Biopsychology TEST 3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:12 AM on 3/31/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
1
New cards
Theories of Emotion
Common Sense Theory, James-Lange Theory, Cannon-Bard Theory, Papez-Maclean “Theory”/System, Schacter- Singer Theory, Ekman’s Facial Feedback Hypothesis, Modern Theory, Right Hemisphere only theory, Valence Hypothesis
2
New cards
Common Sense Theory
emotions are simply a class of feelings, differentiated by their experienced quality from other sensory experiences like tasting chocolate or proprioception like sensing pain in one's lower back
3
New cards
James-Lange Theory
physical changes in the body happen first, which then leads to the experience of emotion
4
New cards
Cannon Bard Theory
that we feel emotions and experience physiological reactions such as sweating, trembling, and muscle tension
5
New cards
Papez Maclean theory
the experience of emotion was determined by activity in the cingulate cortex and, less directly, other cortical areas, the hypothalamus, expanded system and theory, said for more primitive emotions named it the limbic system
6
New cards
Schacter- Singer Theory
emotion is formed from physiological arousal and a cognitive label. This theory also explains that a person's emotional response is formed from an interpretation of their immediate environment
7
New cards
Ekman’s Facial Feedback Hypothesis
individuals' emotional experiences are influenced by their facial expressions. For example, smiling should typically make individuals feel happier, and frowning should make them feel sadder
8
New cards
Duchenne Smile (authentic smile)
looking into the mirror and faking a smile will trick your brain into thinking that you are happy
9
New cards
“Modern” Theory
judgments, desires, physiological changes, feelings, and behavior as possible constituents of emotion
10
New cards
Right Hemisphere (only) Hypothesis
emotional stimuli are perceived more efficiently by the right hemisphere than by the left hemisphere. ^^The current research examines this hypothesis by examining hemispheric asymmetries for the conscious and unconscious perception of emotional stimuli^^
11
New cards
Valence Hypothesis
negative emotions and related display behaviors are modulated by the ^^right hemisphere and positive emotions and related display behaviors are modulated by the left hemisphere^^
12
New cards
Amygdala
commonly thought to form the core of a neural system for processing fearful and threatening stimuli (4), including the detection of threat and activation of appropriate fear-related behaviors in response to threatening or dangerous stimuli
13
New cards
Hemispheric Differences
Left- Positive
Right- Negative
Right- Negative
14
New cards
Insular cortex
Brain region involved in emotional processing, self-awareness, and social cognition. Located in the cerebral cortex, it's responsible for regulating our emotional responses, interpreting social cues, and helping us understand our own thoughts and feelings. Dysfunction in this area has been linked to various psychiatric and neurological disorders, including anxiety, depression, and autism.
15
New cards
Papez Circuits
A neural circuit that connects the limbic system to the thalamus and cortex. It is involved in the regulation of emotions, memory, and learning.
16
New cards
Circuit 1
amygdala and hypothalamus survival
17
New cards
Circuit 2
cingulate gyrus, septum, \n hypothalamus - pleasure - especially sexual \n pleasure
18
New cards
Circuit 3
hypothalamus & thalamus - \n cooperative social behaviors
19
New cards
Schachter-Singer famous experiment
The experiment where two confederates were either happy or sad which influenced the participants way of thinking about the experiment
20
New cards
Kluver-Bucy syndrome
Symptoms of this neurological disorder include hyperorality, hypersexuality, visual agnosia, and disinhibited behavior. It is caused by damage to the temporal lobes of the brain.
21
New cards
Charles Whitman
Had a brain tumor pressing on his amygdala, which caused him to kill his mother and sister and then opening fire on a university in Texas
22
New cards
Types of Agression
Irritable and Fear-Induced
23
New cards
Irritable Aggression
Amygdala is medial
24
New cards
Fear Induced Aggression
central and basal nuclei, medial - \n increase; ventral basal and lateral inhibit
25
New cards
Research on Testosterone
higher levels of circulating testosterone in men are associated with increases in male-typical behaviors such as physical aggression and anger
26
New cards
Anti-anxiety medications and the neurotransmitter
enhance the activity of the neurotransmitter GABA—a chemical in the brain that helps you to feel calm
27
New cards
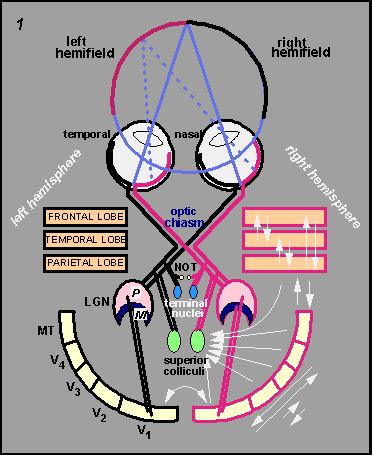
The wiring of the visual system
The complex network of neural connections that transmit visual information from the eyes to the brain, where it is processed and interpreted to create our perception of the world around us. This wiring includes the optic nerve, which carries visual signals from the retina to the brain, and various visual processing regions in the brain that work together to create a cohesive visual experience.
28
New cards
Split-Brain Patients
surgical resection of the callosal fibers in an attempt to reduce the spread of epileptic foci between the cerebral hemispheres
29
New cards
Research regarding split-brain patients
the left hemisphere of the brain was responsible for language understanding and articulation, while the right hemisphere could recognize a word, but could not articulate it
30
New cards
Wada Test
A test design to find the trigger for seizures by looking at both hemisphere of the brain including looking how each hemisphere looks at memory and language comprehension
31
New cards
Lateralization
The division of cognitive functions between the left and right hemispheres of the brain, with each hemisphere specializing in certain tasks
32
New cards
Lateralization w/ Language
refers to the phenomenon in which one hemisphere (typically the left) shows greater involvement in language functions than the other
33
New cards
Thalamus and Consciousness
conscious experience is based on the interactions between thalamic nuclei and areas of the cortex, shifting attention
34
New cards
Binding Problem
the problem of how objects, background, and abstract or emotional features are combined into a single experience
Neural synchrony across many areas (40 Hz gamma)
Attention
Neural synchrony across many areas (40 Hz gamma)
Attention
35
New cards
Executive for Conciousness
claustrum, ACC, thalamus
36
New cards
Type 1 alcoholism
Chronic alcoholism caused by genetic predisposition and environmental factors. Onset is usually before age 25 and characterized by physical dependence, tolerance, and withdrawal symptoms.
37
New cards
Type 2 Alcoholism
A chronic condition characterized by a strong urge to drink, even when it causes negative consequences. It typically develops gradually over time and is often associated with genetic factors and environmental triggers. It can lead to physical and mental health problems and social and occupational impairment. Treatment may involve therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
38
New cards
Korsakoff’s syndrome
Memory disorder caused by thiamine deficiency, often due to alcoholism. Symptoms include confusion, memory loss, and difficulty with coordination.
39
New cards
Psychedelic Drugs
Classification of Psychedelic Drugs \n **– Anticholinergic** \n • Scopolamine \n **– Catecholamine-like** \n • Mescaline \n • Ecstasy \n • Nutmeg \n **– Serotonin-like** \n • LSD \n • DMT \n • Psilocybin \n **– Anesthetics** \n • PCP & Ketamine
40
New cards
Tolerance
how much you need for the drug to effect you
41
New cards
Addition Withdrawal
anxiety, fatigue, sweating, vomiting, depression, seizures, and hallucinations from quitting a drug
42
New cards
Conditioned Tolerance
a higher dose of a drug can be tolerated when external stimuli associated with prior administration of the drug are present
43
New cards
Affinity
describes strength of drug binding with receptor (“fit the lock
44
New cards
Efficacy
describes ability of drug-bound receptor to produce a response (“turn the key”)
45
New cards
Mechanisms for agonistic
Increases synthesis \n • destroys degrading enzymes \n • increases release of neurotransmitter \n (affects Ca channels) \n • blocks inhibitory effect of autoreceptors \n • activates postsynaptic receptors \n • inhibits degradation or reuptake
46
New cards
Mechanisms for antagonistic
Blocks synthesis of the neurotransmitter \n • increases leakage from vesicles \n • blocks release \n • activates auto receptors \n • blocks postsynaptic receptors
47
New cards
Methylphenidate
A central nervous system stimulant used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and narcolepsy. It works by increasing the levels of dopamine and norepinephrine in the brain, which helps to improve focus and reduce impulsivity.
48
New cards
Anandamide
Endocannabinoid neurotransmitter that acts as a natural painkiller and mood enhancer. It is produced in the brain and binds to cannabinoid receptors.
49
New cards
cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are a group of chemical compounds that interact with the endocannabinoid system in the body to produce various effects, including pain relief, relaxation, and altered perception. These compounds can be found in cannabis plants or produced naturally in the body.
50
New cards
Delirium tremens
a psychotic condition typical of withdrawal in chronic alcoholics, involving tremors, hallucinations, anxiety, and disorientation.
51
New cards
Treatment of delirium Tremens
Alcoholism treatment may start with detoxification at a medical facility. Sedatives may prevent delirium tremens.
52
New cards
Effects of Mary Jane
\
May be some immuno-suppression (are cannabinoid \n receptors in lymphatic system) \n • Can lower sperm count in males and ovulation in \n females \n • Long-term effects of pre-natal exposure are being \n studied – may be some
May be some immuno-suppression (are cannabinoid \n receptors in lymphatic system) \n • Can lower sperm count in males and ovulation in \n females \n • Long-term effects of pre-natal exposure are being \n studied – may be some
53
New cards
Reinforcement circuit
\
Nucleus accumbens \n • Medial Forebrain Bundle \n • Hypothalamus (lateral and pre-optic area) \n • Dopaminergic
Nucleus accumbens \n • Medial Forebrain Bundle \n • Hypothalamus (lateral and pre-optic area) \n • Dopaminergic
54
New cards
Dopamine
The neurotransmitter dopamine is vital to reinforcement learning. The phasic activity of dopamine neurons, which in part encodes reward prediction error, is thought to reinforce the behavior of animals to maximize chances of receiving rewards in the future
55
New cards
The Nucleus Accumbens
is considered as the neural interface between motivation and action, playing a key role on feeding, sexual, reward, stress-related, drug self-administration behaviors