Geog 213 miterm practice
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
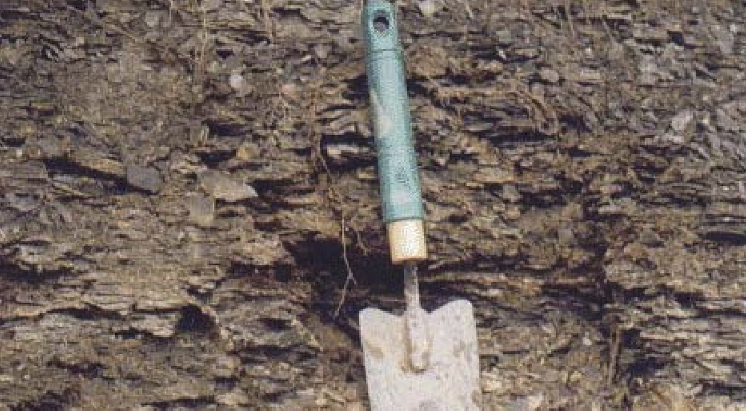

Shale Slaking
Hydration weathering. Water molecules bind to minerals causing expansion
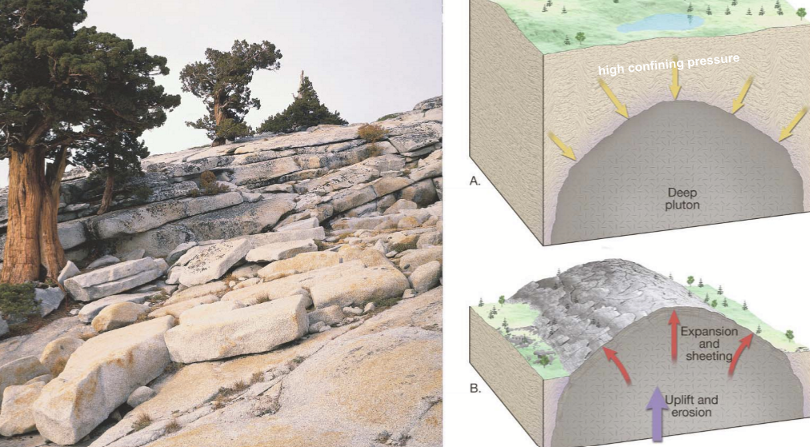
Pressure Release
Unloading. Pressure from the surrounding rocks is released once weathered away. The batholith can then expand and sheet

Exfoliation
Rocks break apart in parallel layers and expands resulting in cracks

Exfoliation dome
Non uniform heating leads to expansion of the exposed rock

Grus
Thermal expansion. Minerals have different rates of thermal expansion. When expanding the rock breaks apart into small chunks
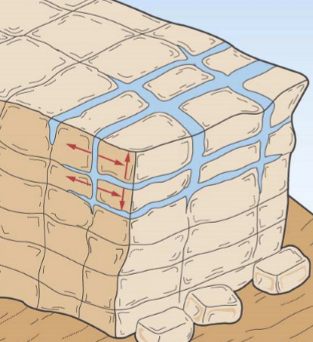
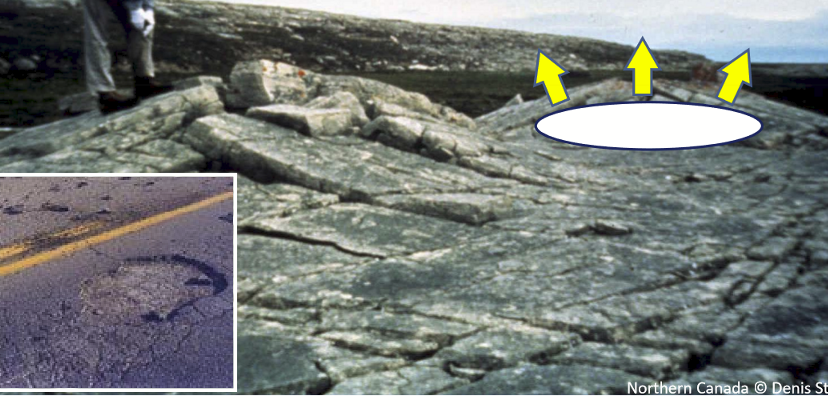
Freeze thaw
Changes in void space. Freezing expands repeatedly increasing the void space in the rock.

Ice lenses
Ice below the rock surface expands as it freezes creating blisters.
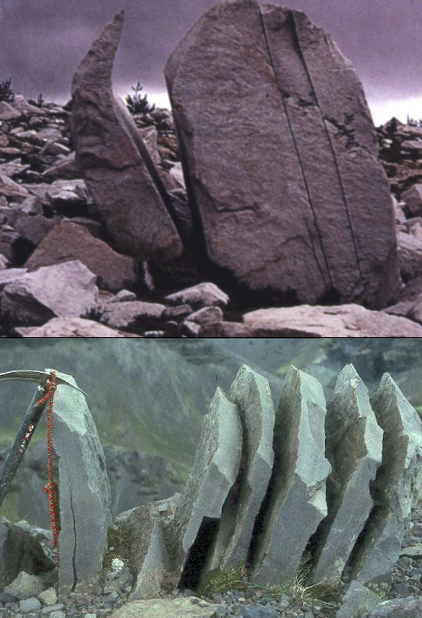

Frost Wedging
Ice freezes in layers of the rock creating neat slices
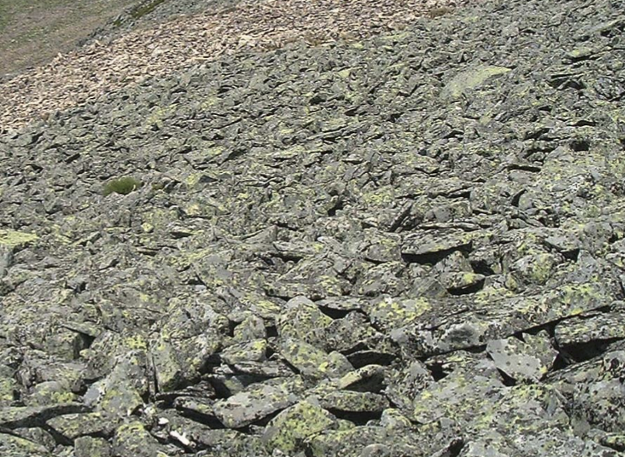

Frost wedging Felsenmeer (rock Sea)
comes from the large splitting of rock by frost wedging

Salt weathering
Crust from salt crystals. The salt crystals expand when wet. Breaks apart rock

Taifoni salt weathering
Salt spray evaporates quickly breaking apart the rock

Evaporites, chemical weathering
Precipitation of soluble minerals

Carbonation, chemical weathering
Breakdown of minerals through acid creating solution

Granite Hydrolysis
Weathering pits. Chemical weathering. Granite undergoes hydrolysis

Oxidation
Oxidation of sulfides. chemical decomposition. can increase strength of rock

Corestones
Rounded joints surrounded by broken down material. Chemical weathering

Tor
Chemical Weathering. stacks of blocky rocks formed as remnants of weathered jointed bedrock

Rock avalanche
Long run out landslide. Long deposit following the detachment scar. Debris apron at bottom

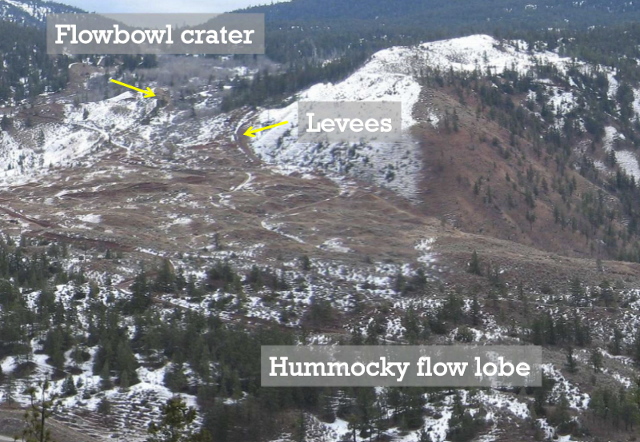
Debris flow
Channels, levees and lobes. Rapid process happening in areas of steep slope and sparse vegetation. Lots of moisture

Mudflow
Saturated clay rich material, flows like a liquid. Low slope angle, low angle in friction. Caused by saturation

Slump
Rotational slide (slump) of sand/silt/clay, concave failure surface. Soft materials. Undercutting of slope and irrigation, Slump blocks

Slump
Rotational slide (slump) of sand/silt/clay, concave failure surface. Soft materials. Undercutting of slope and irrigation, Slump blocks
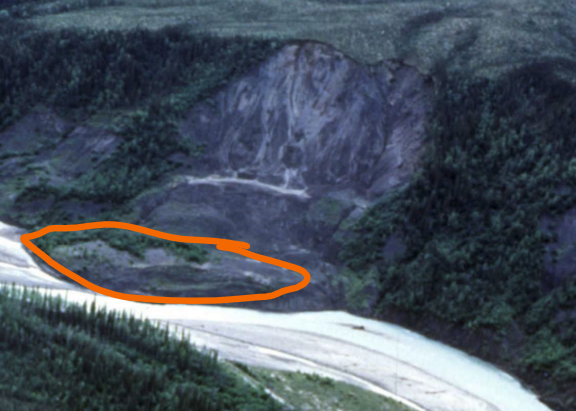

Slump
Rotational slide (slump) of sand/silt/clay, concave failure surface. Soft materials. Undercutting of slope and irrigation, Slump blocks
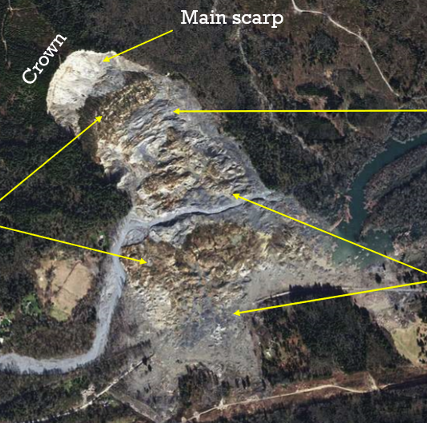

Rapid Slump
Rotational slide (slump) of sand/silt/clay, concave failure surface. Soft materials. Undercutting of slope and irrigation, Slump blocks

Slow Earth flow
Slow landslide moving meters per year. Made up of fine earth. high ground water discharge moving clay into valley. has jumbled trees

Slump
Rotational slide (slump) of sand/silt/clay, concave failure surface. Soft materials. Undercutting of slope and irrigation, Slump blocks

Slow earth flow
Slow landslide moving meters per year. Made up of fine earth. high ground water discharge moving clay into valley. has jumbled trees

Heave
Due to freeze thaw cycles the grains of sediment are pushed up, thaw and slide down. This repeats. Evidence is pistol butt trees

Soilfluction
Saturated water and thawed soil. lots of water

Gelifluction
like soilfluction, but over frozen soil

Rock Slide
Parallel beds of rock. smooth failure plane. Triggers from mass movements and changes in pore water pressure.

Wedge Failure
Homoclines, weak sedimentary rock. follows converging joints, bedding or fractures. Triggered by high pore water pressure, weathering or temps

Rock fall
Shear cliff face with talus at base. Talus is blocky and loose. Falls directly downward
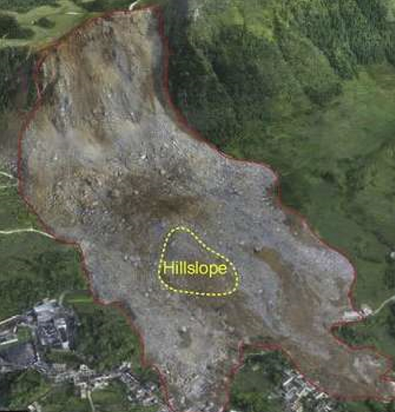
Rock Avalanche
Began as topple on steep hillslope. Continued super far

Abrasion
Wear of bedrock in river from grinding
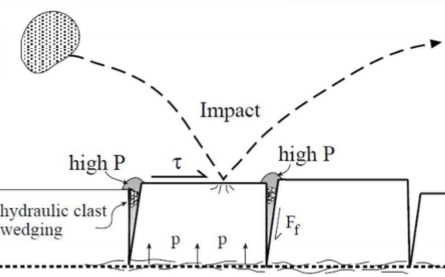
Plucking
Erosion from bedrock in river from low pressure zones lifting blocks out of floor
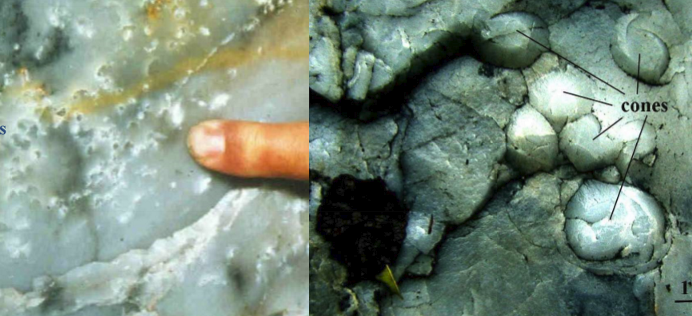
Cavitation
popping of bubbles in bedrock floor creating erosion. High periods of flow
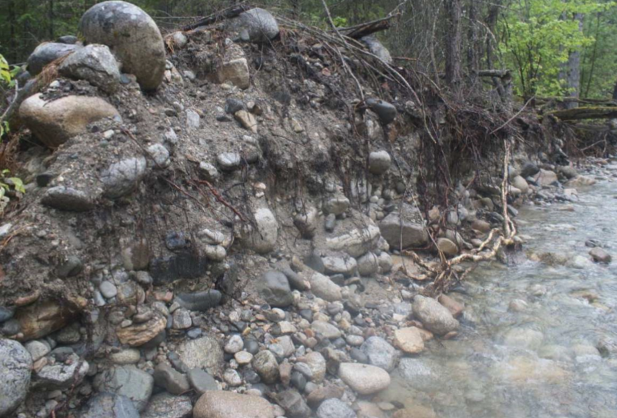

Upland stream
Low flow, high slope. Lots of sediment. Episodic discharge. Mountains, Common with pools and steps/riffles. Steps = high grain size and steep. Riffle, smaller grain size and less steep.
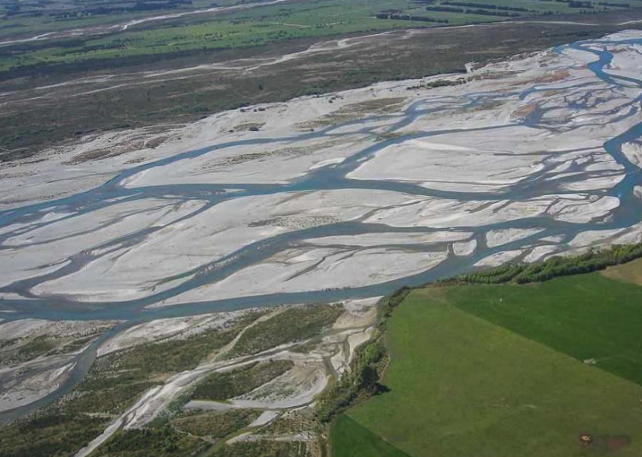

Braided river
Wide shallow multi thread river. Network of smaller streams. High sediment supply. Slower = more aggrradation = steeper

Braided river glacial outwash
High sediment supply. Broad ungraded river system

Meandering River
Single channel with low stream power moving fine sediments. Cutbanks are areas on outer with high erosion. Point bars are areas of high deposition.

Anastomosing RIver
two or more connected channels that enclose flood basins. Highly sinuous channels. Flat low gradient with frequent abandonment

Wandering River
multi channel with one dominating channel. Sand/gravel. has bars (no plats) and islands (plants.) high stream power and sediment supply