BIOL1020
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
3 domains of life
Bacteria, archaea, eukarya
Endosymbiosis
The process through which prokaryotic cells adapt to become eukaryotic cells
Addition of sugar onto protein
Glycosylation
Addition of phosphate onto protein
Phosphorylation
Nucleoid
Region in prokaryotes in the cytoplasm where DNA is
Golgi apparatus
Receives newly made proteins
Transport proteins
Fimbriae
Projections from cell walls in bacteria
Involved in attachment to and movement on surfaces
Glycocalyx
Polysaccharide capsule that surrounds cell membrane
Protects bacteria from dehydration, allows adhesion to surfaces
Helps evade immune system
Function of cell membrane
Controls flow of molecules in and out of cell
Encloses and protects cell contents
Links to structures that provide cell shape/movement
Oligomers
Chains of 20 monomer units
Functions of carbohydrates
Store energy
Structural
Food source
Three types of cytoskeletons
Microtubules
Microfilaments
Intermediate filaments
Functions of proteins (8)
Structural
Enzymes
Defensive proteins
Transport
Hormonal
Receptor
Contractile and motor proteins
Metabolism
The sum total of all chemical reactions in an organism that sustain life
first and second law of thermodynamics
Energy in the universe is constant, not created nor destroyed
Every energy transfer or transformation increases entropy (disorder) of the universe
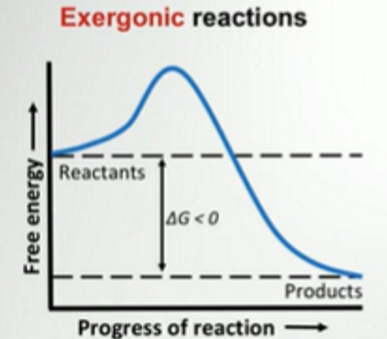
Exergonic
Delta G
Graph
DG is negative
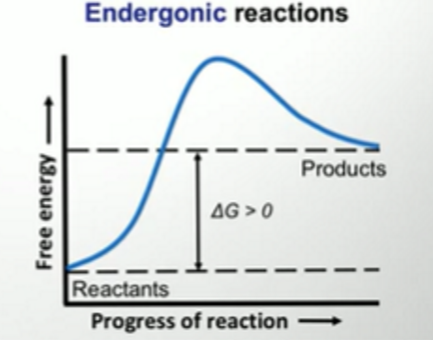
Endergonic:
DG
Graph
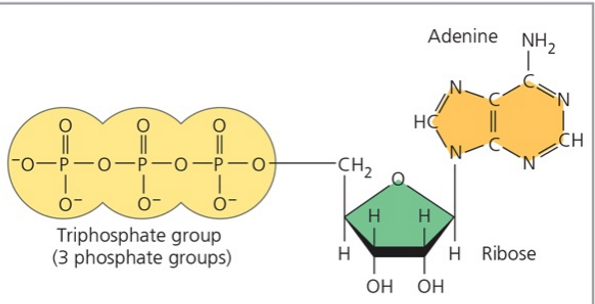
Components of ATP
Stages of respiration
glycolysis
pyruvate oxidation
citric acid cycle
oxidative phosphorylation
electron transport chain
chemiosmosis
Theoretical and actual ATP yield
Theoretical = 32
Actual = 30 to 32
products per glucose molecule from glycolysis
2 ATP
2 NADH
2 H2O
2 pyruvate
products per pyruvate molecule from pyruvate oxidation
1 NADH
NO ATP
1 CO2
1 acetyl CoA
products per acetyl-CoA molecule from citric acid cycle
2 CO2
3 NADH
1 FADH2
1 GTP (an equivalent of ATP)
Cell membrane links to
Cytoskeleton, extracellular matrix, cell wall, and cell-cell junctions
3 types of proteins in cytoskeleton
Microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments
Microtubules shape, monomer, diameter, purpose
25nm diameter
helical hollow structure
tubulin monomer
Dynamic (can be rapidly formed and broken down)
Structural - help cell resist compression
Used in movement of whole cell, organelles within cell, and chromosomes in cell division
Microfilaments cc
7nm diameter
actin monomers
dynamic
supports shape and bears tension
endocytosis
spirally shape
Intermediate filaments shape, monomer, diameter, purpose
8-12nm
Coiled together
can be made of different monomers e.g. keratin
Structural framework of cell
Only in animal cells
Interphase stages
G1 (Gap 1)
S
G2
G1
Normal metabolic activity and cell growth
Synthesise proteins
S
DNA replicates
G2
Centrosomes appear (starting point for mitotic spindle)
Prophase
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes
Prometaphase
Nuclear membrane breaks down
Mitotic spindle attach to kinetochores
Metaphase
Mitotic spindle moves chromosomes to middle of cell
Anaphase
Sister chromatids separate
Cohesion protein at centromere degrades as chromosomes separate (mitotic spindle degrades centromere)
Telophase
Nuclear membrane forms
Checkpoints
G1 - does the cell have energy and resources to reproduce?
G2 - is DNA from S phase ok?
M - Are chromosomes attached to spindle?
GC as X H-bonds and AT has Y H-bonds
GC has 3
AT has 2
Purines have X rings, pyrimidines have Y rings
purines = 2
pyrimidines = 1
DNA polymerases
I - removes RNA primers
II - repairs DNA
III - adds nucleotides to growing strand
RNA polymerases
I - transcribes for rRNA
II - produces mRNA transcripts
III - transcribes for tRNA
sites in a ribosome
A
tRNA tested for codon match
P
Added to polypeptide chain
E
tRNA is ejected into cytoplasm
electron transport chain in cellular respiration vs photosynthesis
In contrast to mitochondrial electron transport chain
Water donates electrons to the chain and is oxidised to form oxygen
NADP+ is terminal electron acceptor
Reduced to NADPH
Light energy drives electron transport
Light reaction
Occurs in thylakoid
Light absorbed by chlorophyl
Electrons are excited and move through electron transport chain
Water donates electrons and is oxidised into oxygen
Produces ATP and NADPH
Dark reaction
Occurs in stroma
ATP and electrons from NADPH are used to convert carbon dioxide into glucose
Direction of polypeptide chain synthesis
N-terminus → C-terminus
7 stages of viral life cycle
Attachment
Penetration
Uncoating
Transcription/translation
Genome replication
Assembly
Release
Retrovirus
Positive sense single stranded RNA that integrate themselves into DNA using reverse transcriptase
When glucose is not present, what happens to lac operon
Glucose = low means cyclic amp = high
Cyclic AMP binds to CAP and activates it
CAP binds to activator region on DNA
Increases transcription of lac operon (breaks down lactose)
Gene regulation in eukaryotes
Chromatin remodelling
Transcription
RNA processing
mRNA stability
Translation
Post-translational levels
Bacteria DNA modification
Conjugation
Sharing F plasmid via sex pilus
Transformation
Uptake of naked DNA into the bacterial cell
Transduction
Virus (bacteriophage) transfers DNA from one bacteria to another
Missense vs nonsense mutation
Missense = change in amino acid
Nonsense = early stop codon
When does crossing over occur
Prophase I (pachytene)
When does independent assortment occur
Anaphase I
Plant lifecycle from zygote
Zygote
Sporophyte (2n)
meiosis
Spore
Gametophyte
fusion of gametes
Zygote
Egg making gametophyte
Archegonium
Sperm making gametophyte
antheridium
Temperatures for each stage of PCR
Denaturation - 96
Annealing - 55
Extension - 72
Human genome components largest to smallest
Repetitive DNA (transposable)
Repetitive DNA (nontransposable)
Introns
Unique noncoding
Regulatory
Protein coding
forward vs reverse primer
forward
codes for strand written 3’ to 5’ left to right (antisense)
reverse
for strand written 5’ to 3’ (sense)
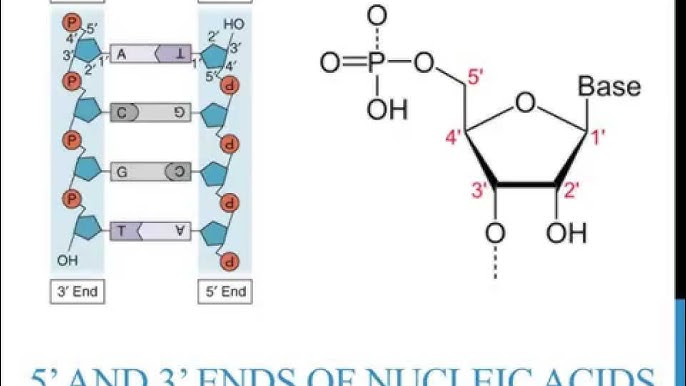
is the phosphate on the 5’ or 3’ carbon
Alpha glucose and beta glucose diagram
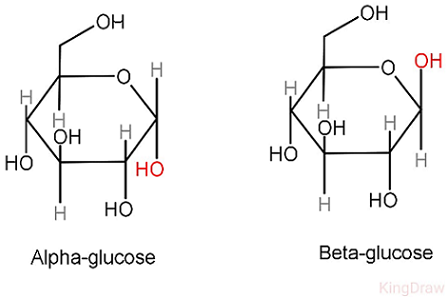
How many electrons does FADH2 transport
2
Difference between DNA pol and RNA pol
DNA pol needs primer, RNA does not
DNA pol uses DNA nucleotides
Which carbon connects to the nitrogenous base, phosphate, and hydroxyl
N base = 1
Phosphate = 5
Hydroxyl = 3
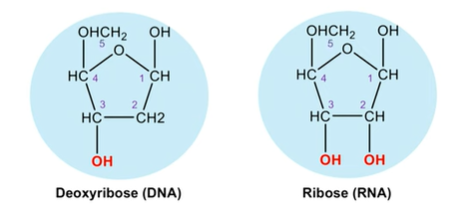
deoxyribose sugar vs ribose sugar
Energy released for cellular respiration
-686kcal/mol
Cyclin levels
Begins production in S, increases through G2 and decreases after mitosis
Binds to CDK to form MPF, which phosphorylates mitosis proteins to bypass G2 checkpoint
oncogenes
genes that when activated, cause cancer
normal form - protooncogene
protooncogene normally promotes cell growth
Mutation in promoter region turns it into an oncogene (protooncogene is overexpressed)
Mendel’s first law and its exceptions
Law of segregation - alleles are independently inherited
Aneuploidy and polyploidy
Mendel’s second law of inheritance and its exceptions
Law of independent assortment
Genes assort independently
Parthenogenesis, haplodiploidy, sex-linked traits, mitochondrial DNA
cloning - recombinant plasmid is blue/white
white (lacZ gene is not intact)
Transposons vs retrotransposons
Transposons
Directly transcribed and inserted into genome
Retrotranspons
Translated into RNA
Reverse transcriptase synthesises DNA complimentary to RNA
Reverse transcriptase synthesises second DNA strand complementary to first DNA strand
Two strands are inserted into the genome