Week 4- Basic US principles, measurements and views
1/277
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
278 Terms
echocardiography Hz range
1-10 MHz
AE TTE Frequency
2 - 5 MHz
Pediatric Probe Frequency
3.5 - 5 MHz
TEE Echo Probe frequency
2-10 MHz
what happens with increased acoustic impedance
increased sound return
What incidence is best for 2D imaging
Perpendicular
Examples of tissue producing impedance in the heart
walls, valves, blood
What incidence is best for doppler
Parallel
scattering occurs when
structures are less than 1 wavelength in lateral dimension
refraction occurs when 2 structures have different
impendance
refraction results in
“double image” artifacts
attenuation is concerted into (3)
heat
reflection
scattering
how to avoid airs high acoustic impednace (4)
Air has a high acoustic impendace
gel elimates air between skin and xducer
placing pt. on left side will help reduce lung interferance
move heart beyond the sternum
poor lateral resultion in far field causes
“blurring”
how does frequency affect lateral resolution
higher = better
how does frequency affect axial resolution
higher = better
how to make measurements for accurate
get cardiac structures perpendicular to xducer
temporal resolution limited by
sweep speed
what improves spatial resolution
increased frequency
spatial res def
ability of the system to image strucuter’s close together
penetration vs. resolution
cant have increased resoluition with optimal penetration- there is a tradeoff
optimal resoltion =
poorer penetration
patients that require deeper penetration and less optimal resolution
COPD, Body habitus, etc.
near field aka
fresnel zone
far field aka
fraunhaufer zone
MC type of xducer
phased array
pencil probe (pedoff, non-imaging probe) pros
small footprint for getting between ribs
superior at detecting high velocities, mainly aortic valve stenosis
2 crystals 1 send-1receive
pedoff cons
no image,
anatomical sound guidance only which can be difficult to obtain
image quality and resolution depend on
scan-line density
ways to improve scan line density / frame rate
decrease sector width
use zoom
decrease sector width
X_axis m mode
time
y_ axis m ode
depth
sampling rate of m-mode
1800 times per second
m-mode can aid in visualization of
endocardium
high frequency fluttering on valve leaflets
m-mode for measurements
should ONLY be used if perpendicular to structure
harmonic imaging
bypasses tissue frequencies and only looks at the harmonic frequencies
harmonic imaging originally used for
was originally to be used with contrast but tissue also produces different frequencies (harmonic frequencies) which was thought to be noise
harmonic frequency realted to transmitted frequency
harmonic is double the hz as transmitted
S:N ratio with harmonic imaging
increased
what resolutions are increased with harmonic imaging
contrast and spatial
harmonics used with
contrast
harmonics improve visualization of
endocardium in 2D imaging
ALARA
Minimized scan time and power
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
who discovered the doppler effect
johann Christian Doppler (1803-1853)
doppler frequency when fluid moving toward xducer
positive
doppler frequency when fluid moving toward xducer
negative
a sound wave refelcted from a moving object changes _______ in proportion to ________
frequency, velocity
doppler records
velocity and direction of blood flow
doppler allows measurement of
pressure gradient -
pressure gradient measured by -
Bernoulli principle
can be visualized as (3)
color
spectral (PW & CW)
doppler interrogation, uses (6)
Various windows
views (traditional and non-traditional)
Planes,
tools
color
patient adjustment
sound
etc.
intercept angle Θ (theta)
Must be parallel to flow as possible for increased accuracy of velocity
intercept angle degrees
less than 20 = good
more than 20 = underestimation of velocity
color doppler uses PW or CW?
PW, Has range resolution
color doppler can be overlayed on
2D or M-mode
large area or minute area (color doppler)
large
color doppler has limited
temporal resolution
color doppler use
very good at determining extent and area of regurgigation
color doppler can distinguish between
laminar and turbulent flow
color doppler angle
parallel to flow
color doppler scale setttings
50-60 cm/s
color maps
velocity (2color) variance (4 color)
how to set solor doppler gain
turn up unitl speckling appears then lower until speckling is gone
3 parts of the color doppler jet
vena contracta
PISA
jet area
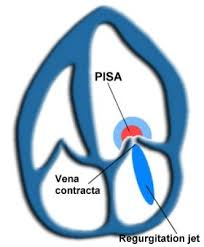
vena contracta
narrowest part of the stream where the velocity is the highest
PISA Stands for
Proximal Iso-velocity Surface Area
PISA def
(flow convergence) - The hemispheric - shaped flow formed when fluid flows towards a flat surface.
PISA used for
calculating diameter of an oriface
Jet Area
The area of the regurgitant jet into the downstream oriface
examples of velocities CW can resolve that PW can not
AS (Aortic stenonsis)
MR (Mitral regurgitation)
AI (Aortic insufficiency)
what is spectral doppler used for
measuring velocities and assessing timing
what 2 dopplers create a spectral doppler
CW and PW
temporal res of spectral doppler
excellent
“zero” line or baseline is adjusted how?
up or down
x-axis spectral doppler
time
y-axis spectral doppler
direction and velocity (frequency shifts)
how is flow towards displayed on spectral doppler
above “0” line
how is flow away displayed on spectral doppler
below “0” line
how to determine turbulence with CW?
Envelope if filed in
how to determine turbulence with PW?
will vary depending on interogration style
spectral broadening: what is it?
possible causes
The broadening or filling of a PW waveform due to various velocities, non-laminar flow (sample volume/gate is too large
VTI Stands for
velocity time integral
VTI AKA
Flow velocity integral
VTI / FVI definiton
distance blood travels in each stroke (cm)
How is VTI / FVI Calculated
by the machine by tracing the doppler spectral curve
nyquist limit =
FRF/2
How to improve your nyquist limit
adjust depth (higher PFR = Better nyquist limit)
How created the bournoulli equation
Daniel Bernoulli (1700-1782)
Bernouli equation:
ΔP = 4V² (V = Doppler velocity) is Simplified Bernoulli Equation
explain bernoulli equation in words
Change in pressure across a small oriface is proportional to the square of the velocity of the fluid flowing through the oriface
3 steps to obtaining Pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) or Right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP)
Obtain peak velocity of the tricuspid reguigitant jet
Change the velocity to a pressure gradient using the bernoulli equation
then add the estimated right atrail pressure by assessing the degree of collapse of the IVC
PAP=
PVSP In the absense of pulmonic stenosis
Right atrail pressure is estimated by
size and collapability of the IVC
Application of Bernoulli equation
changes velocity (m/s) into pressure gradient (mmHg)
bernoulli equation uses
peak velocity of TV regugitent jet
RVSP or PAP =
4(Tricuspid regigitation veloctity)² + right atrial pessure
PAP or RVSP =
ΔPRV-RA + RAP
How is RAP (right atrial pressure) estimated
by evaluating the degree of collapse of the IVC