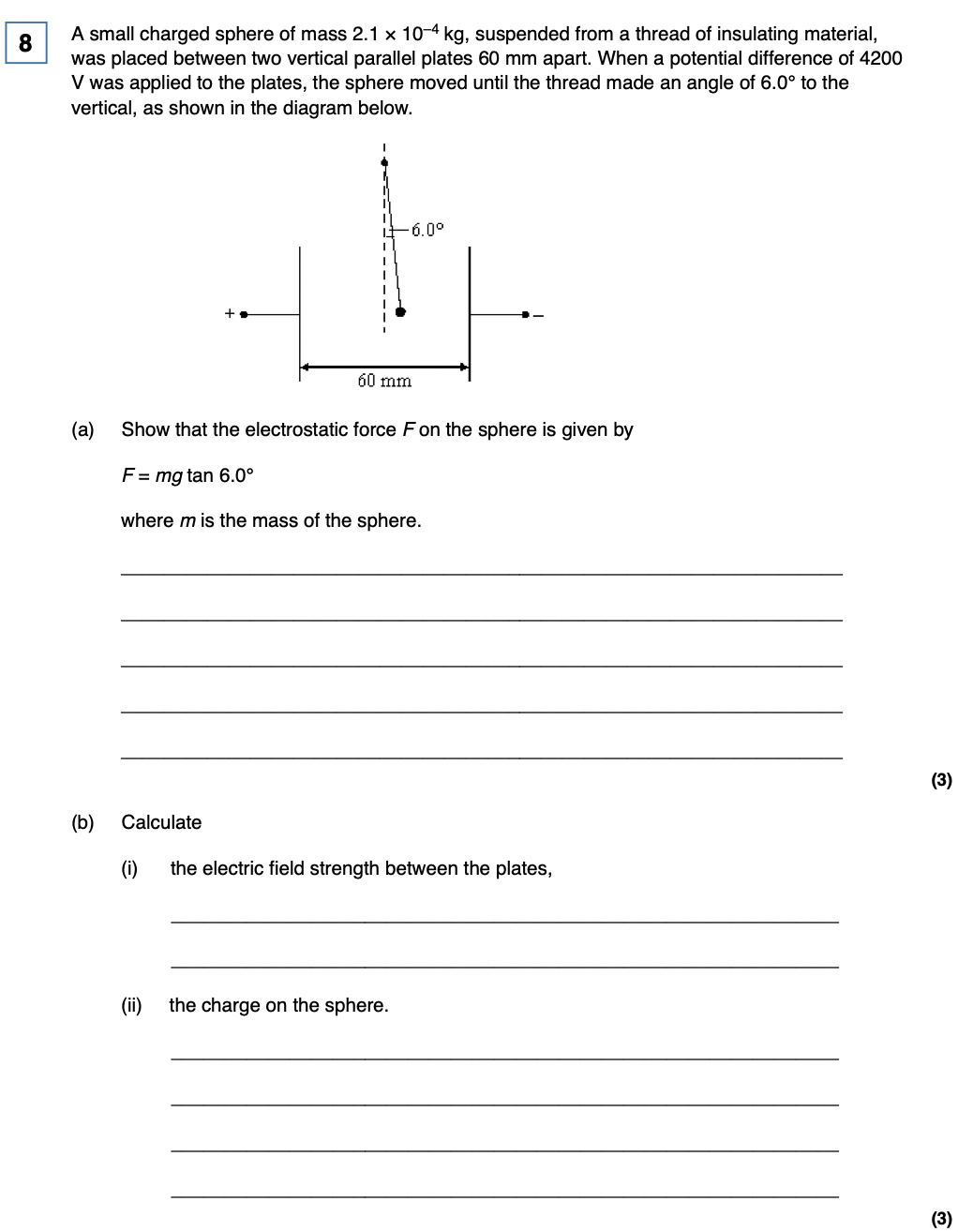
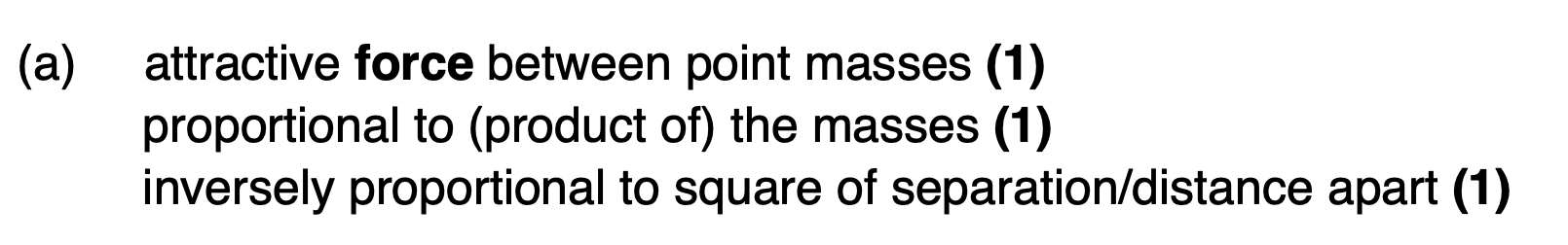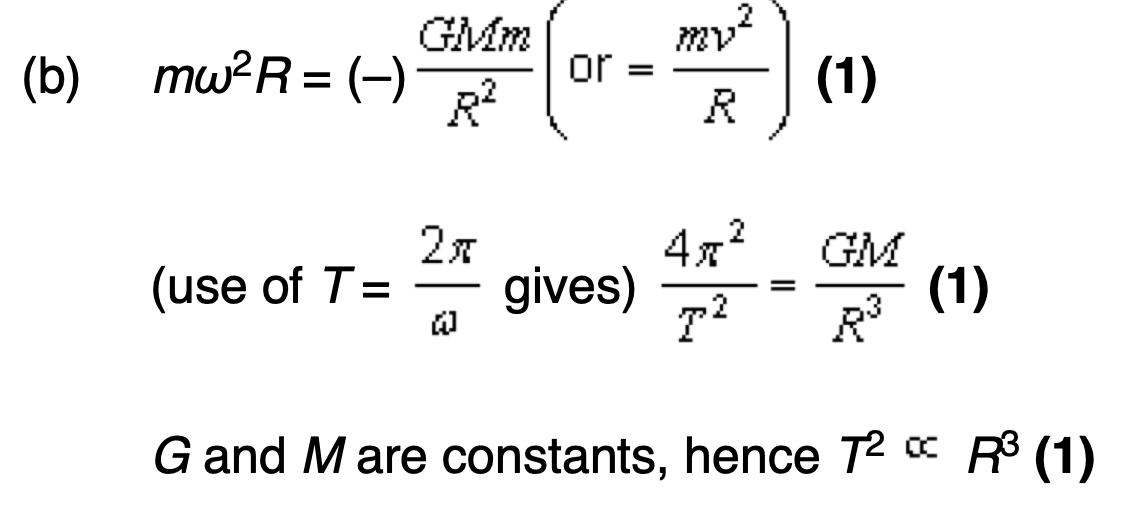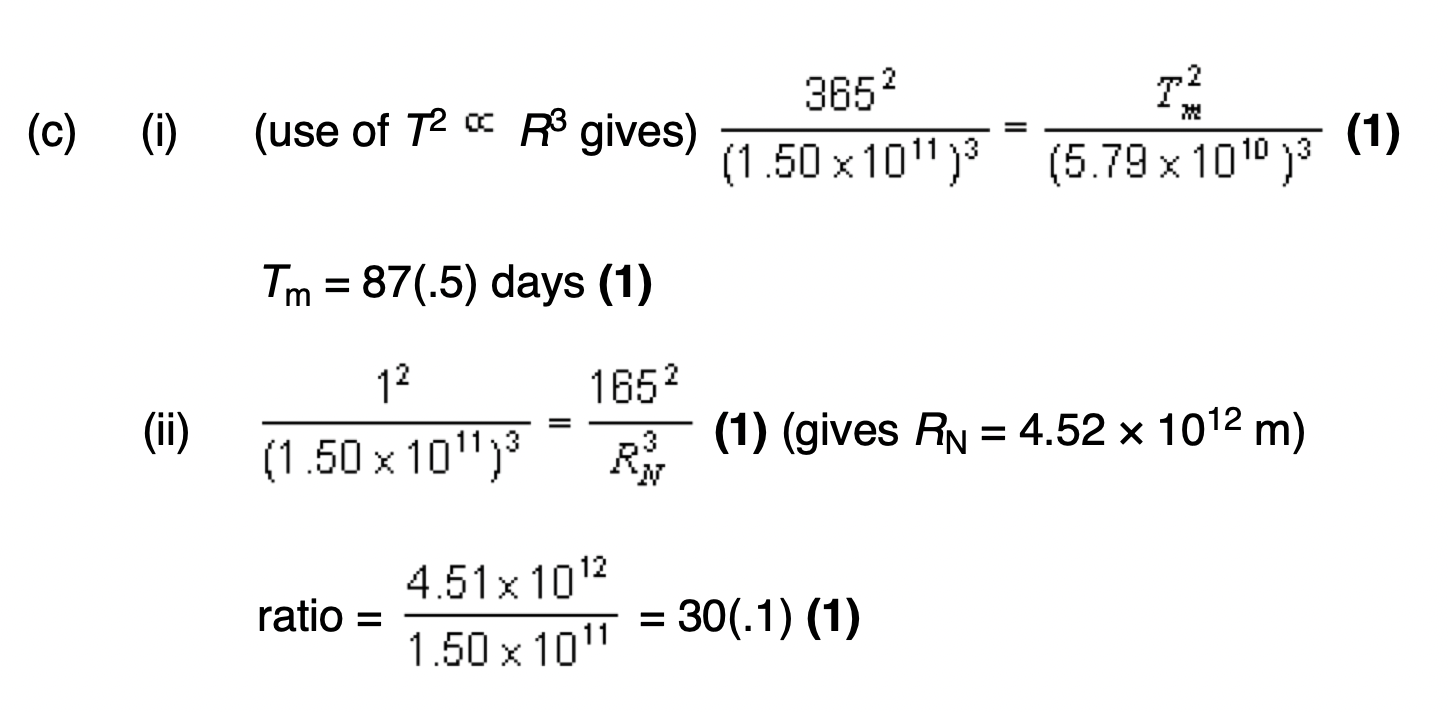electric and gravitational Fields
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Fields
area of space where mass/charge experience a force
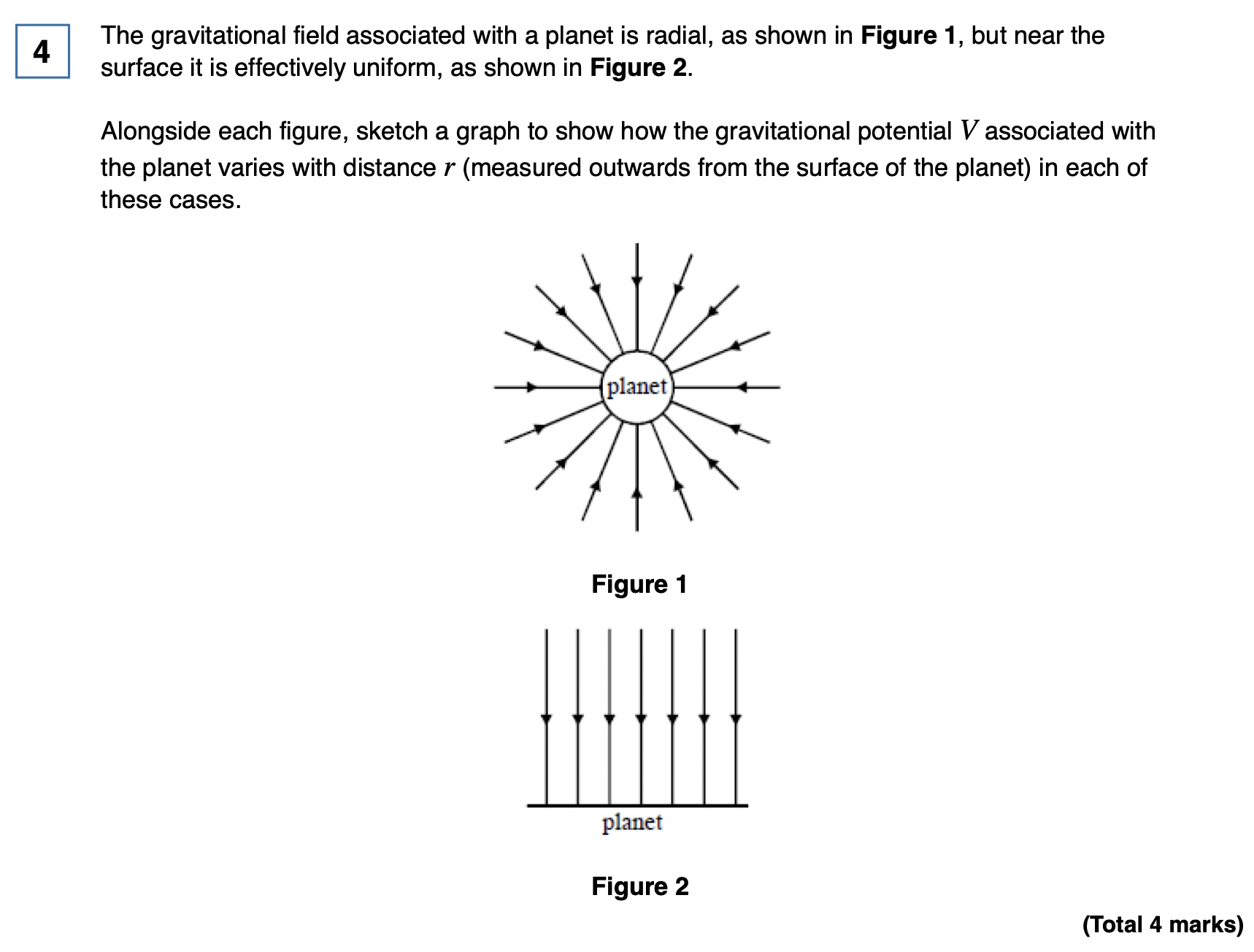
Gravitational Fields
A region of space where a mass experiences a force.
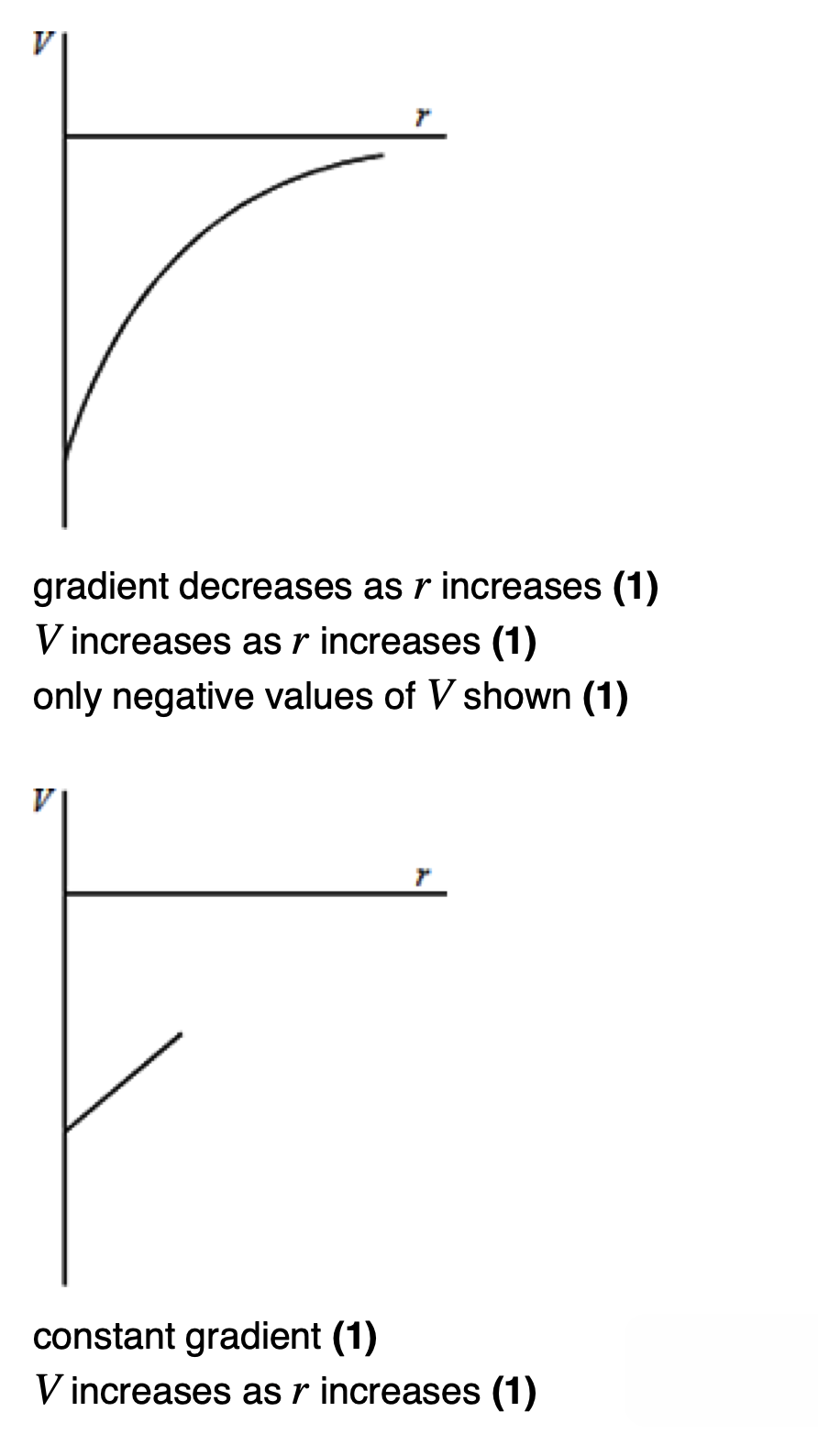
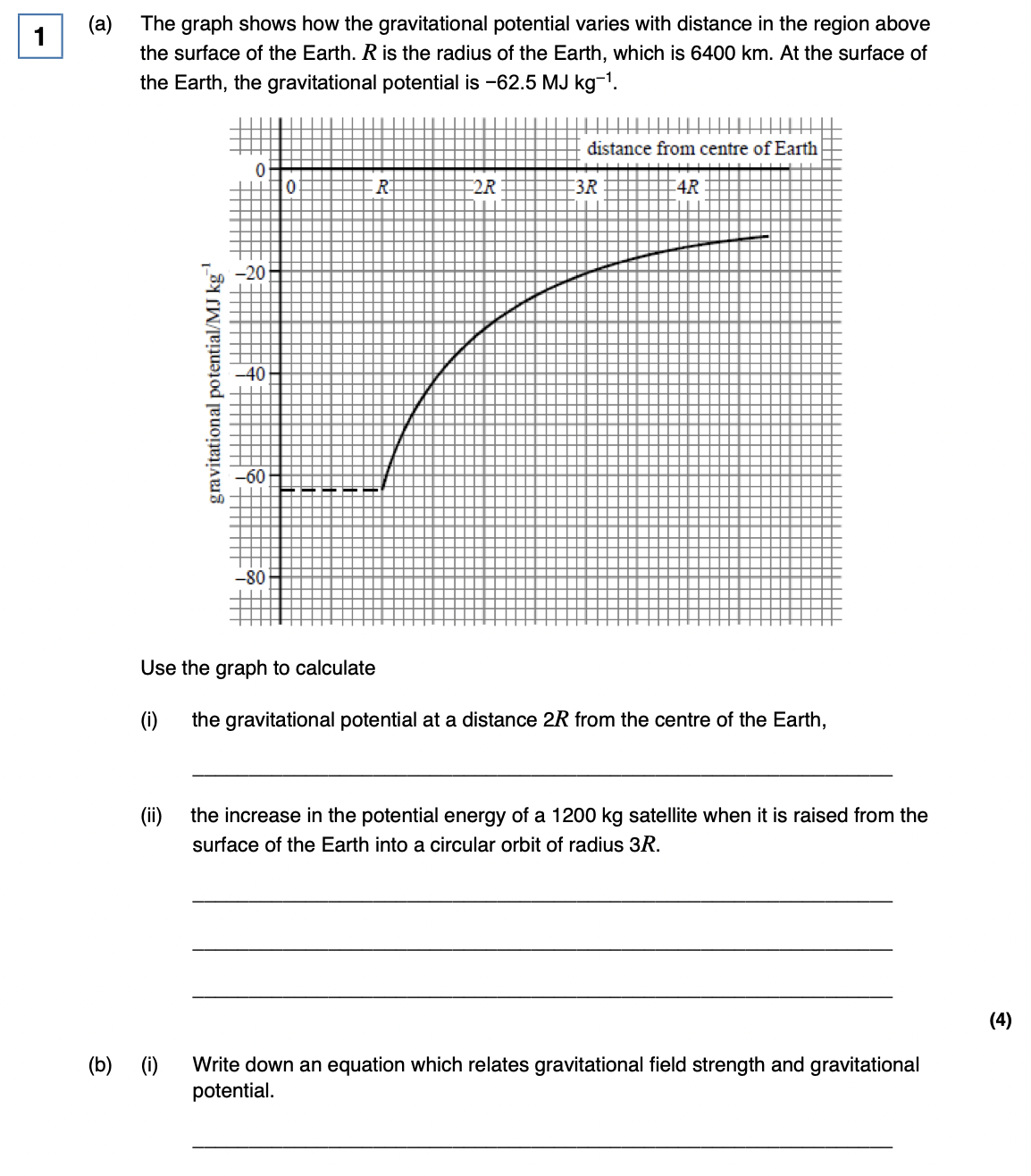
gravitational potential at a point.
The work done per unit mass to bring a small test mass from infinity to that point. Units are J kg⁻¹.
significance of gravitational potential being zero at infinity?
reference point, as potential energy is zero when objects are infinitely far apart.
Field lines
show the direction of the force on a point mass/test charge
if field lines are away its a positive charge
force to energy
to get from the force of gravitational field strength, to energy its workdone = Fx r
so goes from F=GMm/r² → E= GMm/r
F= KQq/r² → E=KQq/r
force for gravitational fields can only be attractive
force for electric fields can be negative and positive
field strength
how much force an object would feel
field strength equations
divide F=GMm/r² by m to give u g=GM/r²
divide F= KQq/r² by q to give u F=KQ/r²
to find the potential energy (how much energy should something need to move from infirnity to that point 1kg/1C) divide by r and equation becomes negative
V= -GM/r
V= -KQ/r
Newton's Law of Gravitation.
The force between two point masses is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. F = G m₁ m₂ / r²
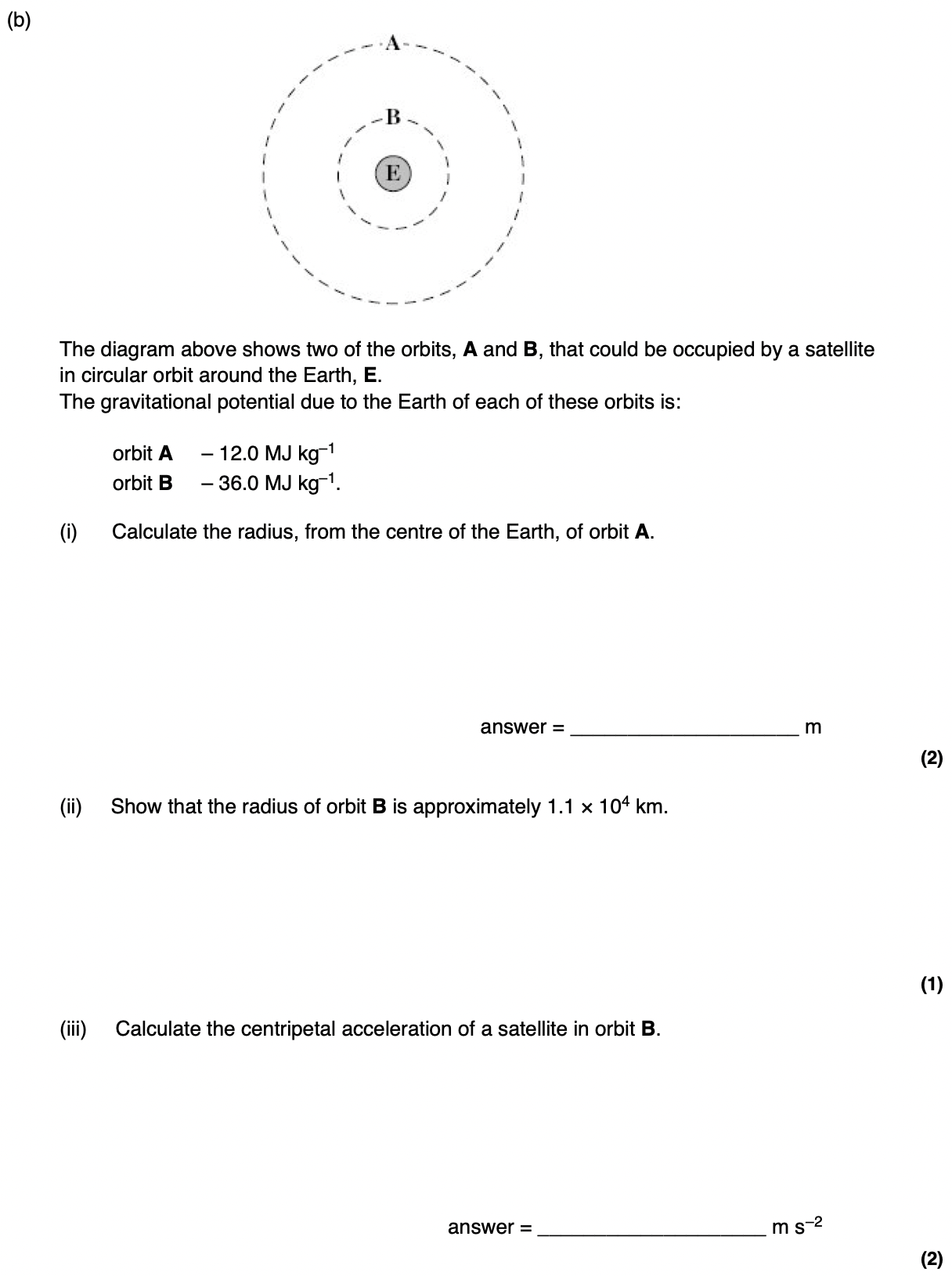
For a satellite in a circular orbit, what provides the centripetal force?
The gravitational force between the satellite and the planet.
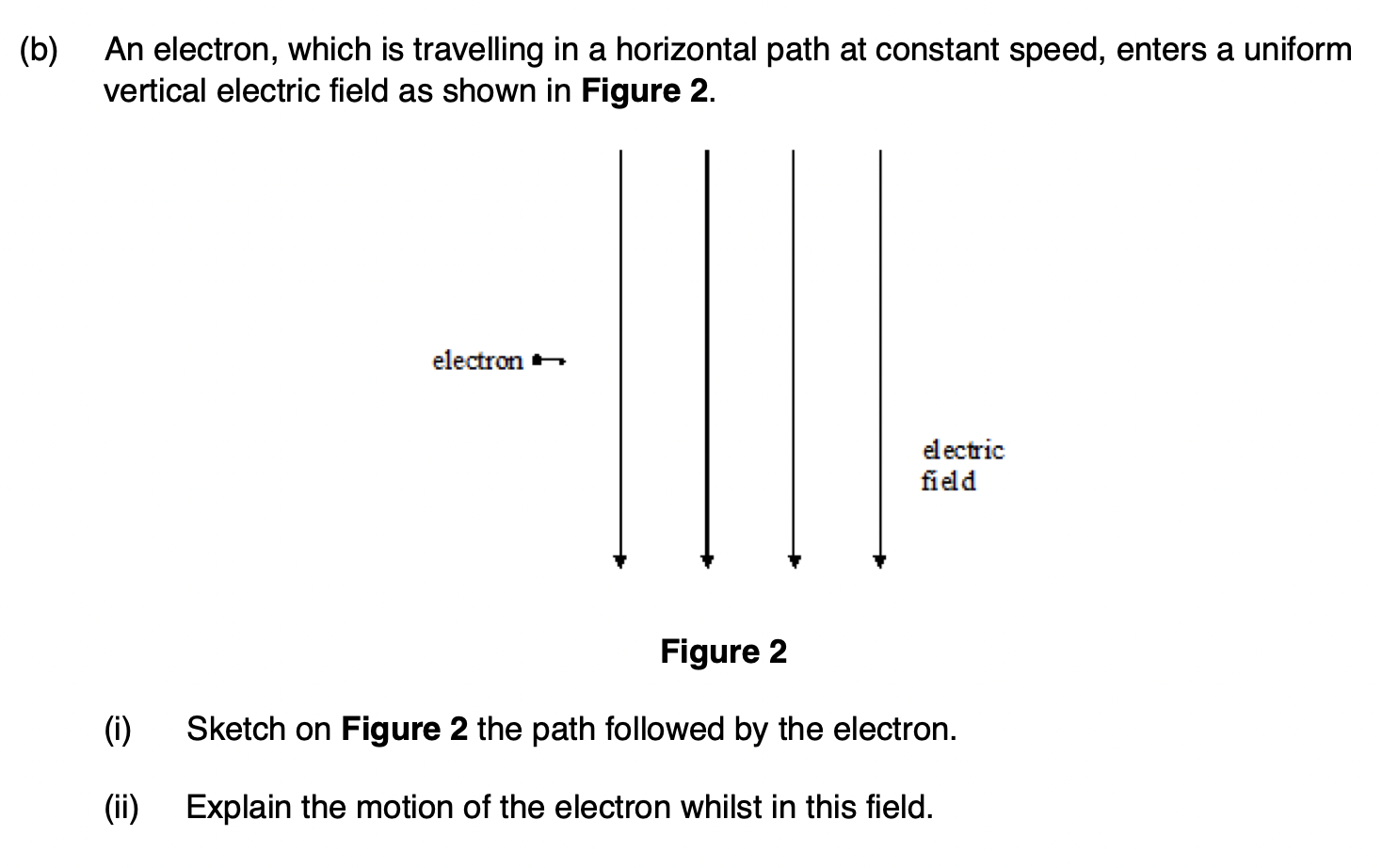
electric field
A region of space where a charged particle experiences a force.
electric field strength
The force per unit positive charge experienced by a small positive test charge placed in the field
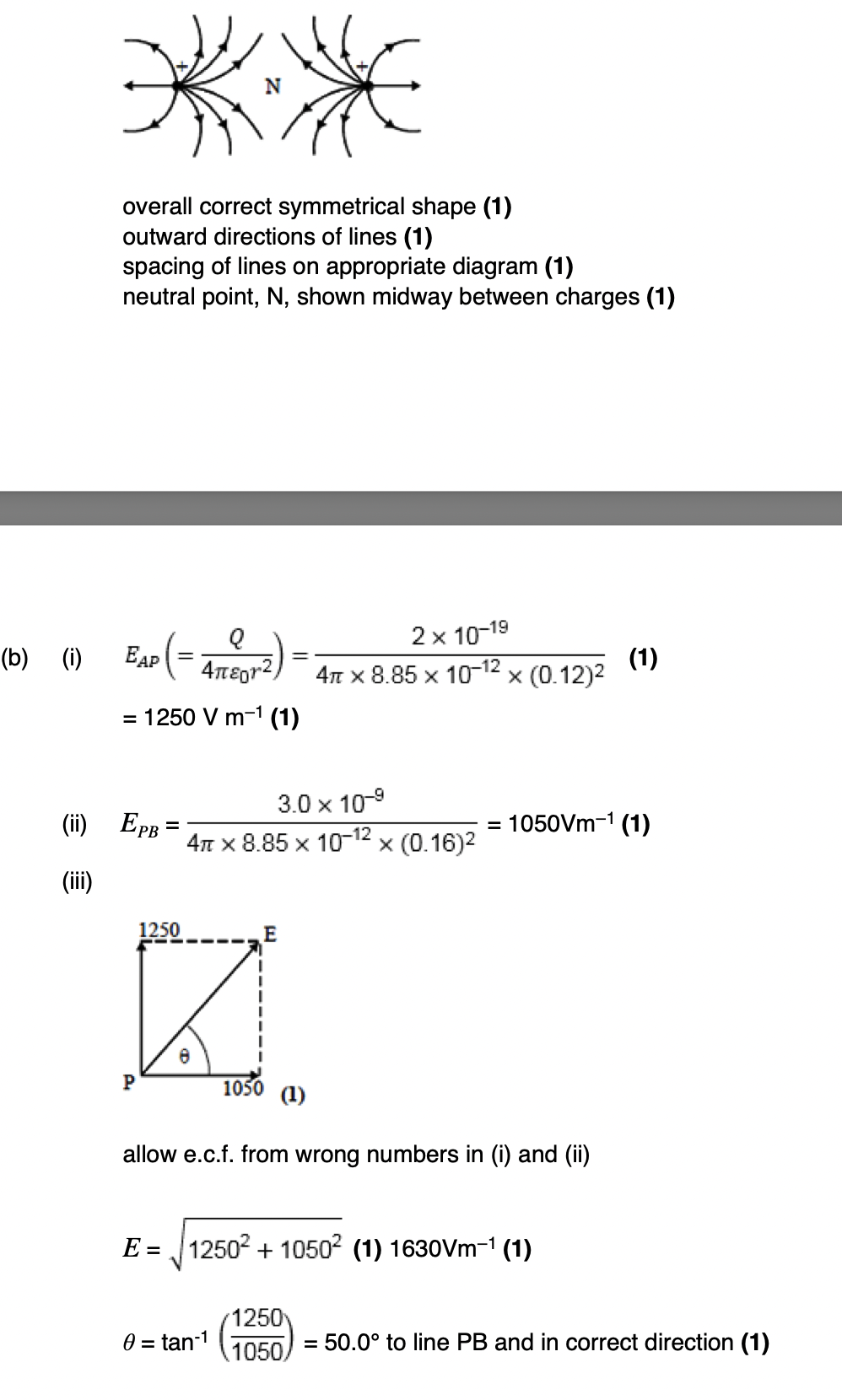
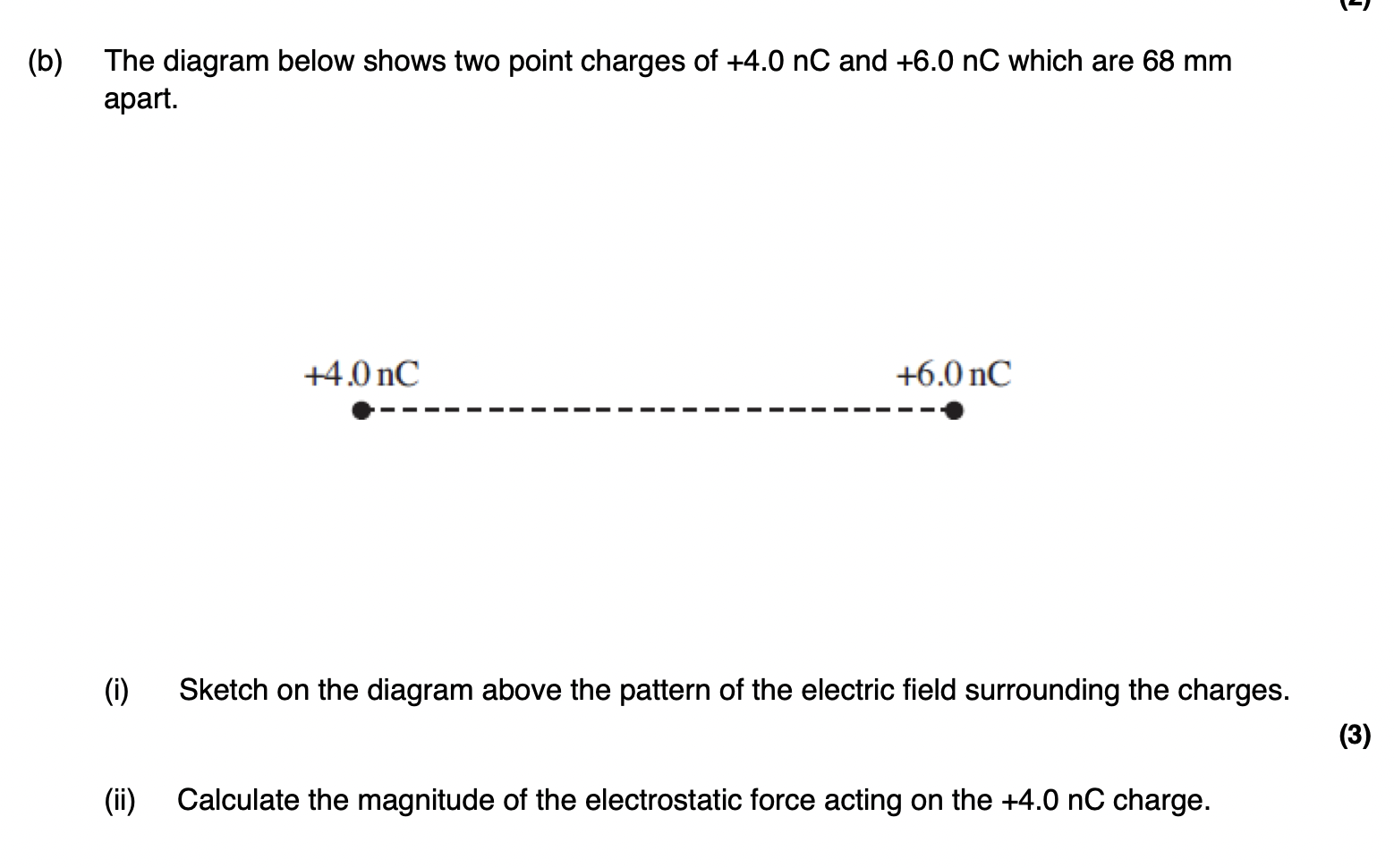
electric field pattern for an isolated positive point charge.
Radial lines pointing away from the charge. (the circle)
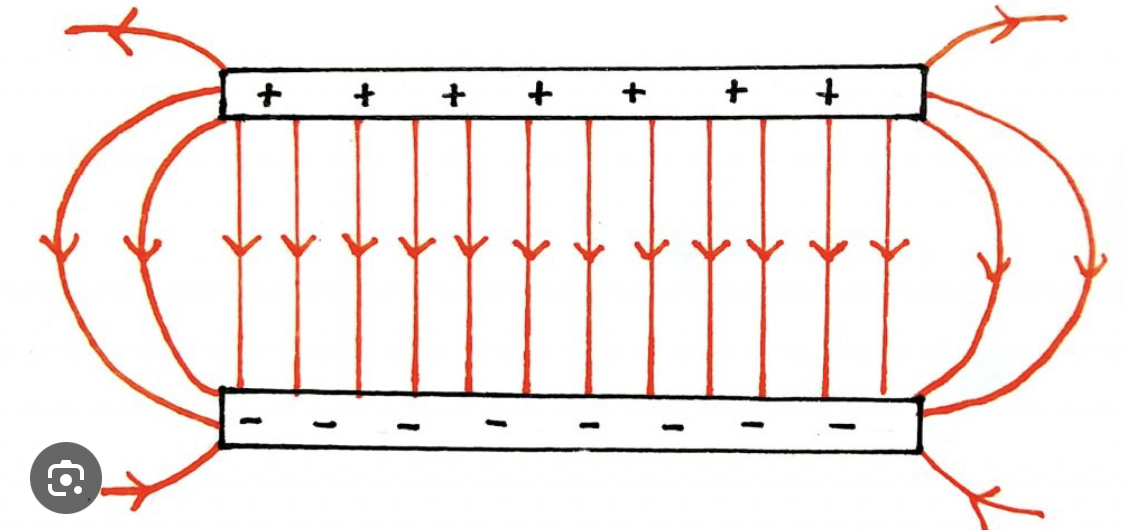
electric field pattern for a uniform field between two parallel plates.
Equally spaced, parallel lines from the positive plate to the negative plate.
electric potential at a point.
The work done per unit positive charge to bring a small positive test charge from infinity to that point
Coulomb's Law.
The force between two point charges is proportional to the product of their charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
F=KQq/r²
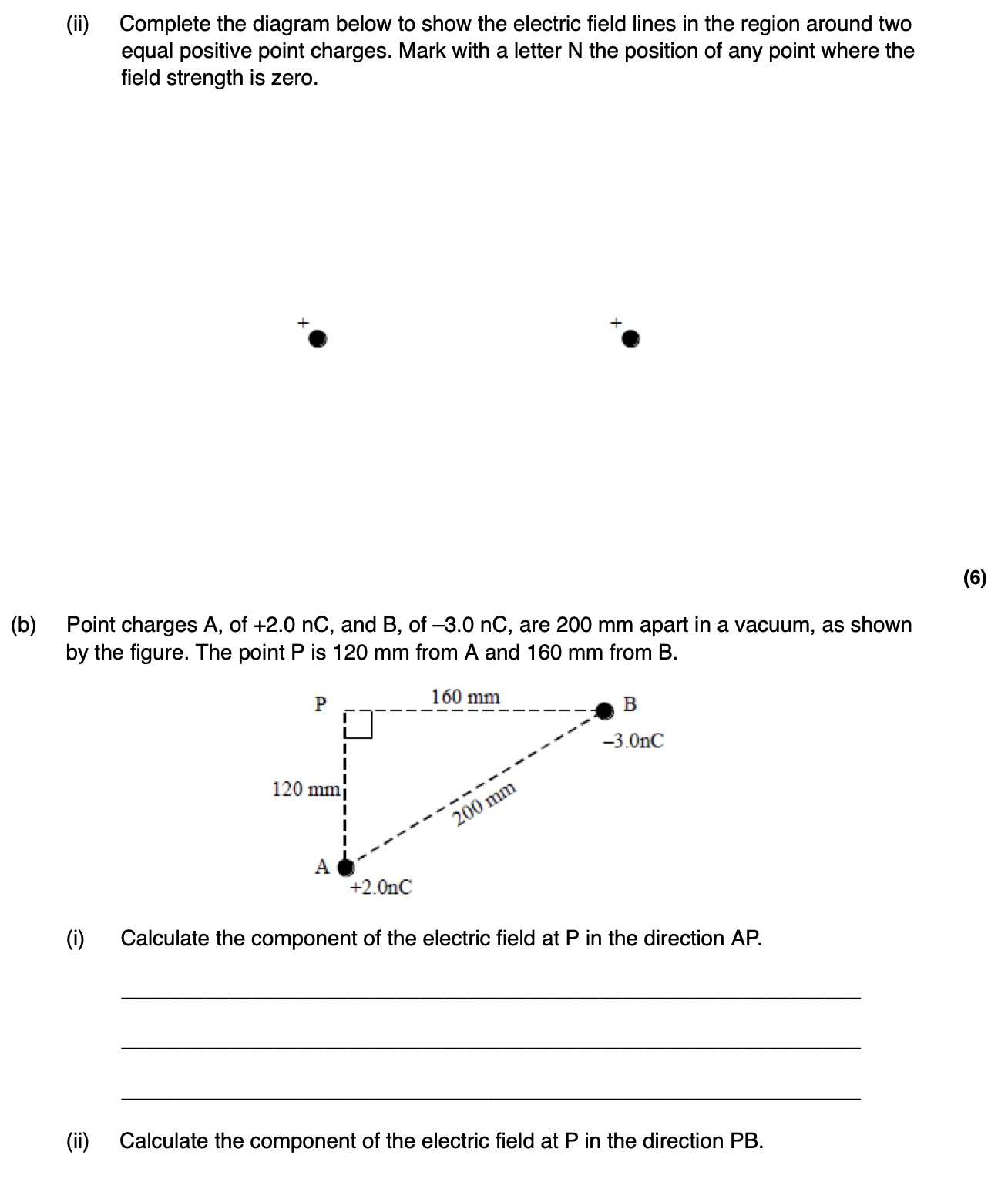
How do you find the resultant electric field or potential at a point due to multiple charges?
Field Strength: Calculate the vector sum of the individual electric fields.
Potential: Calculate the scalar sum of the individual electric potentials.
one key similarity between electric and gravitational fields.
Both follow an inverse square law with distance
two key differences between electric and gravitational fields.
Force: Gravity is always attractive; electric forces can be attractive or repulsive.
Source: Gravity depends on mass; electric forces depend on charge.
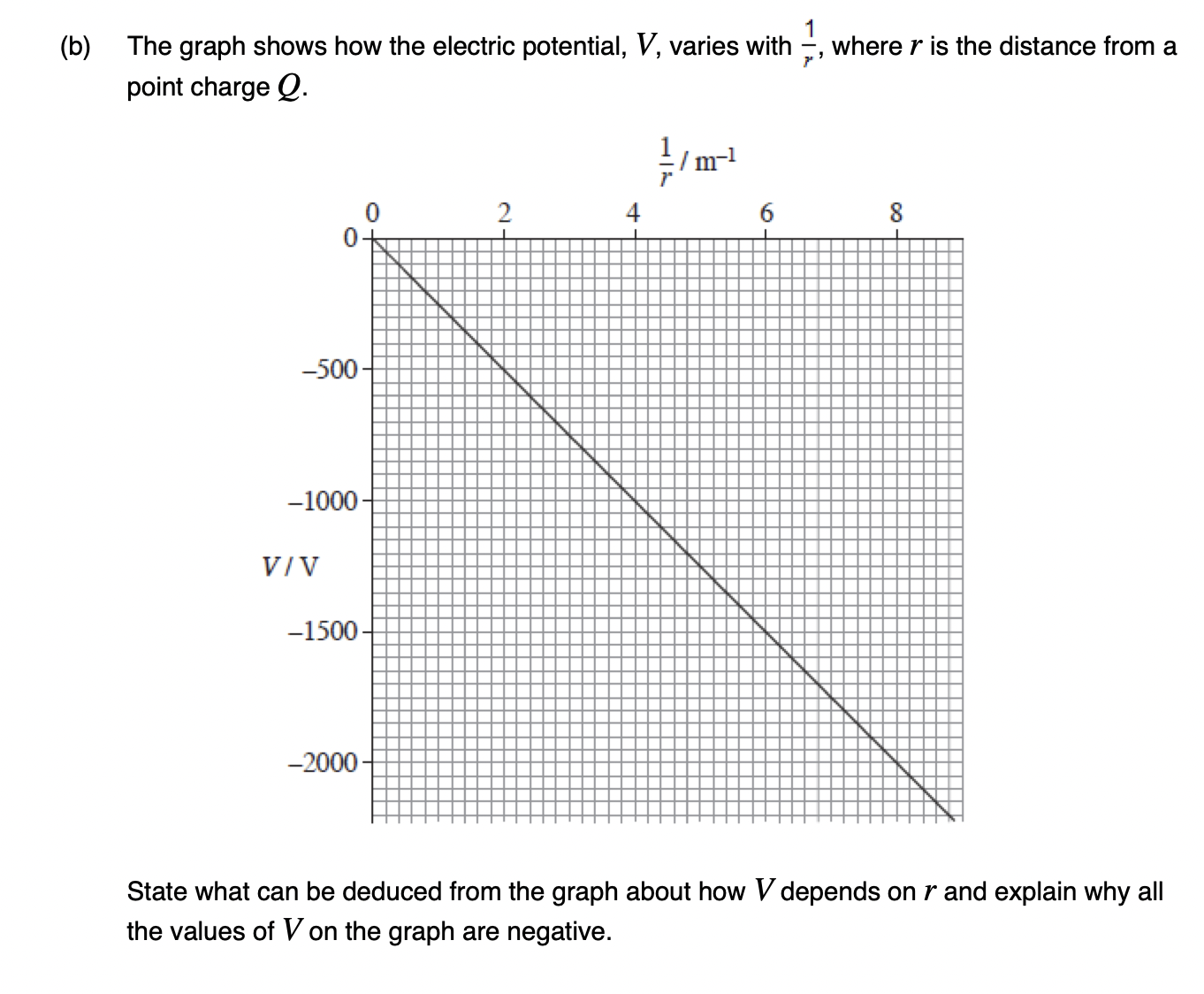
What is the relationship between potential and field strength for a radial field?
The electric (or gravitational) field strength is equal to the negative of the potential gradient. E = -dV/dr (and similarly for g).
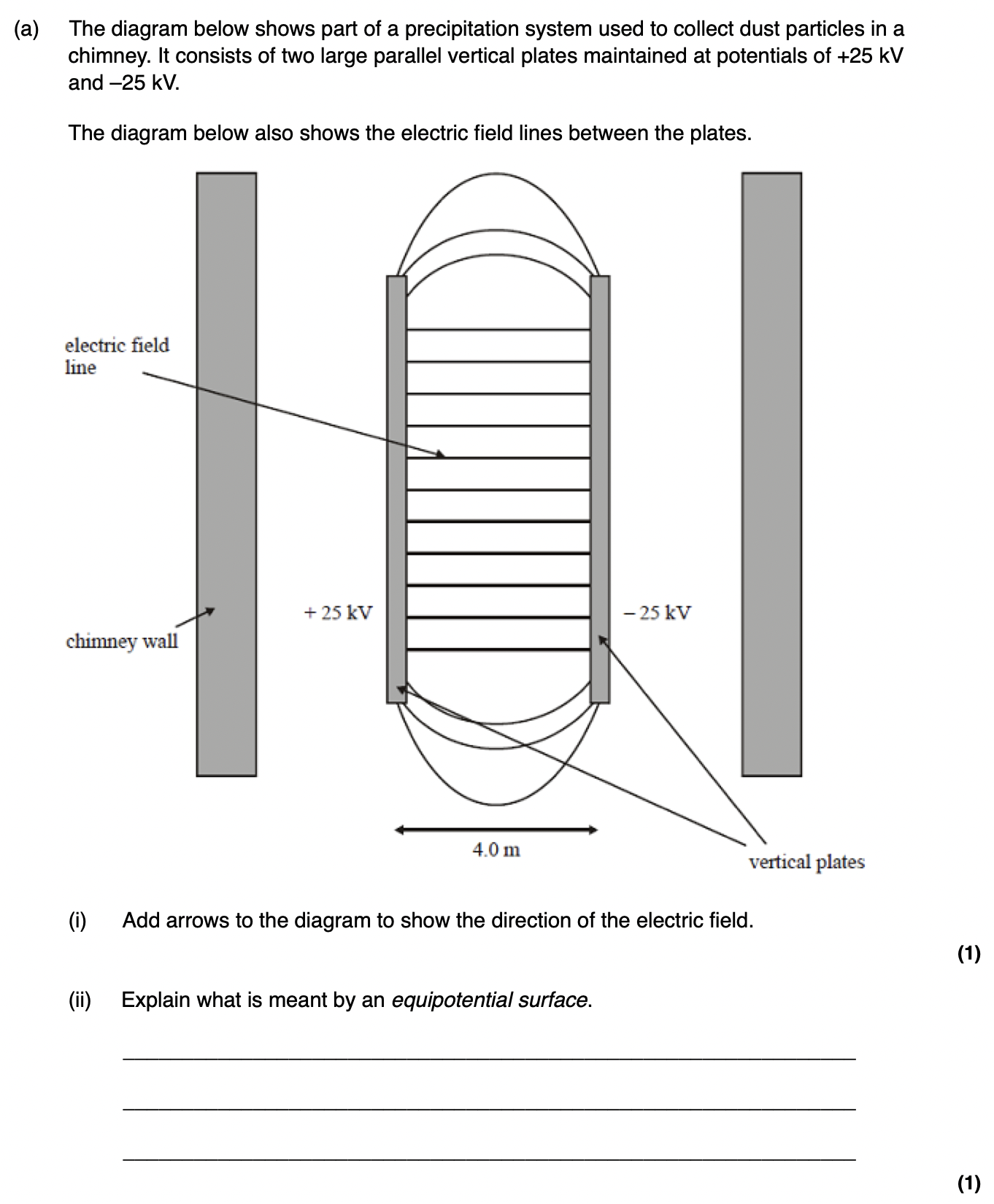
equipotential surfaces
Surfaces on which the potential is constant. No work is done moving a charge (or mass) along an equipotential.
How are equipotential surfaces related to field lines?
Equipotential surfaces are always perpendicular to field lines
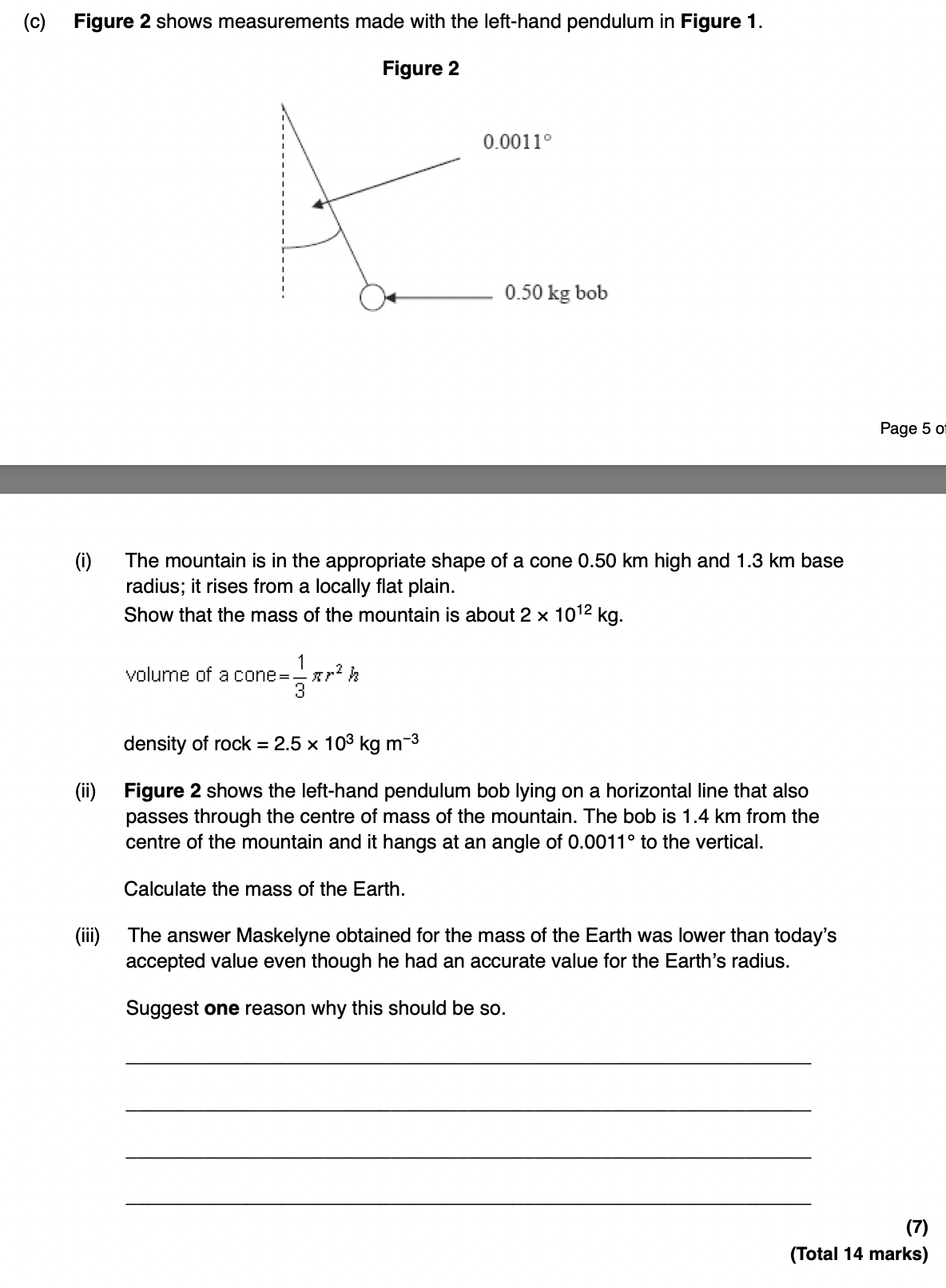
escape velocity
the minimum speed an object must have in order to escape a bodys graviational field (once it gets to infinity v=0)
all KE converted to GPE at infinity