Chapter 5 pt. 1: Cell respiration & metabolism
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What is metabolism?
All of the chemical reactions in the body needed to maintain homeostasis
what are the 2 categories metabolism can get divided into?
- anabolism
- catabolism
What is anabolism?
The process that requires the input of energy to synthesize large molecules.
- EX: testosterone, estrogen
What is catabolism?
The process that releases energy by breaking down large molecules into small molecules.
- EX: cortisol
What is the primary purpose of cellular energy?
To release energy from food and generate ATP for cellular work.
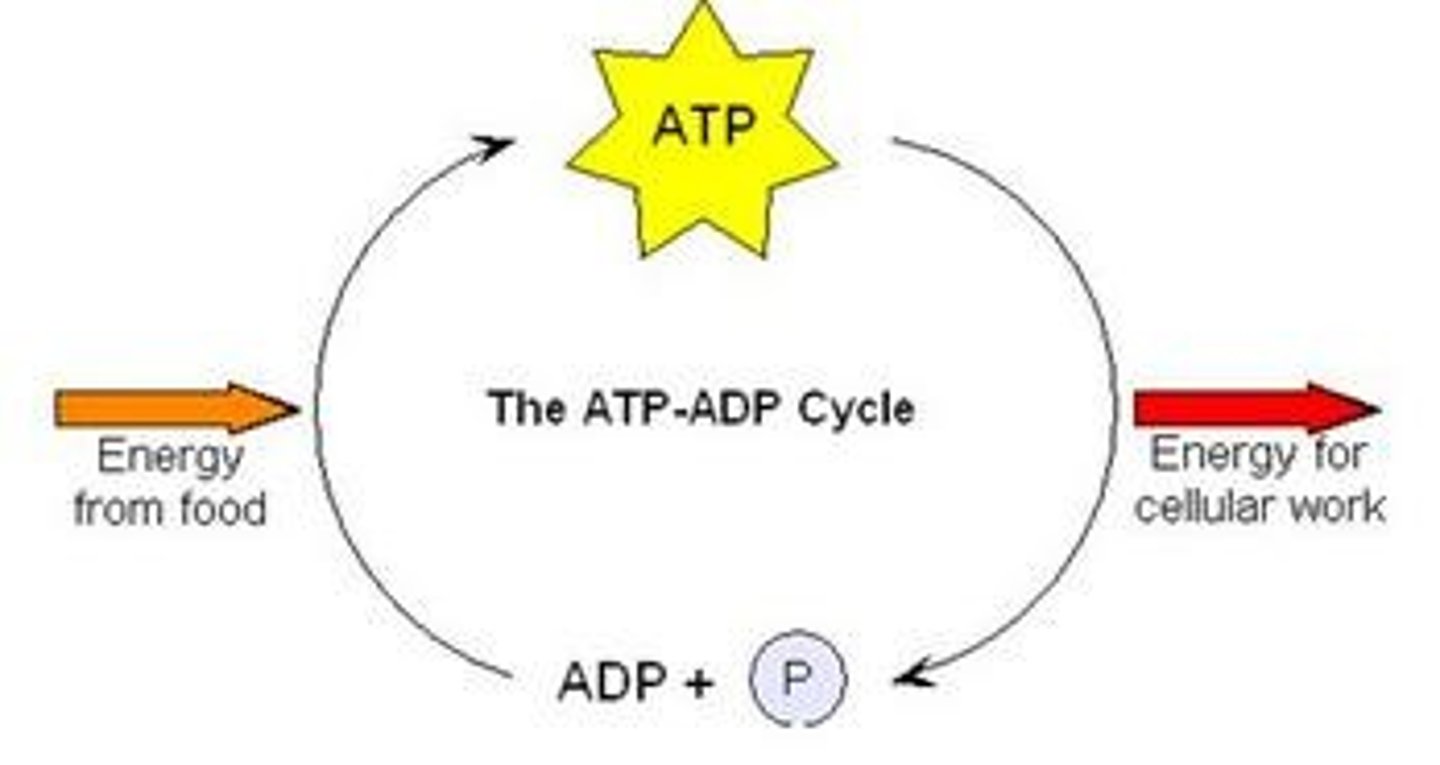
What are the three types of cellular work that ATP is used for?
- Chemical work
- transport work
- mechanical work
What are the two methods of breaking down food?
- Aerobic respiration (having O2 present)
- anaerobic respiration (without O2)
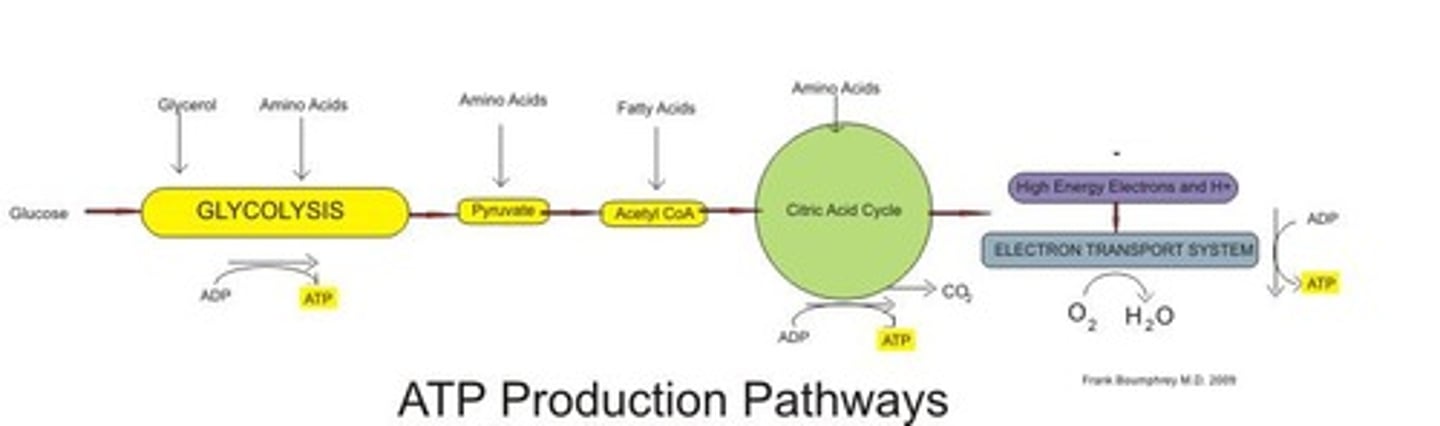
What are the three steps of aerobic respiration?
- Glycolysis (get pyruvate & ATP)
- the citric acid (Krebs) cycle (we get NADH & FADH)
- ETC
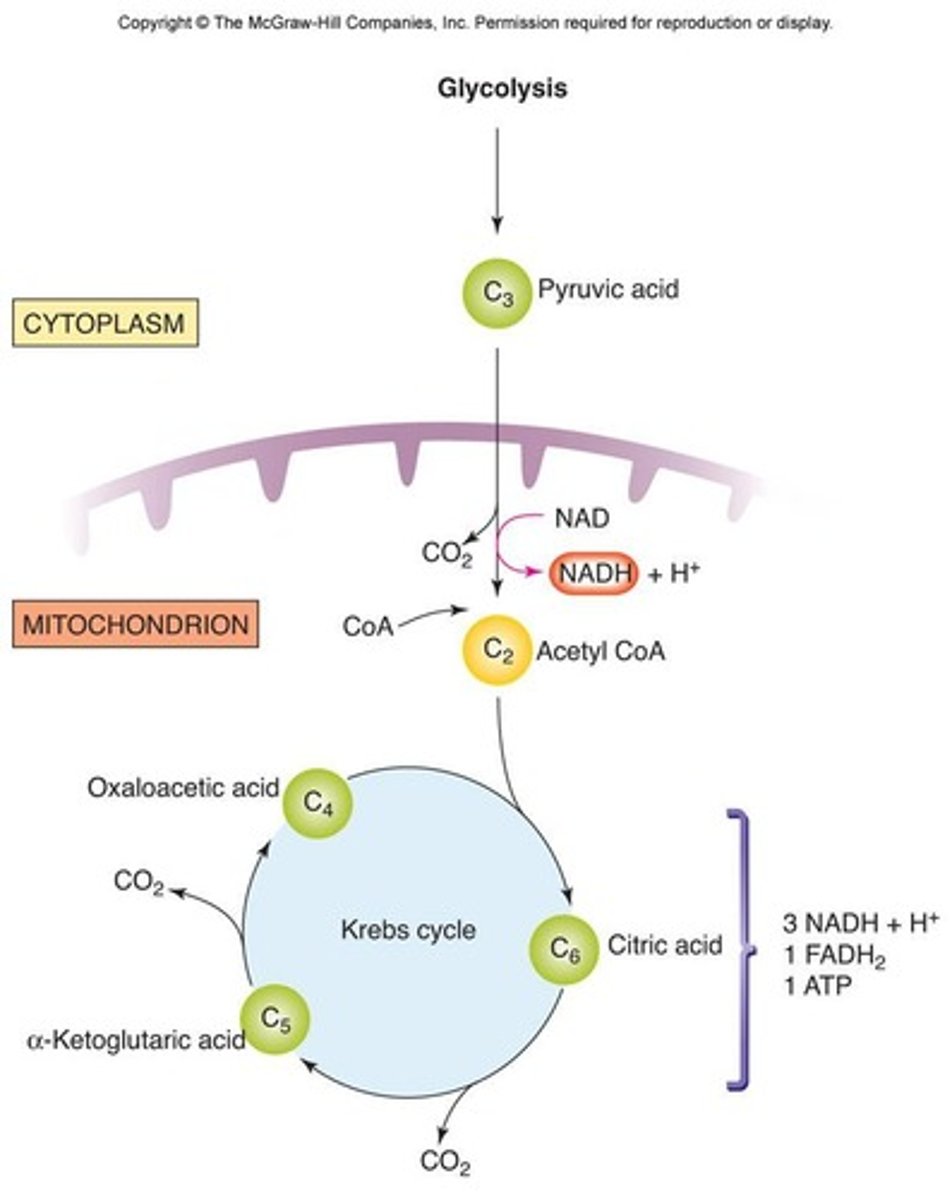
Where does glycolysis occur?
In the cytoplasm
What is produced during glycolysis?
2 ATP
2 pyruvate
2 NADH.
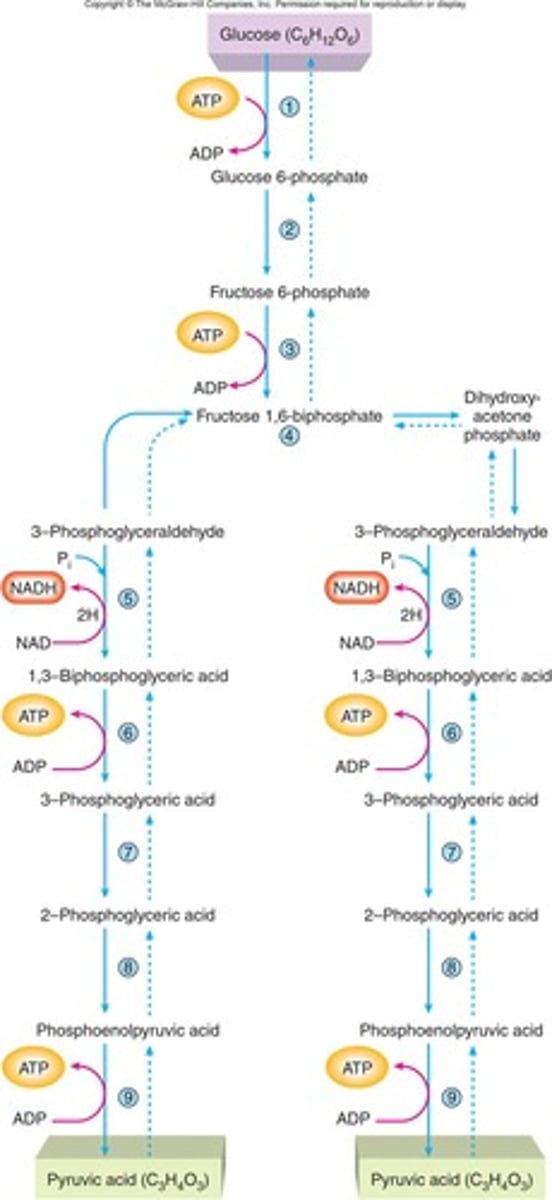
*PROCESS of glycolysis*
- we start out with a substrate of glucose
- then we take that glucose molecule and break it down
What happens to NAD when it picks up a hydrogen?
It gains a hydrogen and becomes reduced to NADH.
What is the fate of pyruvate in aerobic metabolism?
It enters the mitochondrial matrix and combines with coenzyme A to form acetyl CoA.
what is the fate of pyruvate?
- depends on O2
- aerobic metabolism
- used regularly by skeletal muscle and RBC
What happens if theres not enough O2 for the pyruvate to move to the kreb cycle?
the pyruvic acid will get converted into lactic acid
What is the problem if lactic acid builds up too much in high amount in the body?
the pH becomes acidic, which can have a profound effect on the functions of proteins & enzymes
What are the products of one turn of the Krebs Cycle?
- 3 NADH
- 1 FADH2
- 1 ATP
- CO2
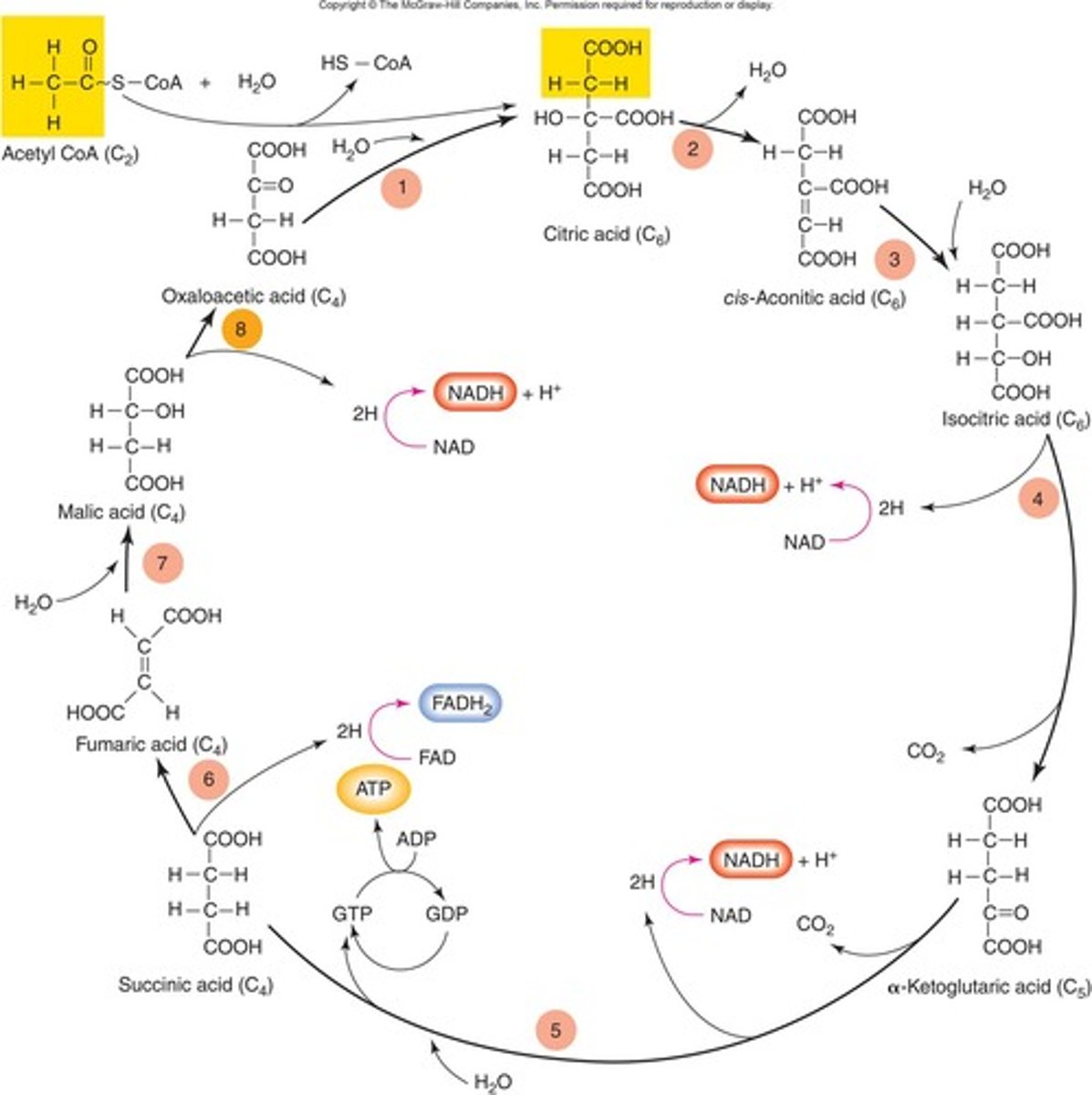
for each glucose the kreb cycle turns twice, what would the numbers be of the products (NADH, FADH, ATP, CO2)?
- 6 NADH
- 2 FADH2
- 2 ATP
- 4 CO2
How many times does the Krebs Cycle turn for each glucose molecule?
Twice.
What is the role of oxygen in aerobic metabolism?
Oxygen acts as the terminal electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
what does released incrementally refer to in aerobic metabolism?
the higher you increase your intensity, the more something increases
what does aerobic metabolism begin with?
glycolysis
what are the two additional metabolic pathways in aerobic metabolism?
- the krebs cycle
- oxidative phosphorylation
If you cant get O2 in the body, what cant you do?
you cant power/drive aerobic respiration.
- this leads to not being able to power glycolysis, kreb cycle or ETC
what is oxidative phosphorylation in terms of aerobic metabolism?
- something loses an e- to allow us to phosprhylate something
- we want to add a phosphate to the ADP to form ATP
*PROCESS of Aerobic metabolism beginning with pyruvate*
- Pyruvate leaves the cytoplasm and enters mitochondrial matrix (inner portion)
- then, in the mitochondrial matrix, the pyruvate gets converted from pyruvic acid to acetyl coA
- then acetyl coA starts the kreb cycle
how many NADH would we get in traditional NADH production?
2, because 2 pyruvic acid gets produced also
what are the 2 components of the ETC & oxidative phosphorylation?
1. ETC (found in inner-membrane space)
2. ATP synthase
If we are trying to pump out things in the inter-membrane space but cant move through the pumps/ ATP synthase channel, what energy is this?
potential energy
what are we doing at the ETC with our e- carriers?
trying to create a H+ concentration gradient located in the inter-membrane space
which protein will diffuse the floating H+ ions found within the inter-membrane space?
the ATP synthase
as the H+ moves through the ATP synthase protein, what does it phosphorylate?
ADP --> ATP
what is our final e- acceptor?
O2 to then form H2O
FINAL PROCESS**
start out with glycolysis which occurs in cytoplasm, end up with a NET total of 2 NADH & 2 ATP
↓
- then NADH goes off into the ETC
↓
- In aerobic setting, the pyruvate goes to mitochondrial matrix
↓
- we then send the acetyl coA to the citric acid cycle
↓
- then at the citric acid cycle, we produce 2 ATP & 6 NADH (per 1 glucose) and go to the ETC
↓
- need to shuttle the H+ to the inter-membrane space in the mitochondrial matrix to create a H+ [ ] gradient
↓
- then the H+ diffuses through ATP synthase to phosphorylate ADP & ATP
↓
- then to maintain the H+ [ ], the final e- acceptor is the O2 molecule to help form water
what is glycogenesis?
the creation of glycogen
where does glycogen get stores in body?
liver & skeletal muscle
what is glycogenolysis?
- breakdown of glycogen into glucose
- occurs in the liver
why did we produce lactic acid?
- we converted pyruvate to lactic acid due to the anaerobic environment
- lactic acid gets produced in muscle because theres not enough O2
What is the Cori cycle?
The process where lactic acid produced in muscles is converted to pyruvic acid and NADH in the liver.
What is gluconeogenesis?
The formation of new glucose from non-carbohydrate sources.
what are some substrates of gluconeogenesis?
- amino acids
- lipids
- glycerol
what is white adipose tissue (white fat)?
fat stored in adipose tissue as triglyceride
What is lipolysis?
The breakdown of triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol using enzyme lipase
we can take that glycerol backbone & we can put it through gluconeogenesis to become?
glucose molecule
What is beta oxidation?
is where we take the triglyceride from that lipid tissue and we convert it to acetyl coA
What is the difference between white fat and brown fat?
- White fat stores energy as triglycerides
- Brown fat is involved in thermogenesis (maintain body temp)
where does Brown fat tend to get stored?
in adults it tends to get stored near their necks
What are ketone bodies?
Products formed when the rate of lipolysis exceeds utilization via beta oxidation.
where do people on low-carb diets get their energy from?
lipids. when we break down lipids, you take triglycerides to make ATP through beta-oxidation
How can amino acids be used for energy?
Through transamination and oxidative deamination.
what does transamination refer to in AA energy?
meaning that it can give that amino group to a keto acid
What is the significance of essential vs non-essential amino acids?
- Essential amino acids must be obtained through diet
- non-essential amino acids can be synthesized by the body.
What is the significance of the lactic acid pathway?
It allows for ATP production in the absence of oxygen, particularly during intense exercise.
What is the net gain of ATP from glycolysis?
2 ATP.
What is the primary function of coenzymes NADH and FADH2?
To carry electrons to the electron transport chain for ATP production.