acct 2301 unit 2 review
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
trade discount
the only one INDIRECTLY recorded by making revenue equal to discounted price
d accts receivable; c service revenue
provide services on account w/ trade discount

sales returns
contra revenue acct to sales revenue
d sales returns; c accts recceivable
customer returns product on acct

d sales allowance; c accts receivable
provide a sales allowance for previous credit sale

sales discount
reduction in amount to be received from credit customer if they pay within a specific time period (NOT a reduction in selling price of a good/service)
2/10: 2% discount if pay within 10 days
n/30: if no discount, full payment due in 30 days
d cash, d sales discounts; c accts receivable
collect cash on account with a sales discount
allowance method
GAAP approved method to estimate uncollectible accounts/bad debts
report accts receivable for net amt expected to be collected
estimate current accts receivable that will be uncollectible in the future (contra asset)
estimate future uncollectible accts and report those estimates in the current year
allowance for uncollectible/doubtful accts (contra asset acct, increase by credit)
bad debt expense: cost of est future bad debts reported as an expense in current year income statement
end of yr 1 find bad debt expense thru % accts receivables method, during subsequent year, write off actual bad debts as uncollectible as they occur (no net effect),
Credit Allowance Balance before adjustment- previous estimate was too high, you’ll have a smaller adjustment.
Debit Allowance Balance before adjustment- previous estimate was too low, you’ll have a larger adjustment.
total revenues
educed by sales returns, sales allowances, and sales discounts during the year AND by those expected to occur in the future but relate to the current yr.
d bad debt expense; c allowance
end of yr 1 establish allowance using %age receivables and allowance method

d bad debt expense, c allowance for uncollectible accts
in subsequent est future uncollectible accts using the current balance to determine the adjusting entry. Allowance method, %age receivables.

d accts receivable, c allowance; d cash, c accts receivable
allowance method: collecting cash on an acct previously written off (not effet on net income/total assets)
reverse prior write off
collect cash
percentage of credit sales
income statementmethod
ignore existing balance in allowance and add new estimate to adjusting entry
direct write off method
not GAAP
tax reporting
write off bad debts only when they actually become uncollectible
assets are overstated and operating expenses understated
d bad debt expense; c accts receivable
direct write off method (not GAAP)

d notes receivable; c service revenue
accept notes receivable for services provided
Pay attention to dates. E.g., Jan 1- Dec 31 or Jan 1- Dec 1.

d notes receivable; c accts receivable
replace accts receivable with notes receivable

face value x annual interest rate x frac of yr
interest calculation

d cash; c notes receivable c interest revenue
collect notes receivable and interest revenue

d interest receivable; c interest revenue
accrued interest when note is issued in 1 yr and maturity date is in following yr
need to record the interest revenue in the yr it was incurred
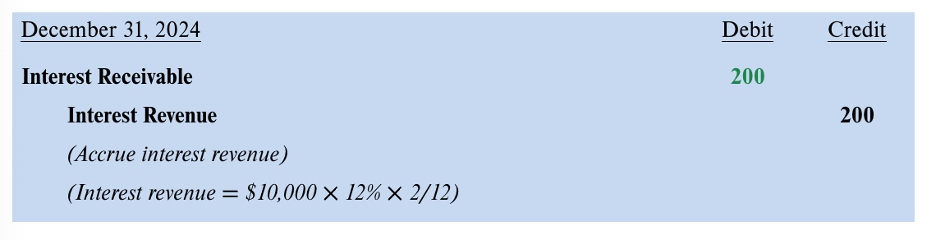
d cash; c notes receivable c interest receivable c interest revenue
on maturity date, collect notes receivable and interest receivable from previous and current yr)

net credit sales/avg accts receivable
receivables turnover ratio
how quickly company can collect cash from accts receivable
365 days/ receivables turnover ratio
avg collection period
approximate days avg accts receivable balance is outstanding
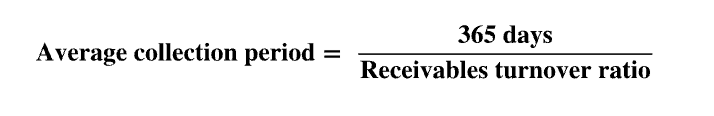
COGS= COGAS-Ending Inventory
cogs eq
gross profit= net revenues-COGS
gross profit eq
operating income= gross profit-operating expenses
operating income eq
income before income taxes= operating income + nonoperating revenues- nonoperating expenses
income before income taxes eq
nonoperating revenues/expenses
gain/loss on sale of investments
investment income
specific identification
§ ID each inventory unit with actual cost
§ Unique, expensive products with low sales volume
FIFO
§ assume beginning inventory sells first, then inventory from first purchase, etc.
§ more closely resembles actual physical flow of inventory
§ when costs rising:
· higher ending inventory
· higher gross profit
o GP= net sales-COGS (and COGS is lower)
§ “balance sheet approach”- better approximates current cost of (ending) inventory
LIFO
§ Assume last units purchased are the first ones sold
§ Calculate once at end of year
§ When costs falling:
· Higher ending inventory
· Higher gross profit
o GP= net sales- COGS (and COGS is lower)
§ “income statement approach”- COGS better approximates current cost of inventory. (however, ending inventory not realistic).
§ Tax savings
· Lower taxable income? Owe less (lower reported inventory and net income, when costs are rising)
· LIFO conformity rule- if use LIFO for tax reporting, then must also use for financial reporting
o Companies reporting LIFO must also report LIFO reserve (difference btw LIFO amount and FIFO amount)
weighted avg cost
assume COGS and ending inventory is random mixture of all goods available for sale
COGAS/# available units for sale
use numbers from beginning of yr
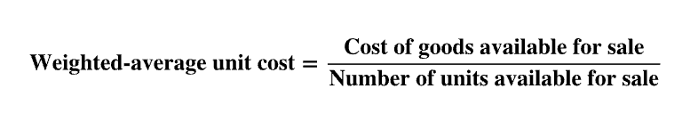
COGAS/# units available for sale
weighted avg unit cost
use numbers from beginning of yr
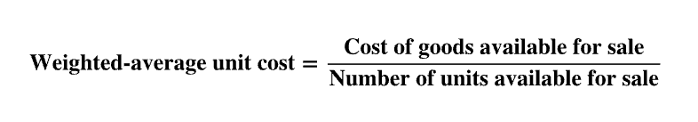
perpetual inventory system
record inventory purchases and sales on continual basis
d inventory; c accts payable
purchase inventory on acct

d accts receivable c sales revenue d COGS c inventory
sell inventory on acct

FOB shipping point
buyer pays for shipping
FOB destination
seller pays for shipping
d inventory c cash
freight in: charges on incoming shipments from suppliers
add to ? balance
when inventory is eventually sold, those freight charges become a part of COGS

freight out
· Cost of freight shipments to customers
· Report in income statement as COGS, operating expense, selling expense..
d accts payable; c inventory c cash
pay on acct with a purchase discount
Ex., when buyer pays off 2/10, n/30 (2nd journal entry)

d accts payable; c inventory
purchase return on inventory previously purchased on acct

periodic inventory
o Calculate inventory balance once per period (at the end) based on physical count on hand
o Record purchases, freight in, purchase returns, and purchase discounts to temporary accts instead of Inventory directly.
o Period end adjusting entry
§ Adjust inventory balance
§ Record COGS
§ Zero out temporary purchases accounts (Purchases, Freight In, Purchase Discounts, Purchase Returns)
net realizable value
report INVENTORY at lower of cost and net realizable value
Net amount a company expects to realize in cash from inventory sale (est selling price of inventory less costs of completion, disposal, and transportation)
d COGS c Inventory
adjust inventory down to net realizable value
decrease total assets, net income, and retained earnings

COGS/avg inventory
inventory turnover ratio
number of times firm sells its avg inventory balance during reporting period

365/inventory turnover ratio
avg days in inventory
# days avg inventory is held
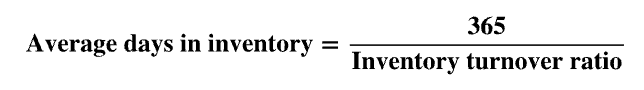
gross profit/net sales
gross profit ratio
amount by which sale of inventory exceeds its cost per dollar of sales
overstate ending inventory
understate COGS
overstate gross profit
overstate net income
overstate retained earnings
understate ending inventory
overstate COGS
understate gross profit
understate net income
understate retained earnings
long term assets
record ? at its purchase price + all expenditures necessary to get asset ready for use
capitalize
record expenditure as an asset (expensed over time)
E.g., Land (purchase price + closing costs, back taxes, clearing, filling, leveling, demolition; if receive cash from selling salvaged building materials, reduce land cost by that amount
DONT INCLUDE LAND IMPROVEMENTS
expense
record full expenditure as expense immediately
buildings
purchase price + realtor commissions + remodeling costs
equipment
purchase price + sales tax+ shipping + deliver insurance, assembly, installation, testing, legal fees to est title
don’t include recurring costs like annual property insurance or property tax since we expense them as we incur them
basket purchases
o Purchase more than one asset at same time for one purchase price
o Allocate total purchase price based on est fair values of each of the individual assets
o Allocation percentage * amount basket purchase= recorded amount
§ Allocation percentage: est fair value of X / est total fair value
allocation percentage*amount basket purchase= recorded amount
for basket purchases how to find the recorded amount
allocation percentage= est fair value of X/ est total fair value
allocation percentage in basket purchase
expensed
internal R&D costs are ? as incurred
patent
Purchase price + legal and filing fees
§ 20 years
§ Externally purchased patent would higher valued intangible asset, while internally developed would be lower (only legal and filing fees)
copyright
life of creator + 70 yrs
trademark
e.g., Apple< name
§ Word, slogan, or symbol distinctly ID’ing a company, product, or service
§ 10 years (can indefinitely renew)
§ + attorney fees, registration fees, design costs, successful legal defense (legal, registration, design fees are recorded, NOT est value of trademark)
§ Advertising costs are expensed
goodwill
§ Only record when one company acquires another company
§ Amount purchase price exceeds fair value of acquired company identifiable net assets
d assets d goodwill; c liabilities c cash
JE for goodwill

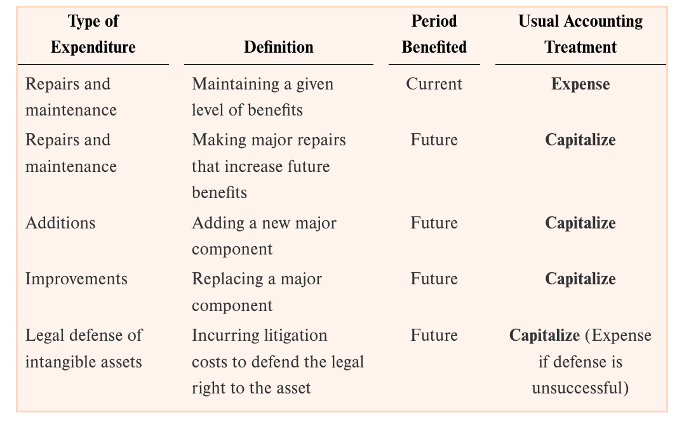
capitalize
? an expenditure if it increases future benefits
addition
improvement
legal defense of intangible (successful)
repairs and maintenance if MAJOR and increasing future benefits
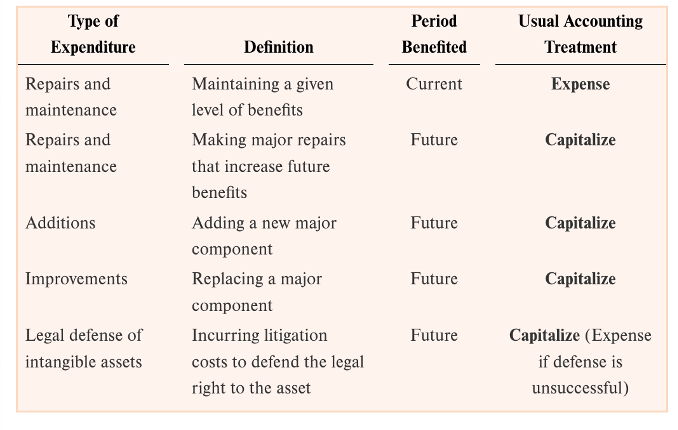
expense
? an expenditure if it only benefits current period
repairs and maintenance
legal defense of intangible (unsuccessful)
not material
depreciation
o Allocation of an asset’s cost to an expense over time
o Book/carrying value= cost of asset- current balance in Accumulated Dep
Straight line method
delcining balance
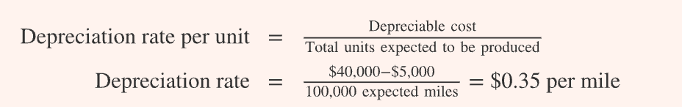
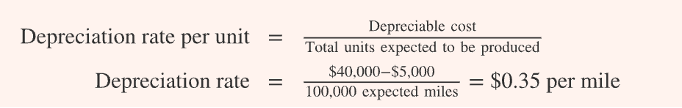
activity based
book value= cost of asset- current balance in accum dep
book value calc
asset cost- RV/service life
straight line dep
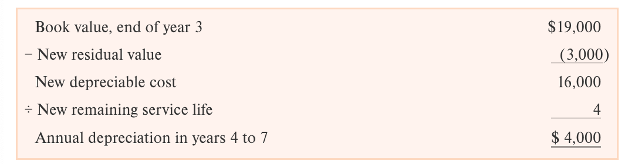
change in dep estimate
subtract new RV from book value at end of yr
divide value by new remaining service life to get annual dep from no until expected end
don’t go back and change previous dep calculations
declining balance method
more dep expense in earlier years
tax
multiply rate by book value (cost- acumm dep) NOT by depreciable cost (cost-RV)
2/est service life
RV doesn’t come into play until last year
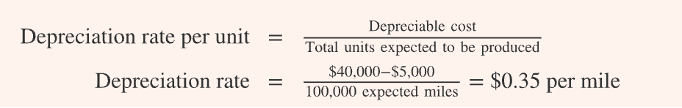
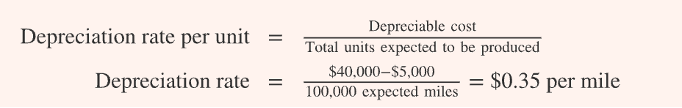
activity based method of depreciation
depreciable cost/ total units expected to be produced
dep cost: cost- RV
zero
amortization of intangibles. expected RV of most intangibles is ?
goodwill and some trademarks
don’t amortize intangibles with indefinite useful life
d cash, d accum dep; c equipment, c gain
gain on an asset (sell for more than book value)
note: credit equipment at purchase price
d cash, d accum dep, d loss; c equipment
loss: sell asset for less than book value

d accum dep, d loss; c equipment
retirement of long term asset

d new asset, d accum dep; c old asset, c cash, c gain
exchange of longterm assets for a gain

impairment
expected future cash flows/benefits generated for a long term asset fall below book value (og cost-accum dep)
Q1: are future cash flows less than book value
omit step 1 for goodwill and certain trademarks w/ indefinite useful lives
Q2 loss= book value-fair value
permanent, can’t write them back up
o future cash flows/benefits generated for a long term asset fall below book value (og cost-accum dep)
d loss; c trademarks
record impairment of trademarko future cash flows/benefits generated for a long term asset fall below book value (og cost-accum dep)
net income/avg total assets
return on assets
compare profitability
amt of net income generated for each dollar invested in assets

net income/net sales
profit margin
earnings per dollar of sales
higher thru product differentiation and premium pricing
o future cash flows/benefits generated for a long term asset fall below book value (og cost-accum dep)

net sales/avg total assets
asset turnover
sales per dollar of assets invested
higher thru lower sales prices (increase sales volume)
