CH 15 - CHEM 120
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
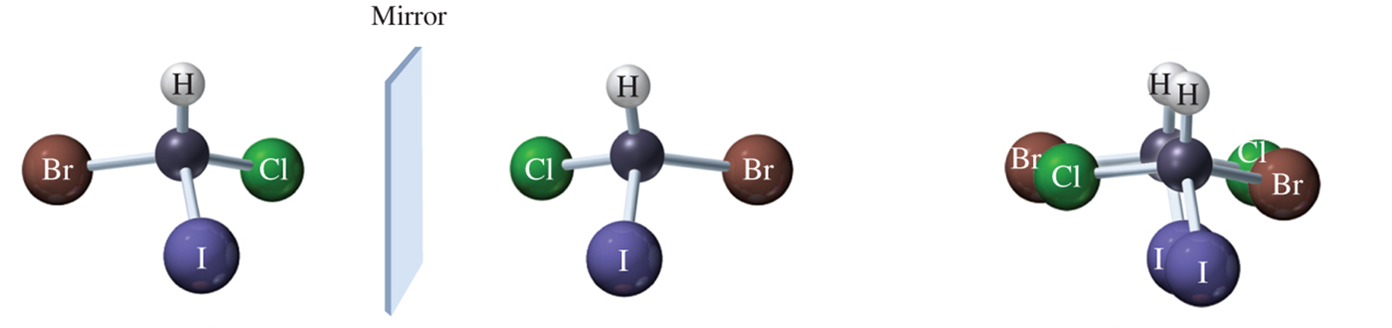
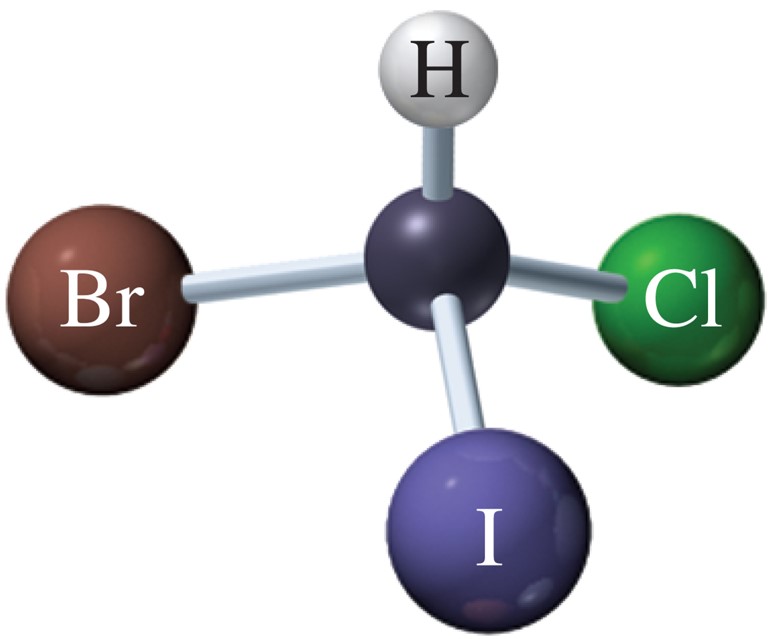
nonsuperimposable mirror images; have same physical properties except interaction w/ plane polarized light
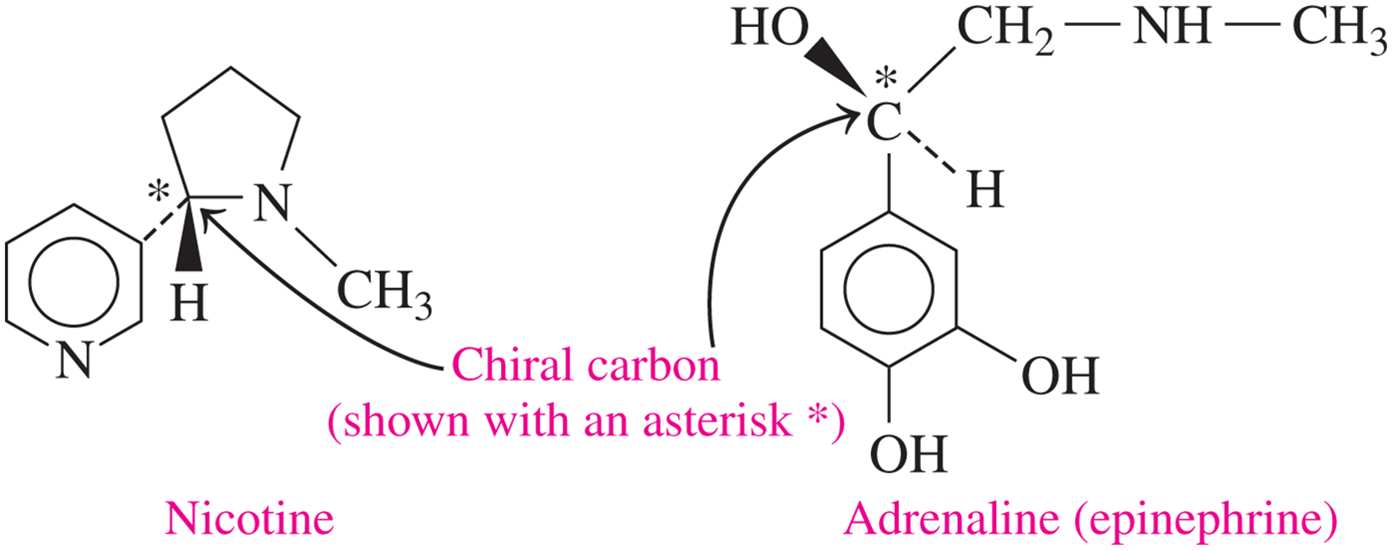
chiral carbon
C6H12O6 or C6(H2O)6
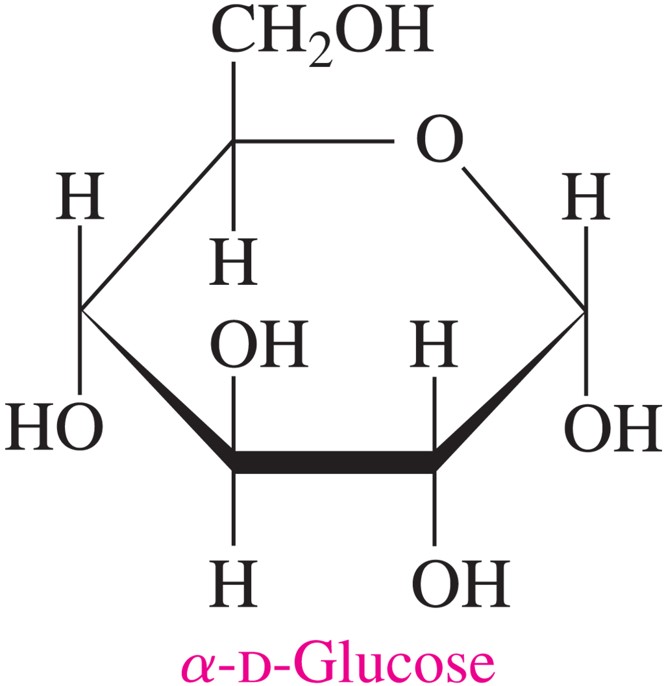
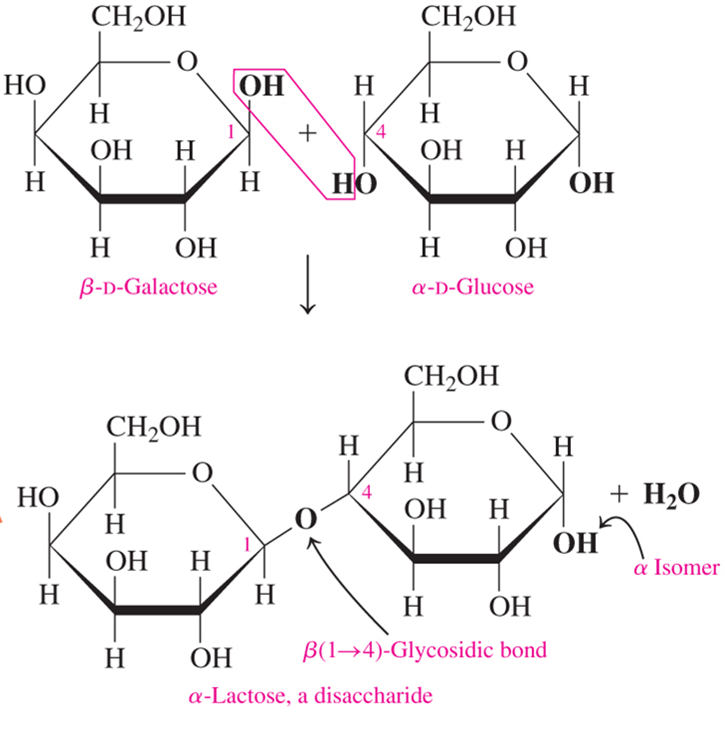
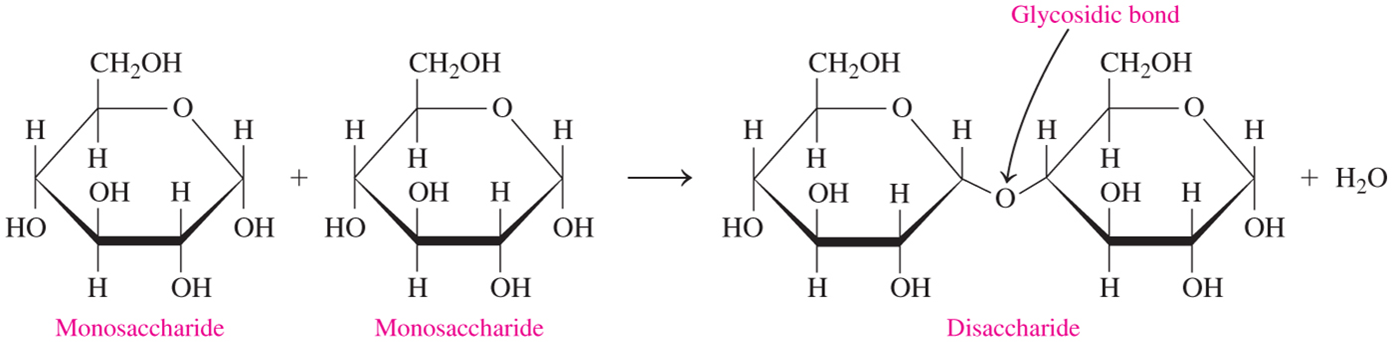
disaccharides
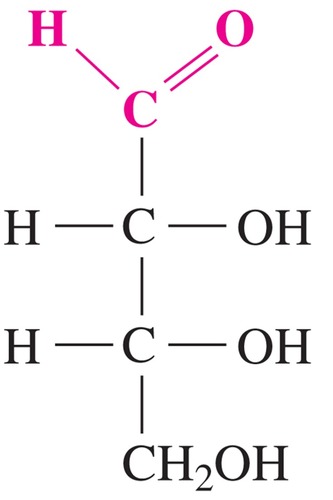
D-glyceraldehyde
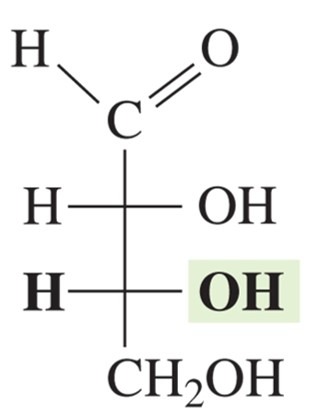
D-glucose
D-fructose
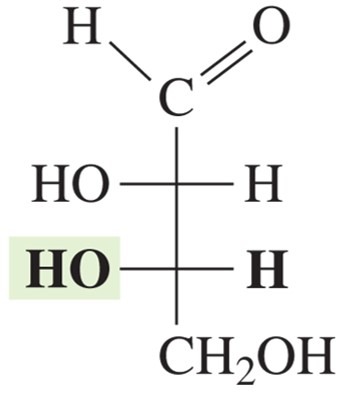
D-galactose
D-ribose
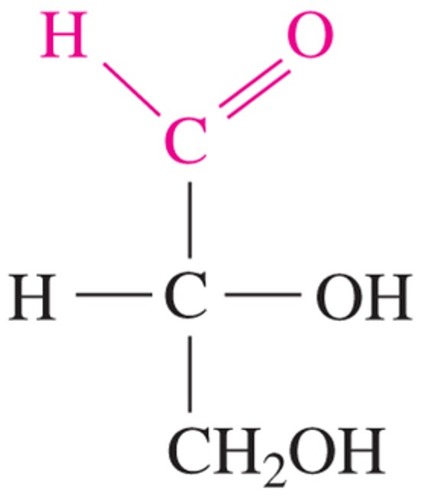
simplest sugar w/ only one chiral center
D-glyceraldehyde
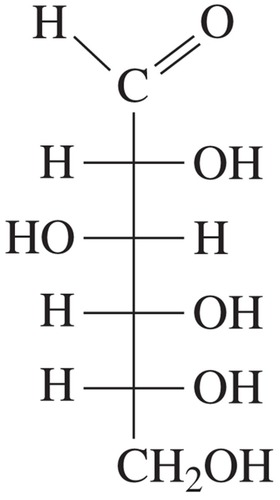
aldohexose; common names include dextrose, grape sugar, blood sugar
D-glucose
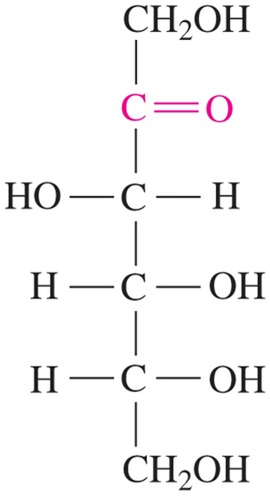
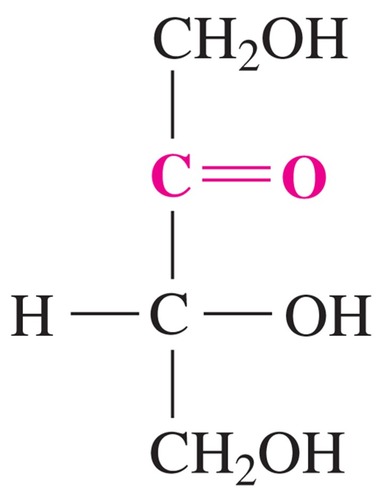
ketohexose; sweetest of all natural sugars
D-fructose
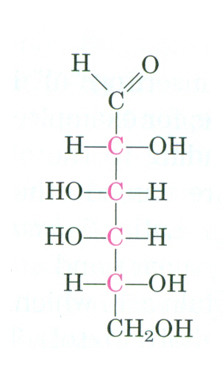
common part of lactose; converts ingested galactose to glucose
D-galactose
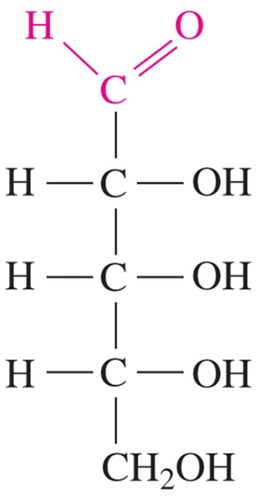
used in genetic material; not used as an energy source, but is a part of the backbone of RNA
D-ribose
cellulose
an unbranched chain of D-glucose units connected by β-1,4-glycosidic bonds
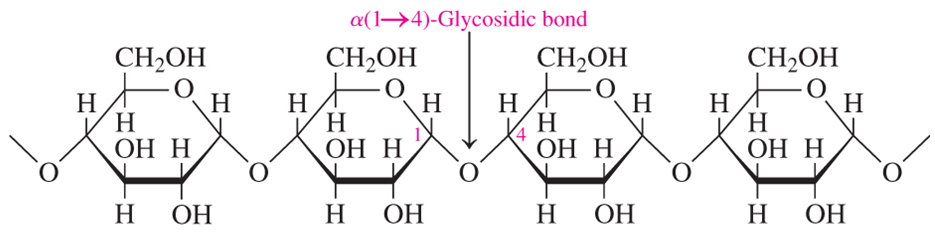
amylose
an unbranched chain of D-glucose units connected by α-1,4-glycosidic bonds
furanoses
five-membered cyclic forms of sugars
pyranoses
six-membered cyclic forms of sugars
anomers
the -OH that forms from the ring closure can either be above or below the plane of the ring
α-anomer
the hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon is in the opposite direction as the CH2OH group (below)
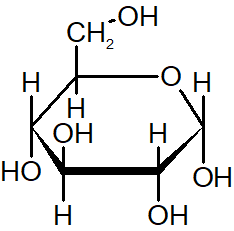
β-anomer
the hydroxyl group on the anomeric carbon is in the same direction as the CH2OH group (above)
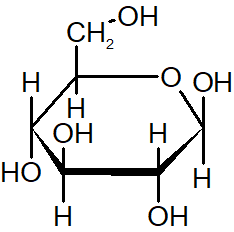
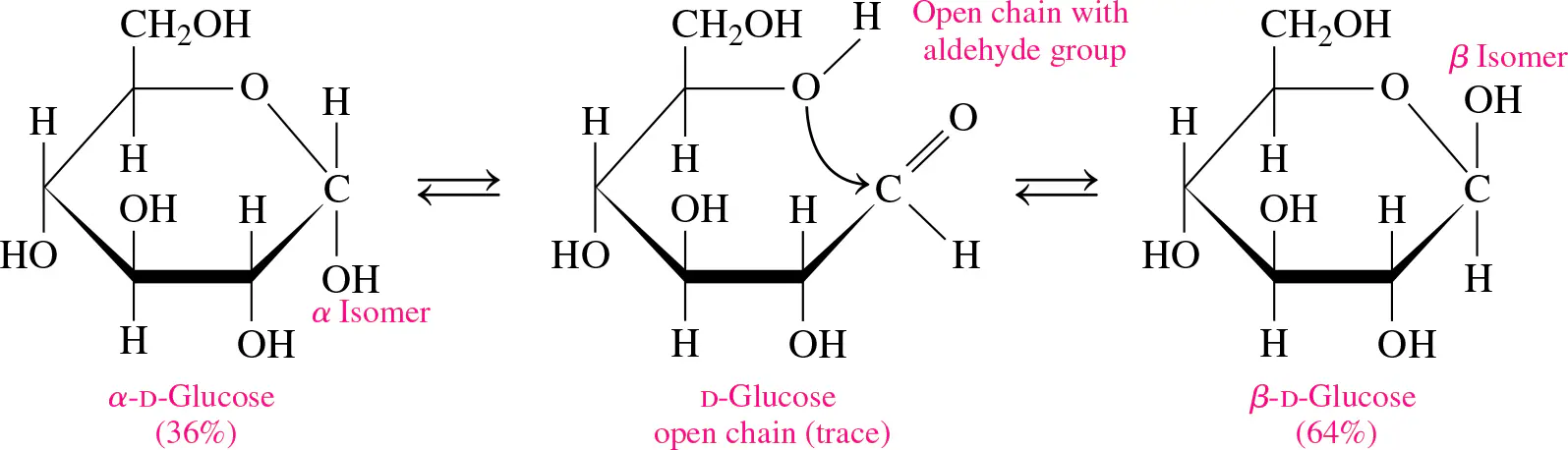
mutarotation
the equilibrium between α and β forms, allowing conversion from one form to another
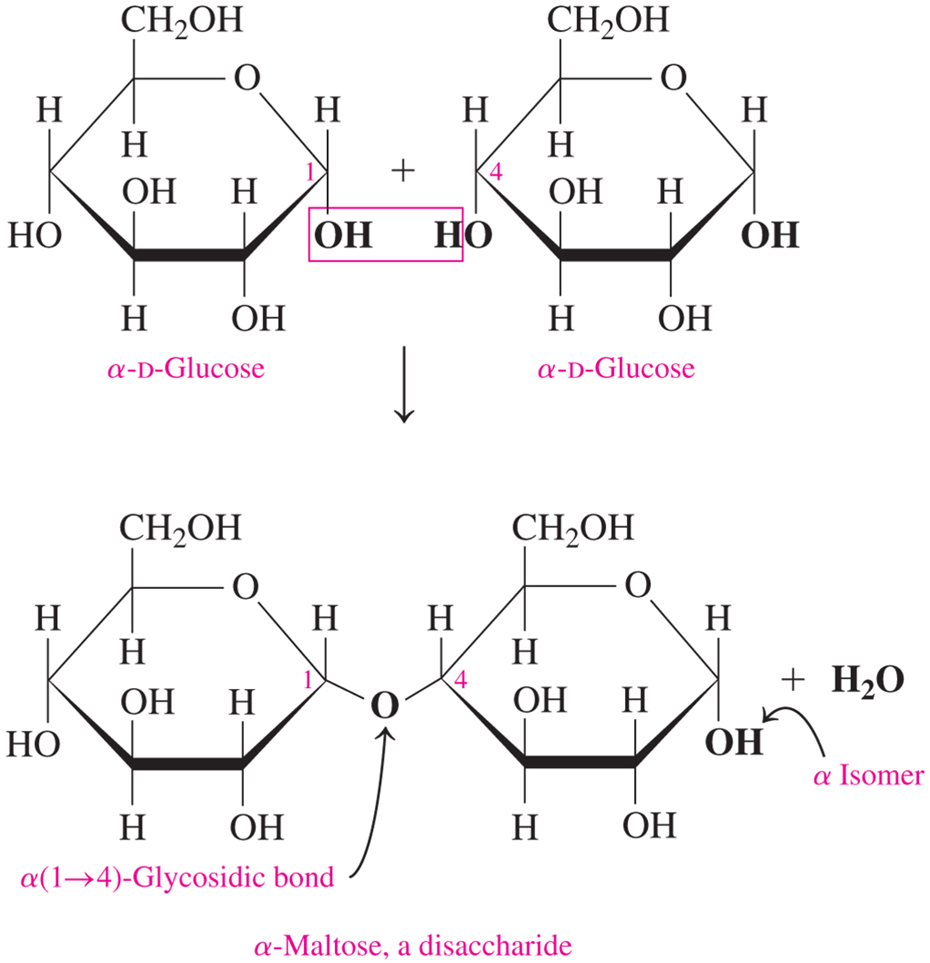
how are disaccharides connected?
by glycosidic bonds between the anomeric carbon of one unit & an -OH of another unit
sucrose is a disaccharide formed by linking what?
α-D-glucose with β-D-fructose
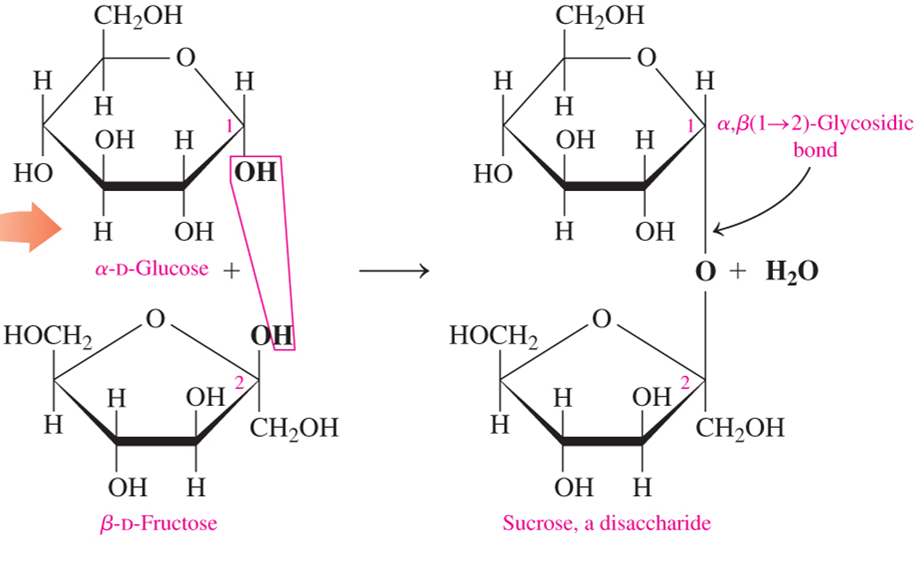
maltose is a disaccharide formed by linking what?
two α-D-Glucose units
lactose is a disaccharide formed by linking what?
β-D-Galactose and α-D-Glucose