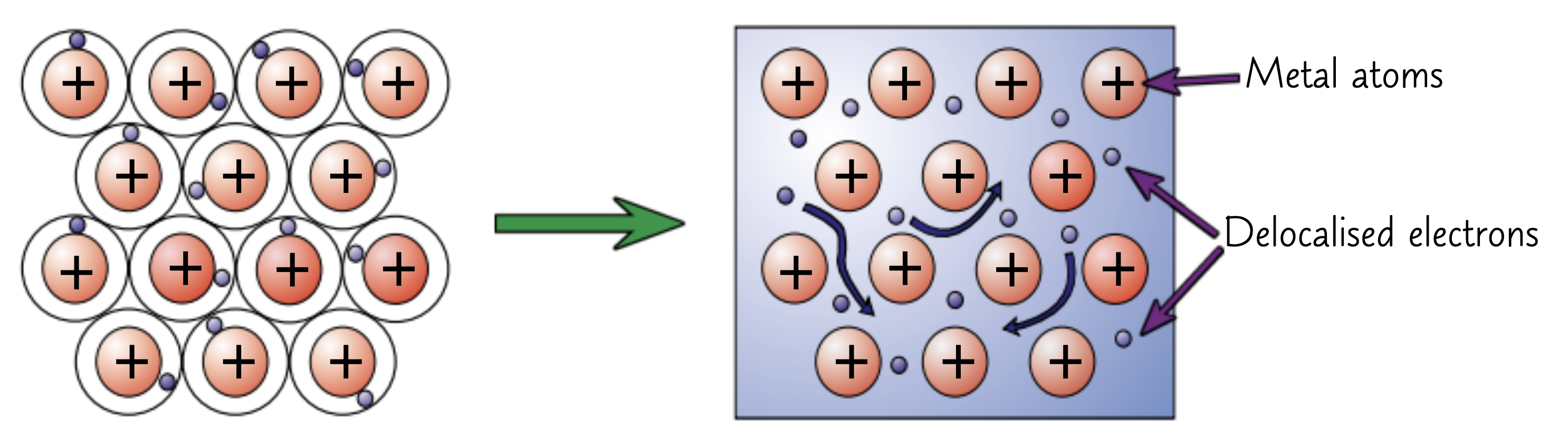
What substances are held together by metallic bonds?
Elements and alloys
Explain why metals are solid at room temperature.
Electrostatic attraction between the metal atoms and delocalised electrons are very strong and require a lot of energy to be broken
Therefore compounds with metallic bonds have high melting and boiling points
What are the properties of metals because of metallic bonds?
Solid
High belting and boiling points
Good conductors of heat and electeicity
Malleable
Why can metals with metallic bond conduct heat and electricity?
The delocalised electrons carry electric charge and thermal energy through the whole structure
Why are most metals malleable because of metallic bonds?
The layers of atoms in a metal can slide over each other
What are some common problems with pure metals?
Not right for specific jobs
too soft
What is an alloy?
a mixture of two or more metals or a metal and another element
Why are allows harder than pure metals?
Different elements have different sized atoms,
when another element is mixed with a pure metal, the new atoms will distort the layers of metal atoms
making it harder for them to slide over each other
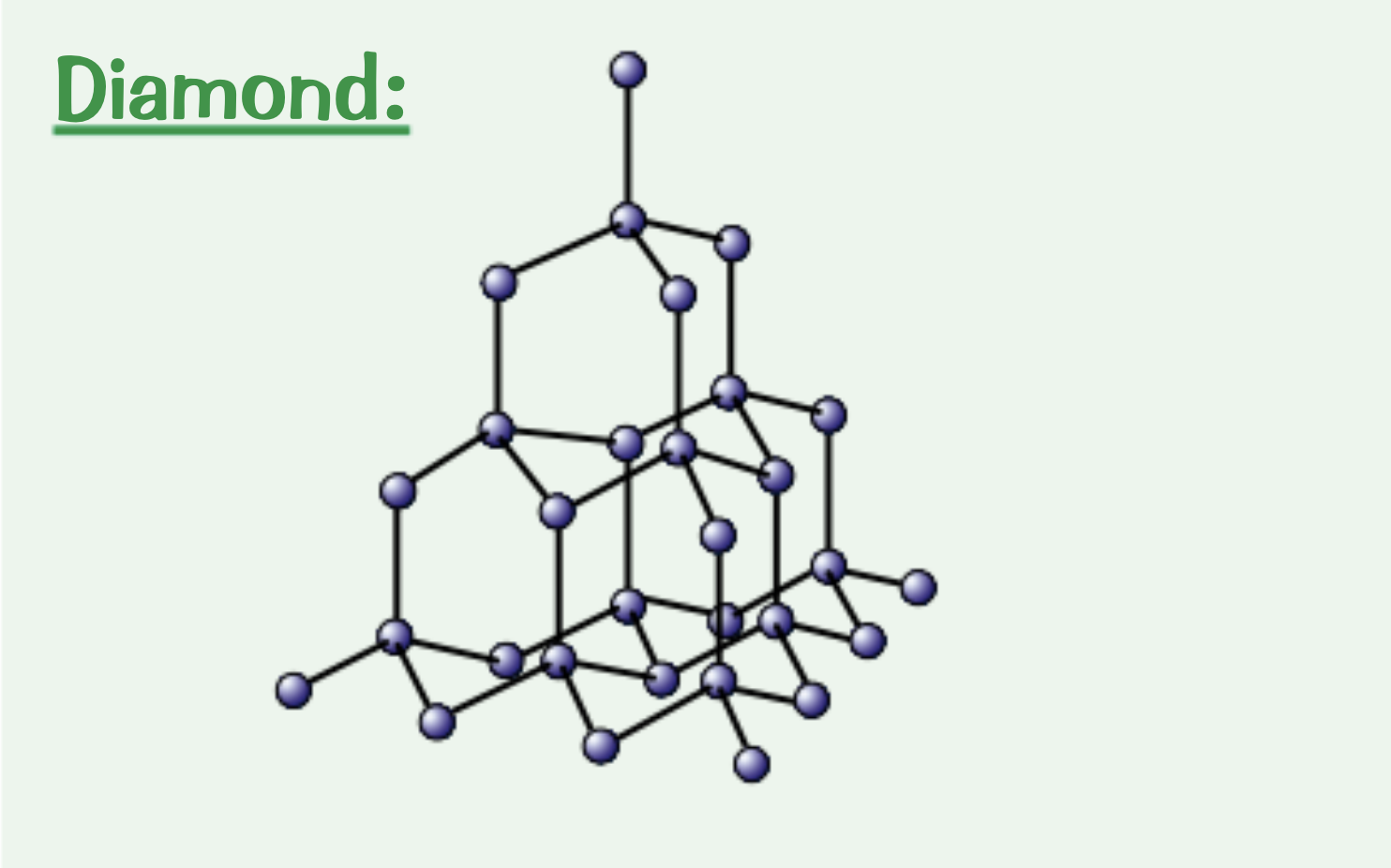
What are the properties of diamond?
Really hard: because of the 4 covalent bonds per carbon atom
High melting point: requires a lot of energy to break the covalent bonds
Doesn’t conduct electricity: no delocalised electrons
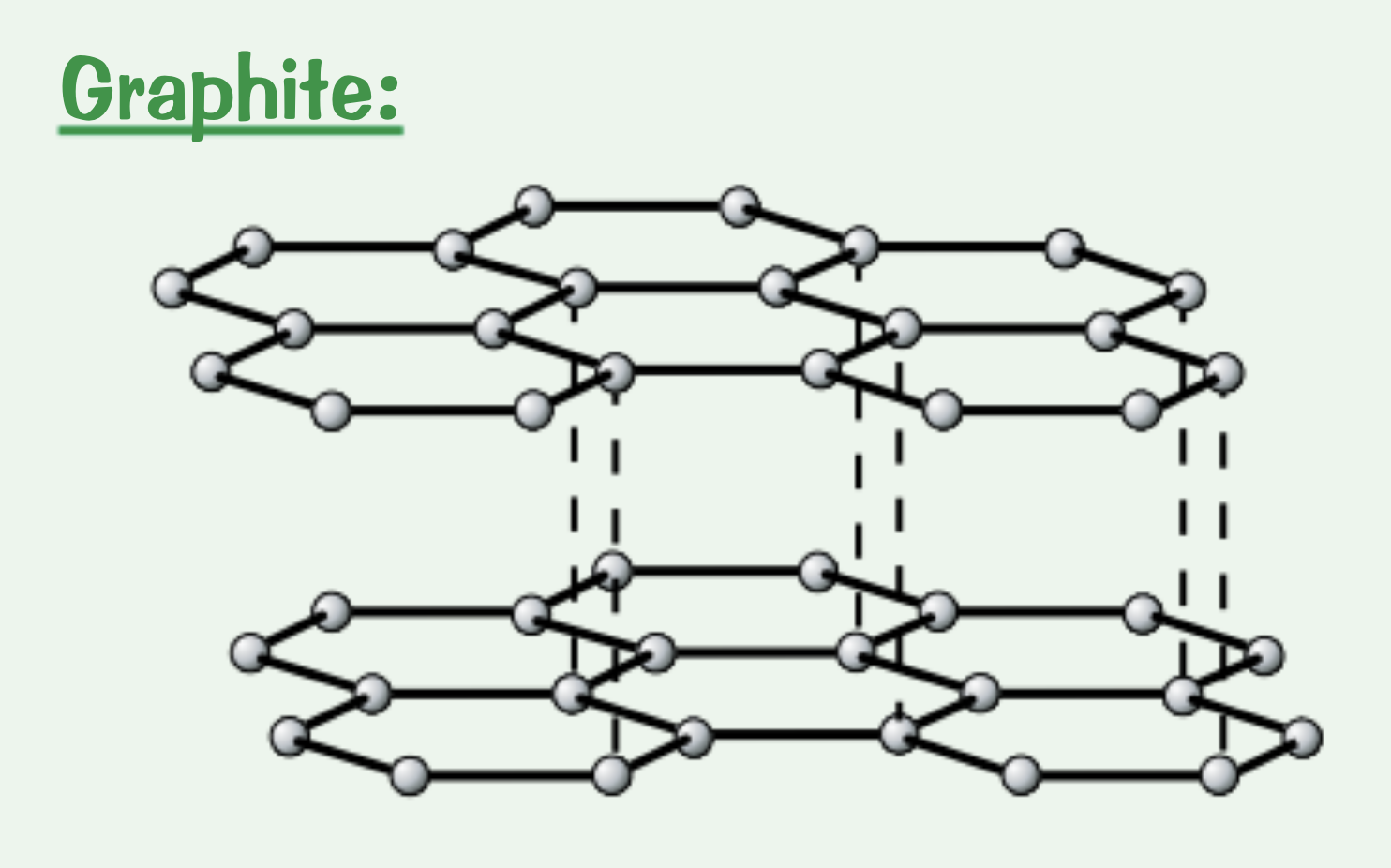
What and why are the properties of graphite?
Soft and slippery → lubricating material: weak bonds between the hexagon layers
High melting point: covalent bonds in the layers require a lot of energy to break
Conducts electricity and heat: each carbon atom has one delocalised electron
What is graphene?
A sheet of carbon atoms joined together in hexagons. Its 2 dimensional and only 1 atom thick
What are the properties of graphene?
Strong: covalent bonds
Light
Conducts electricity: has delocalised electrons like graphite
What is graphene used for?
to strengthen composite materials
Used in electronics
What are fullerenes?
molecules of carbon shaped like closed tubes or hollow balls
What are fullerenes made of?
Carbon atoms arranged in hexagons, pentagons or heptagons
What are fullerenes used for?
Cage: can be used to deliver drugs around the body
Catalysts: huge surface area
Lubricants
What is buckminsterfullerene?
The first fullerene to be discovered
C60 and forms a hollow sphere
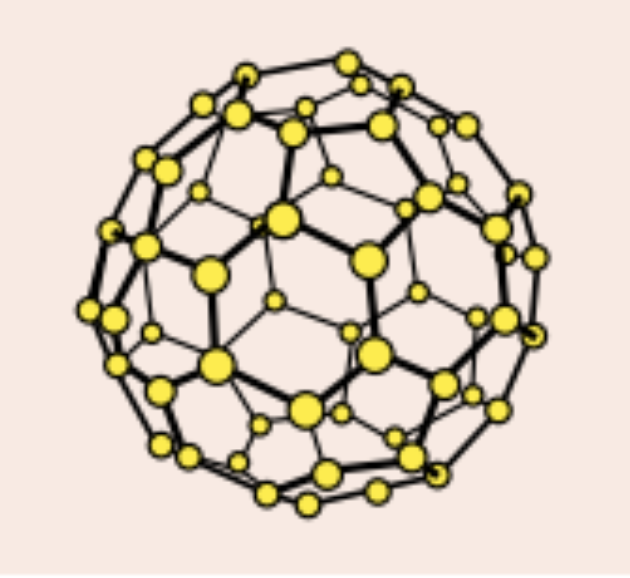
What are nanotubes?
Tiny carbon cylinders
What are the properties of nanotubes?
Length:diameter ratio is high
Conducts electricity and heat
High tensile strength( don’t break when stretched )
What is nanotechnology?
Technology using very small particles such as nanotubes
What are nanotubes/nanotechnology used for?
Electronics
strengthen materials without adding weight
What is a polymer?
Long chains of repeating units
What’s bonds do polymers have?
Covalent bonds
How do you draw a repeating unit?
The repeating unit drawn in brackets
subscript value of n for how many times its repeated
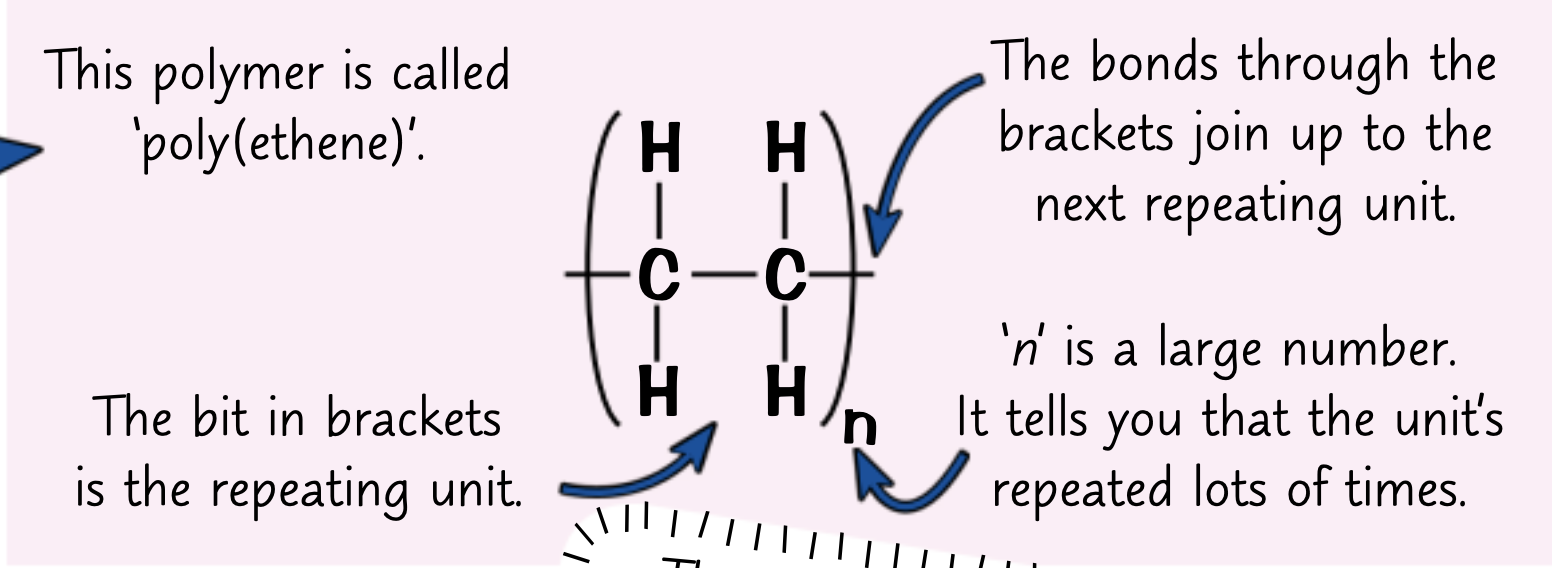
How do you get the molecular formula from a repeating unit of a polymer?
Write down the molecular formula of the repeating unit in brackets and put an n on the outside (C2H4)n
Why are most polymers a solid at room temperature?
The intermolecular forces between the polymer molecules are larger than between simple covalent molecules, so more energy is needed to break them
Why are the boiling points of polymers lower than ionic or giant molecular compounds?
The intermolecular forces are still weaker than ionic or covalent bonds.
What are giant covalent structures called?
Macromolecules
How are molecules bonded I giant covalent structures?
all the atoms are bonded together by strong covalent bonds
Do giant covalent structures have a low or high boiling or melting point and why?
Very high because a lot of energy is needed to break the strong covalent bonds
Explain the structure of diamond.
Each carbon atoms forms four covalent bonds in a very rigid giant covalent structure
Explain the structure of graphite.
Each carbon atom forms three covalent bonds to create layers of hexagons. Each carbon atom also has one delocalised electron
What is sand made of?
Silicon dioxide
Each grain of sand is one giant structure of silicon and oxygen
What are ions?
Charged particles
How to atoms try gain full outer shells?
Through losing or gaining electrons
What happens when metals form ions?
they lose electrons to form positive ions
What happens when a non-metals forms ions?
gain electrons to form negative ions
What is the charge of any ion?
The electrons it gained or lost
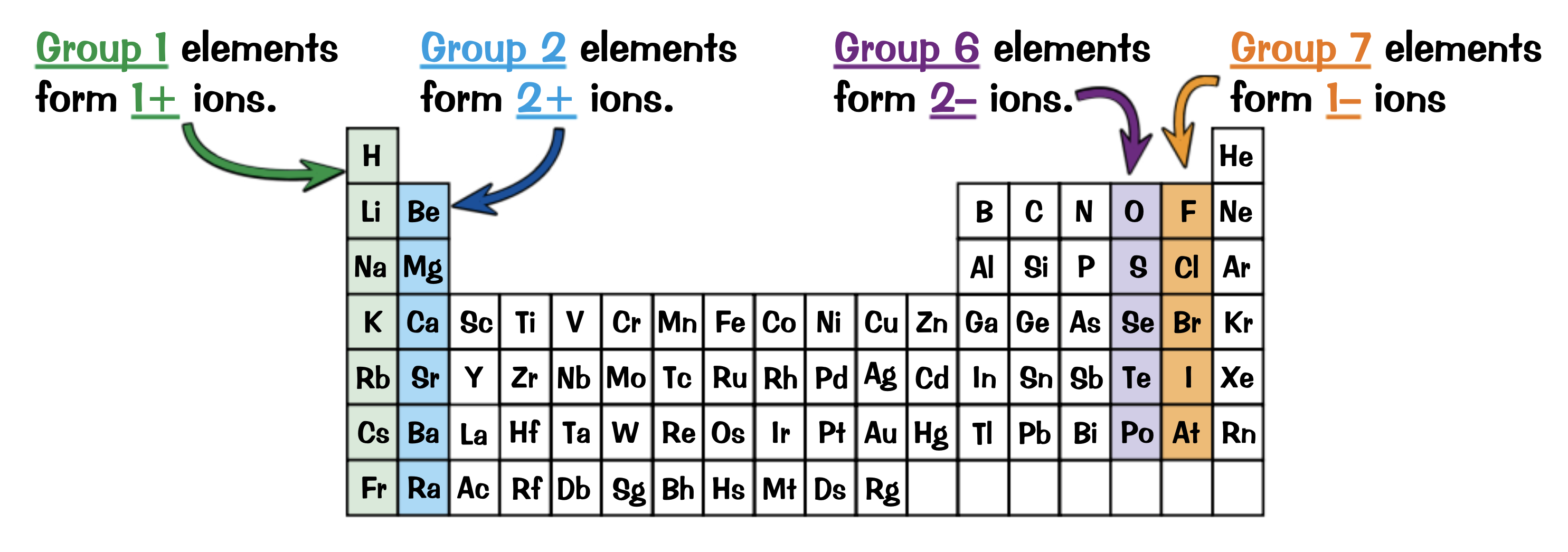
The elements in which groups are most likely to form ions?
1,2,6,7
How do you find an ions charged for an element?
Their group number is how many electrons they have in their outer shell, so they will all need to gain or lose the same number of electrons
Write the ions each group will form and a half equation for an element in each
Group 1: 1+ ions ( Na→ Na+ + e- )
Group 2: 2+ ions ( Mg → Mg2+ + 2e-)
Group 6: 2- ions ( Cl + e- → Cl- )
Group 7: 1- ions ( O + 2e- → O2- )
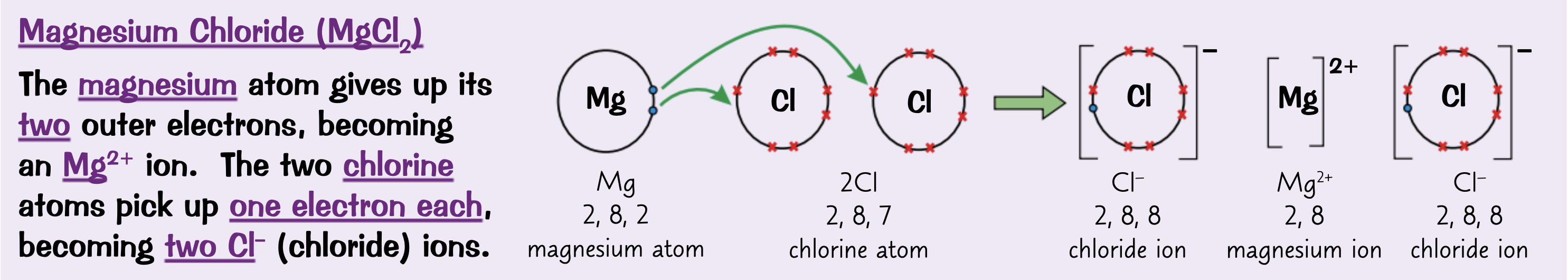
Explain what ionic bonding is.
A metal and a non-metal react, A metal loses electrons to form a positive ion and the non-metal gains that electron to form a negatively charged ion. The oppositely charged ions are strongly attracted by electrostatic forces.
How are ionic bonded elements shown?
Dot and cross diagram
What are 3 problems with the dot and cross diagram?
Don’t show the structure of the compound, size of the ions or how they are arranged
Draw a dot and cross diagram for Magnesium chloride ( MgCl2) with only the outer shells
What structure do ionic compounds form?
Giant ionic lattice
Explain the properties and what an giant ionic lattice is.
The ions form a closely packed regular lattice arrangement with very strong electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions in all directions of the lattice
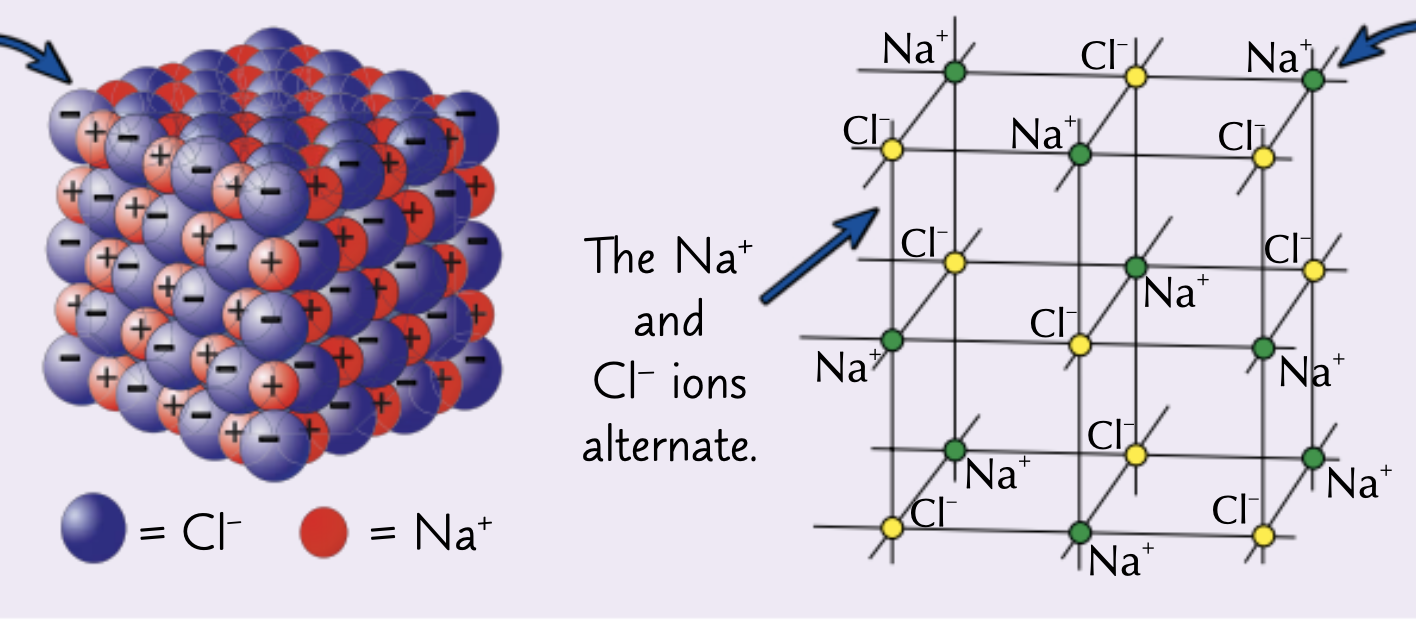
What are the properties of ionic compounds?
High mot and bot’s due to strong bonds between ions that require a lot of energy to break
Cannot conduct electricity as solids as ions are held in place
Can conduct electricity as a liquid when ions are free to move
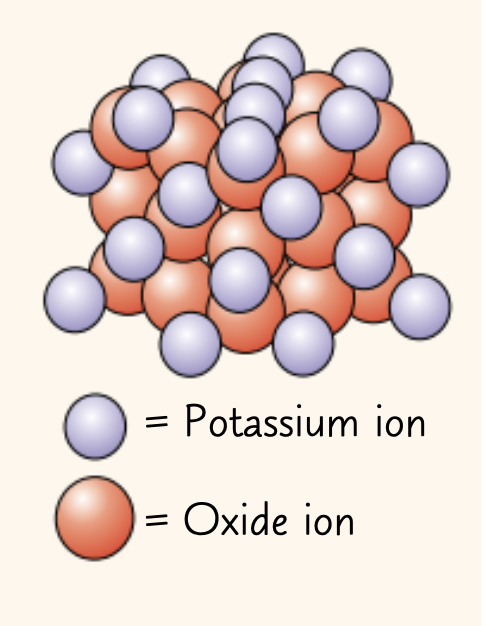
Find the empirical formula of the ionic compound in the image.

What are covalent bonds?
When non-metal atoms bond together. They share a pair of electrons to make covalent bonds.
Why are covalent bonds strong?
The positively charged nuclei of the bonded atoms are attracted to the shared pair of electrons by electrostatic forces.
How do you use a dot and cross diagram to draw covalent bonds?
Electrons drawn in the overlap between outer orbitals of the two atoms are shared between those atoms.
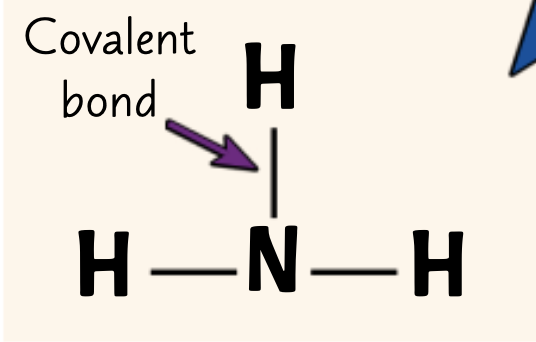
How are covalent bonds shown in displayed formulae?
Draw a dot and cross diagram for Hydrogen, H2

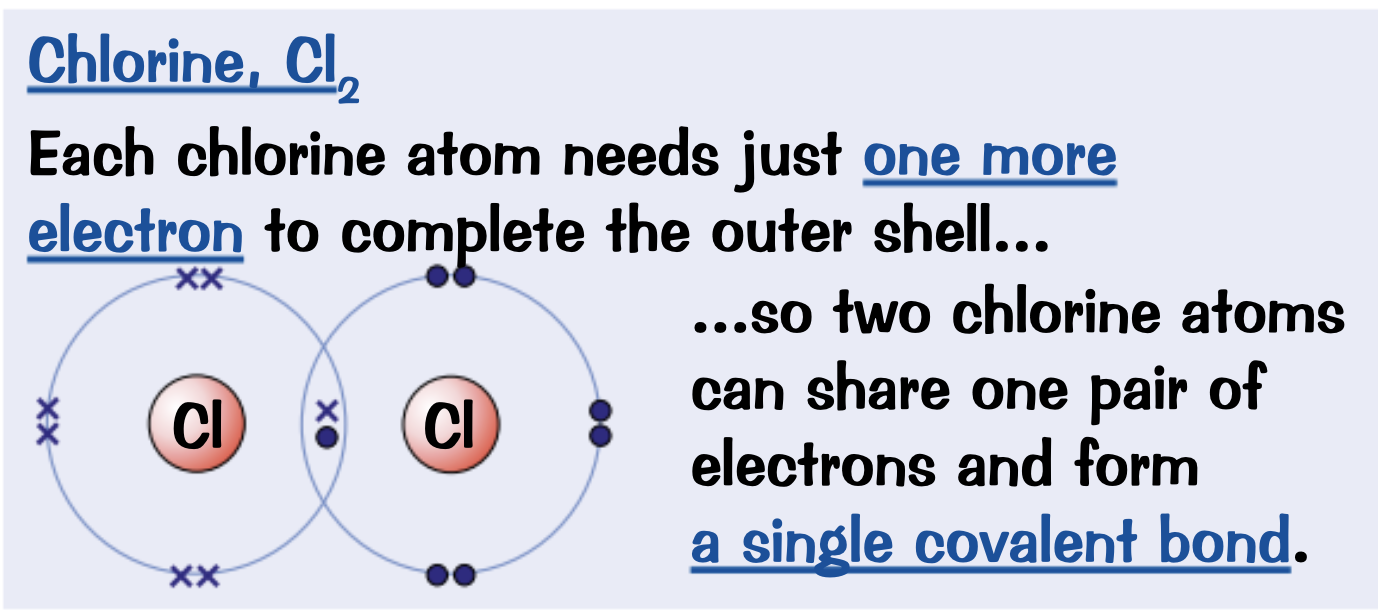
Draw a dot and cross diagram for Chlorine. Cl2
Draw a dot and cross diagram for Oxygen, O2

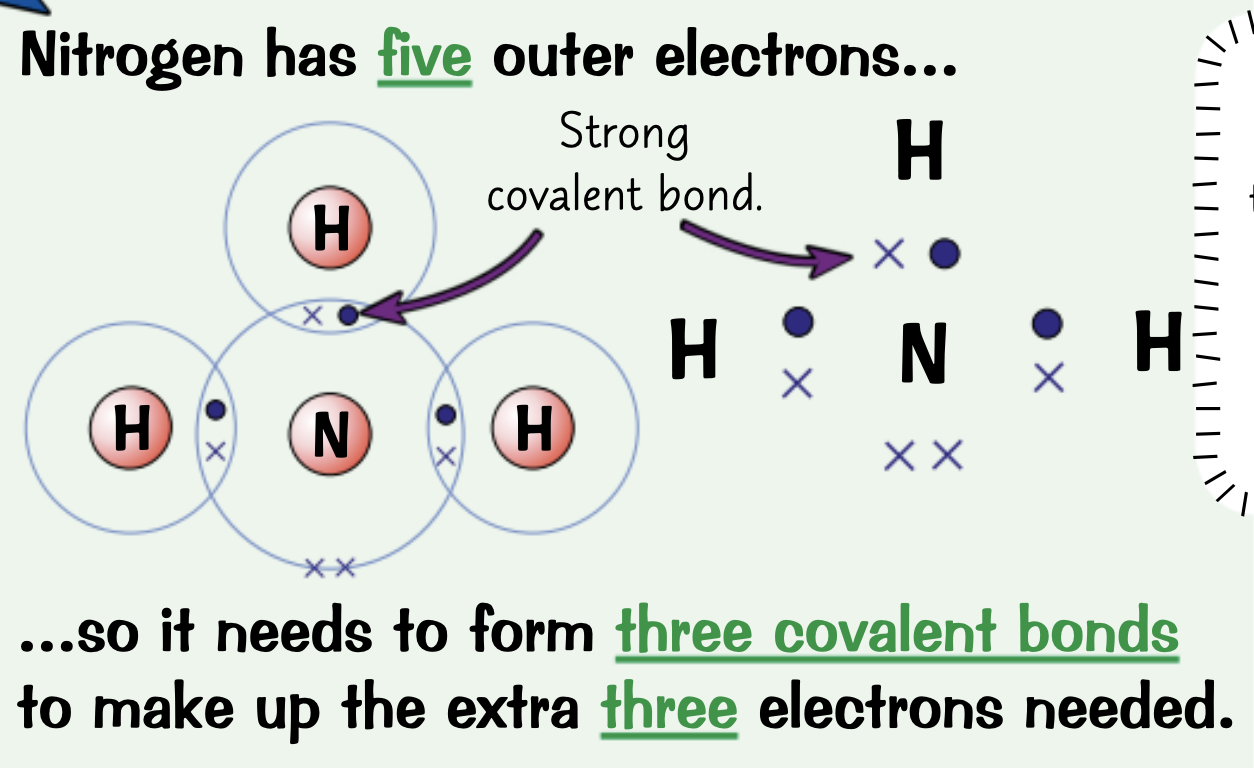
Draw a dot and cross diagram for Nitrogen, N2

Draw a dot and cross diagram for Water, H2O
Draw a dot and cross diagram for

Draw a dot and cross diagram for Methane, CH4

Draw a dot and cross diagram for Hydrogen chloride, HCl

What are the properties of simple molecular substances?
Substances containing covalent bonds usually contain simple molecular structures
The atoms within the molecule are held together by very strong covalent bonds, but the forces of attraction between these molecules are weak
Low bpt and met because the intermolecular forces are easy to break and you don’t need to break the covalent bonds
Mostly gases and liquids at room temp
As the molecules get bigger, the strength of the intermolecular forces increases, so more energy is needed to break them so the mat and bpt increases
Don’t conduct electricity because they have no charge and no free electrons