Plant and Animal Cells
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
cell wall
tough and rigid to provide shape and support
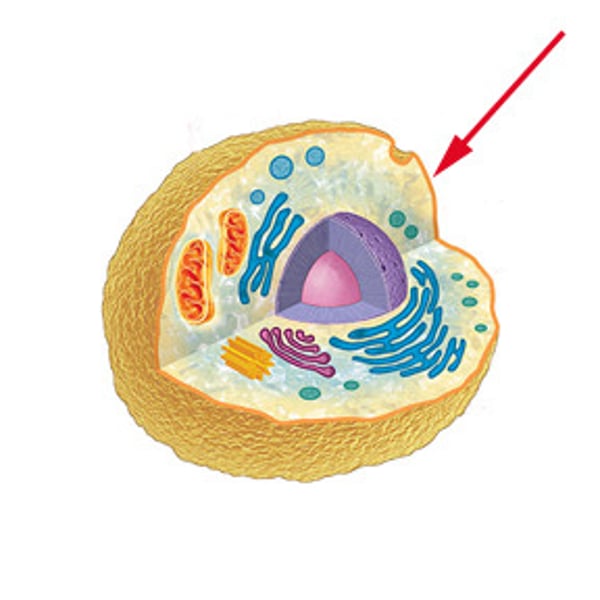
cell membrane
controls what enters and exits the cell
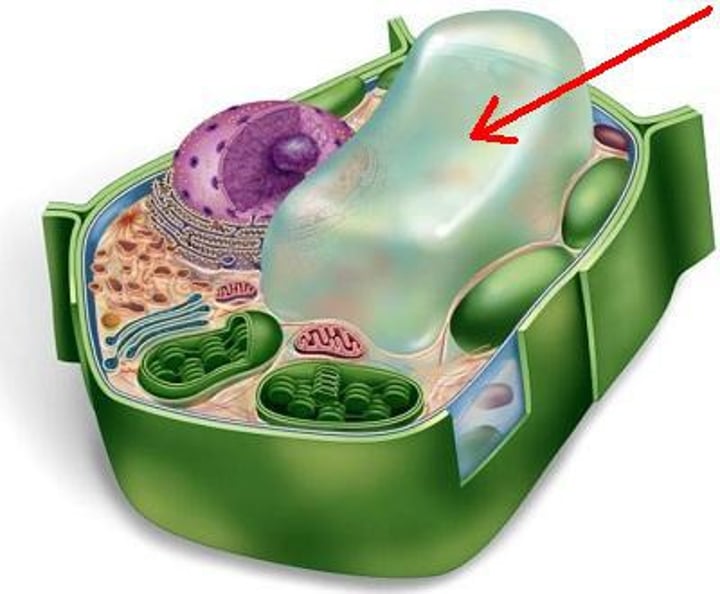
vacuole
stores food, water, and waste. Gives plant cells shape.
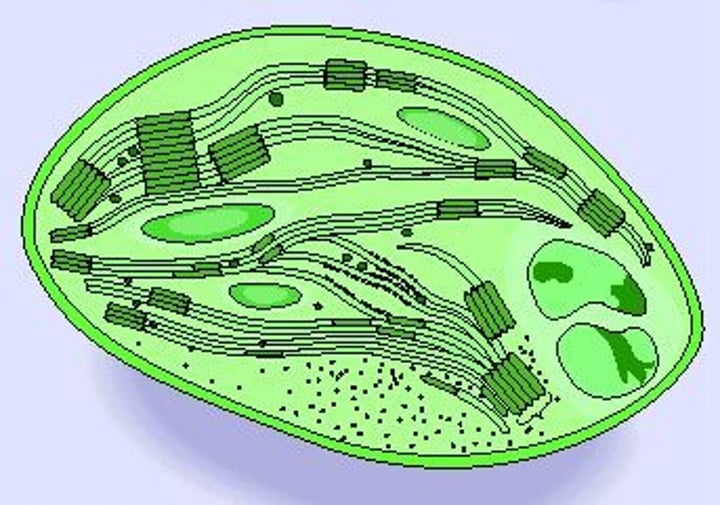
chloroplast
uses light energy to create sugar and oxygen
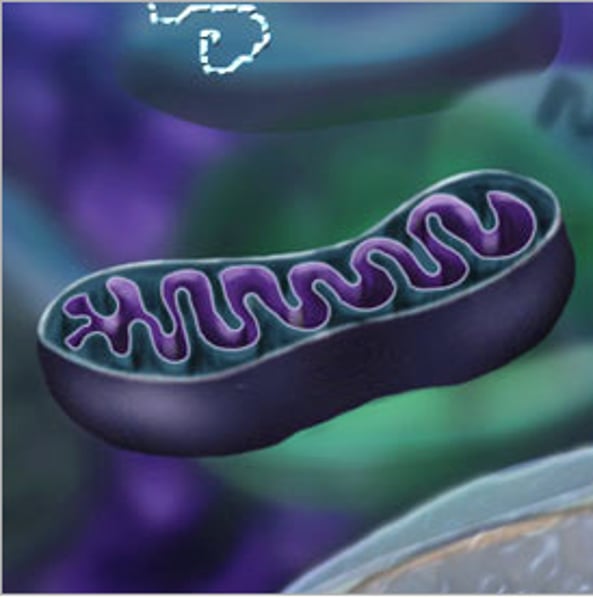
mitochondria
uses sugar to create energy
cytoplasm
watery substance that keeps all organelles in place
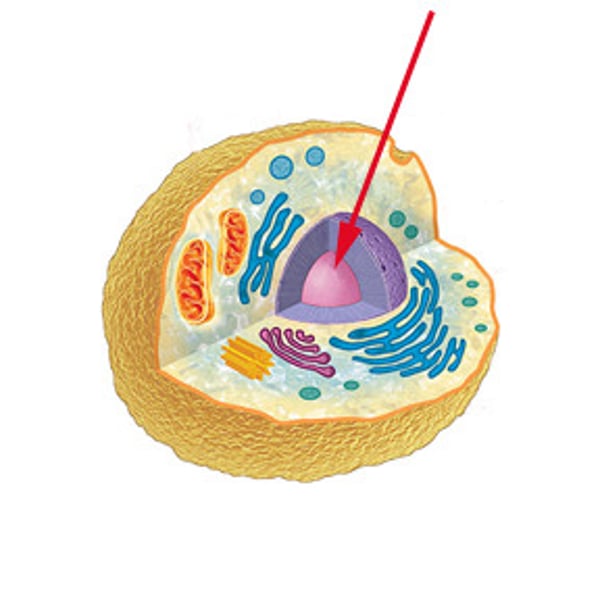
nucleus
controls all cell activities and contains the DNA
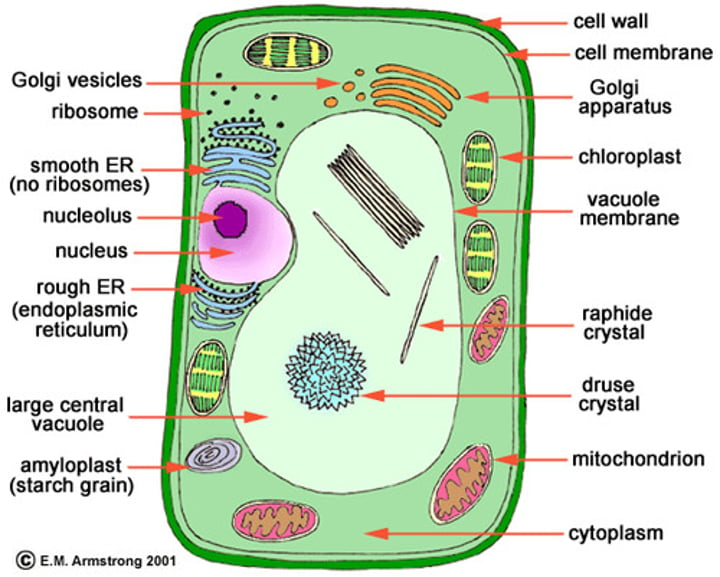
plant cell
boxy-shaped cell with chloroplasts and cell wall
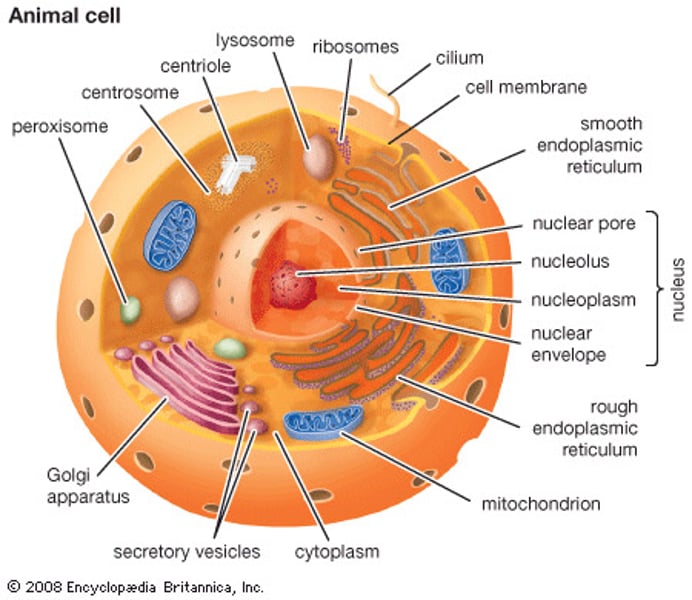
animal cell
cell with no set shape, no cell wall, and no chloroplasts
cell
basic unit of structure and function in organisms
chlorophyll
green pigment that helps the chloroplast during photosynthesis

Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
Concentration
A measurement of how much solute exists within a certain volume of solvent
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
Solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
Osmosis
diffusion of water
flaccid
limp, not firm; lacking vigor or effectiveness
turgid
swollen
Organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
enzyme
A type of protein that speeds up a chemical reaction in a living thing
optimum
best; most favorable; ideal
Denature
A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature or pH (among other things).
Isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
catalyst
substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
active site
The part of an enzyme where the chemical reaction occurs.
Substrate
A specific reactant acted upon by an enzyme
Reactant
A chemical substance that is present at the start of a chemical reaction
collision
the moment when two objects hit each other
enzyme specificity
enzyme only bonds to one substrate due to shape of active site