psc41 units 1-4
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
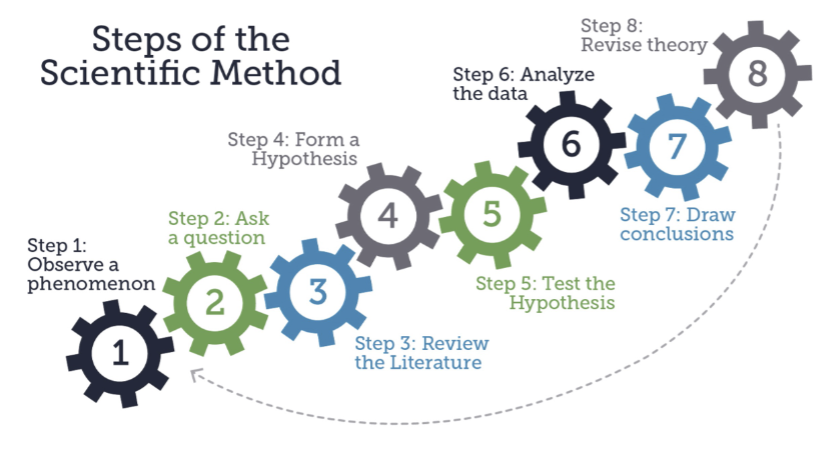
the scientific method
observing phenomenon > asking a question > literature review > forming hypothesis > testing hypothesis > analyzing data > drawing conclusions > revising theory
deterministic
the scientific character that claims that phenomena are causally determined by preceding events or natural laws that can be discovered and explained
empircal
the scientific characteristic that claims that science is based on objective, reproducible evidence and not on pure reason, emotion, or subjective experiences
testable and falsifiable
the scientific characteristic that claims that a theory or hypothesis is not scientific unless it can be tested and shown to be false
provisional
the scientific characteristic that claims that a scientific theoyr is always open for review based on new evidence
public
the scientific characteristic that claims that science is a public good that benefits society and should be available to all
the goals of psychology research
describing the value of a single variable, identifying relationships between measured variables + making predictions from one variable to another variable, isolating the effect of one variable to another by manipulation + understanding cause/effect relationships between varia
construct
a hypothetical quality that is not directly observable, like happiness, satisfcation, or anxiety
variable
a condition or characteristic that can take on different levels, categories, or values and can be quantified/measured
characteristics of variables
label/concise name + operational definition + detail for replication =
operational definition
a description in terms of how exactly the variable was measured/manipulated (procedures, actions, materials, processes)
categorical and continuous
the two types of variable type
categorical variables
variables that have levels of groups or words that vary in quallity or kind; summarized using percentage or frequency
continuous variables
variables that have meaningful numbers along a scale with at least 6 values that vary in quantity/amount ; summarized using the average and standard deviation
observation, self-report, monitoring
the methods of measuring variables
observation
the method of measuring variables that includes watching behavior and studying actions
self-report
the method of measuring variables that includes asking questions about attitudes, beliefs, feelings and ideas
monitoring
the method of measuring variables that includes monitorying physiological changes such as biological responses and physical states
manipulated
if a variable is under the experimenter’s control, than it is __
association claims
a type of claim that correlational research a can make ; identifies the relationship between measured variables
causal claims
the type of claim that experimental reserach can make ; identifies the relationships when the predictor variable is manipulated
predictor variables
the variable in correlational research that is a pre-existing characteristic
outcome variable
the variable in correlational research that is measured
independent variable
the variable in experimental research that is directly manipulated by the experimenter
dependent variable
the variable in experimental research that is the measured response
hypothesis
a testable statement / prediction about the relationship between variables of interest
null hypothesis
a hypothesis that states that there is no difference/relationship between groups/variables
research/alternative hypothesis
a hypothesis that is a specific prediction about the relationshp between the variables
overlap
a hypothesis is directional if the error bars of the data from two groups __
same
in order to conclude causation, two groups must be the __ and one variable must be manipulated while the other is measure
direction ; strength
if both variables are continuous, we indicate the __ and _ of the overall relationship
p value
a probability between 0-1 that indicates if the relationship between variables is likely to not be real
p < 0.5
the p value inequality that is statistically significant and indicates that a relationship between variables is likely to be real
p > = 0.05
the p value inequality that is not statistically significant and indicates that there is no evidence of a relationship between variables
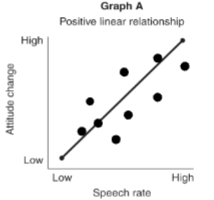
positive linear relationship
this graph shows a __ where an increase in one variable relates to an increase in another
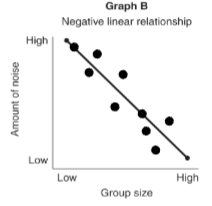
negative linear relationship
this graph shows a __ where an increase in one variable is relative to a decrease in another
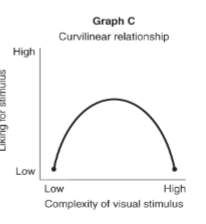
curvilinear relationship
this graph shows a __ where an increase in one variable relative to both increases and decreases in another
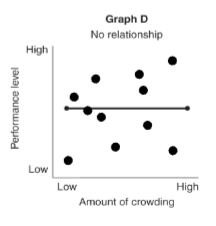
no relationship
this graph shows __ where the variables are not related to each other
correlation coefficient
a statistic that quantifies the linear relationship between two continuous variables ranging from -1>+1
direction and strength
what are the two pieces of information that we can get from the correlation coefficient
causation
correlation does not imply __
validity
the degree to which variables measure what the researcher actually wants to measure and the evidence supports the conclusions/claims made about the data
reliability
the degree to which the value is consistent when the measureme
reliability
correlation coefficients help assess __ because they asses how closely two measures resemble each other
+0.7
the correlation coefficient must be above a value of __ to be acceptable
test-retest, parallel forms, split-half
methods for assessing the reliability of surveys/tests
test-retest
a method for assessing the reliability of surveys/tests where two identical test are given at two time points
parallel forms
a method for assessing the reliability of surveys/tests where two equivalent tests are given at different time points
split-half
a method for assessing the reliability of surveys/tests where one test is given at a time and comparing the even/odds
inter-rater reliability
a method for assessing the reliability of observations where the ratings of different raters are compared for similarity
construct, internal, external, statistical
what four types of validity help evaluate research
construct validity
a type of validity assessing whether the content of the variable really measures the construct (face validity), if the operational definition of the variable is accurate (procedure-method match), and other extraneous variables
face validity
a type of construct validity assessing whether the operational definition accurately measures/manipulates the construc
method-match
a type of construct validity assessing whether the method used was appropriate to measure the variable
procedure
a type of construct validity assessing whether the method used added noise/error
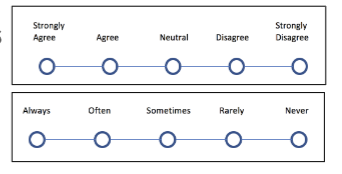
likert-type scales
a type of self-report method where participants are given a range of response choices with equal intervals, normally with an odd number of options
observer expectancy, self-fulfilling prophecies, observer effects, response sets
threats to construct validity
observer expectancy
a type of threat to construct validity in which researchers see what they expect to see
threat of observer expectancy
clearly defining variables, training observers, and using a blind research assistant are all solutions to solve the _
self-fulfilling prophecies
a type of threat to construct validity in which researchers inadvertently affect how participants act
the threat of self-fulfilling prophecies
using a blind research assistant or indirectly interacting with the participants are solutions to solve __
observer effects
a type of threat to construct validity in which people’s expectations affect how they respond
the threat of observer effects
minimizing interactions with participants, being unobtrusive or allowing time to acclimate, phrasing questions neutrally, and establishing reliability are all solutions to solve __
Hawthorne effect and social desirability / faking bad
the two types of observer effects are
response sets
a type of threat to construct validity in which mental shortcuts influence the way people respond as a systematic response manner is used
experimental research
what type of research starts with equivalent groups, manipulates one variable, and observes any effect on the outcome variable
validity
the degree to which the evidence supports the conclusions or claims made about the data
validity
these are all types of what:
construct
internal
external
statistical
internal validity
the degree to which a study or experiment is free from flaws in its internal structure and its results can therefore be taken to represent the true nature of the phenomenon
random assignment
every participant having an equal likelihood of being placed in each of the treatment group; happens during the experiment
random sampling
every member of the population has an equal likelihood of being included in the sample; happens before the experiment
an alternative explanation of results
if an extraneous variable affects groups differently and can provide __; also called a confounding variable
random error
if an extraneous variable affects groups the same and can provide __
common threats to internal validity
what are these called:
selection effect
maturation effect
testing effect
mortality effect / attrition
history effect
selection effect
a common threat to internal validity where there’s an unequal groups to begin with
maturation effect
a common threat to internal validity where changes occur due to time spent in the experiment
testing effect
a common threat to internal validity where there are changes due to measuring the outcome variable more than once
mortality effect / attrition
a common threat to internal validity where there are differences in groups due to some people dropping out or being removed
history effect
a common threat to internal validity where there are changes due to something in the external world
between groups
a type of experimental research design where each participant experiences one level of the independent variable; participating in one condition makes it impossible to participate in the other
within groups
a type of experimental research design where each participant experiences all levels of the independent variable; reduces the effects of individual differences
pre-test, post-test
a type of between groups design where participants are tested both before and after the experiement
post-test only
a type of between groups research design where participants are only tested after the experiment
institutional review board
an institution that reviews proposed studies considering respect for persons, beneficence, and justice
participant rights
informed consent, voluntary participation, and confidentiality are all types of what
deception
not telling the participants the true goal of the study; justified onlly if nondeceptive alternatives are not feasible
debriefing
explaining everything at the end of teh study
external validity
the degree to which results can be generalized beyond the current study to other people, situations, or time periods
population
the entire set of people or products that are of interest to a researcher
sample
a subset of a population
representative probability
a type of sampling technique that uses random sampling with strong external validity
non-representative/non-probability
a type of sampling technique where the sample may not be similar to the population and has weak external validity
random sampling
a type of representative sampling technique where every member of the population is listed, and a random sample is taken from the list
stratified random sampling
a type of representative sampling technique where every member of the population is listed, subgroups are identified, and random proportions of the subgroups are sampled
voluntary response sample
a type of non-representative sampling technique where individuals choose to respond to a general appeal for information
convenience sample
a type of non-representative sampling technique where people that are the easiest to contact and measure are included
quota sample
a type of non-representative sampling technique where the same number of people are selected, regardless of their prevalence in the population
error
the extent to which the sample differes from the population
margin of error
a measure of sampling error in categorical variables based only on sample size