IB Business Management SL - 4.3. Product
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
Product life cycle
Shows different strategies in the life of a product and the sales that can be expected at each stage
2
New cards
Product life cycle stages
Development, introduction, growth, maturity and saturation, decline
3
New cards
Expansion strategies
Used by businesses to extend the life cycle of their products
4
New cards
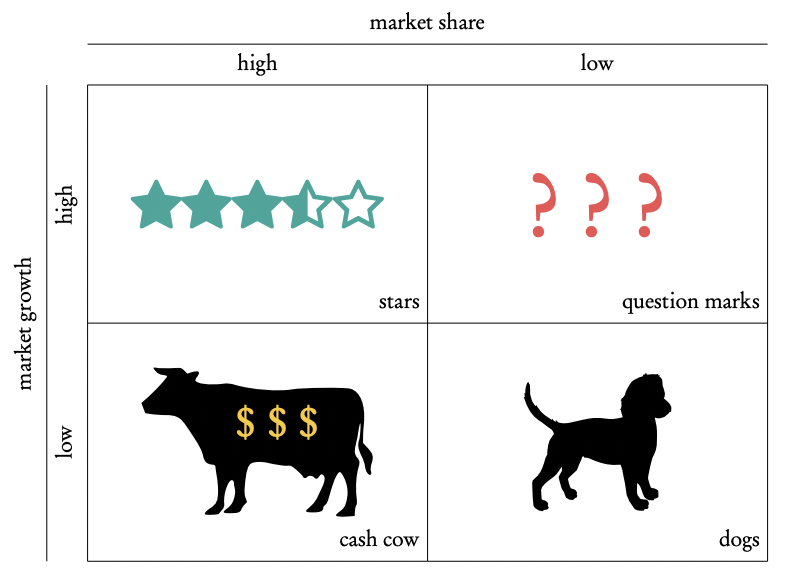
Boston matrix
Used for businesses to analyze their product portfolio better
5
New cards
Cash cows
A product with high market share in a slow growing market. In the maturing stage.
6
New cards
Question marks
Products that have a low market share in a fast growing market. A market follower, so the business has to decide whether the product is worth investing in. In the introduction stage.
7
New cards
Dogs
Products with a low market share in a slow growing market. In the decline stage.
8
New cards
Stars
Products with a high market share in a fast growing market. Leader products that produce the most amount of money.
9
New cards
Brand
A feature that allows consumers to identify a business.
10
New cards
Unique Selling Point
A feature of a product that makes it different from other products in the market.
11
New cards
Consumable product
Bought by individual people for their personal use
12
New cards
Production product
Raw material, components, terrains, machinery, etc.
13
New cards
Fast-moving consumer goods
Products that can't be reused and they are sold quickly at a low cost.
14
New cards
Nondurable consumer goods
Products that have a short life, they decompose quickly.
15
New cards
Durable consumer goods
Manufactured products that can be reused and they are expected to have a longer life.
16
New cards
Prestigious products
Exclusive and expensive products
17
New cards
Service products
They don't have physical evidence, but they satisfy the clients' needs in other ways.
18
New cards
Product mix
The total number of product lines and individual products or services offered by a company
19
New cards
Product line
A group of related products all marketed under a single brand name that is sold by the same company
20
New cards
Product range
Variations of a single product that are made in order to create similar yet distinctly different products