Human health and diseases
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
zoology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Innate immunity and acquired immunity difference in terms of presence, specificity, memory
innate-
present since birth or inborn
no specificity means treat all pathogens same
no memory
Acquired
gained during lifetime or adaptive immunity
specific
memory based (memory cells are there from first encounter from pathogen)
What are 4 barriers of innate immunity
and line of defense
physical barrier
physiological barrier
both are 1st line of defense
cellular barrier
cytokine barrier
both are 2nd line of defense
physical barrier examples
skin
mucous coating of GI tract, respiratory tract, reproductive tract
physiological barrier examples
tears
saliva with antibacterial enzyme Lysozyme
acid in stomach
cellular barrier examples
neutrophils (PMNL)poly morpho nuclear lymphocyte
macrophages and monocytes (phagocytic)
NK cells (natural killer) (target tumor cells) (non-phagocytic) (type of leucocyte)
cytokine barrier examples
Interferons are proteinaceous and they are secreted by virally infected cells to protect normal non infected cells

plasma

both statement correct

cytotoxic t cell

attenuated pathogens
3rd line of defense is
acquired immunity
primary immune response is slow because memory cells formed while secondary immune response is rapid and highly intensified
true false
true
secondary response also called
amnestic response
cells involved in humoral immunity
humor= blood
B- lymphocytes
plasma B cells/ effector B cells= produce antibodies
memory B cells
cells involved in cell mediated immunity and their functions
T lymphocytes
Helper T cell: help Tc cell and also help in prodycing antibodies from B lymphocytes
cytotoxic/ killer T cell: directly kill pathogen
suppressor T cell: suppress Th and Tc to regulate immune response
Memory t cell
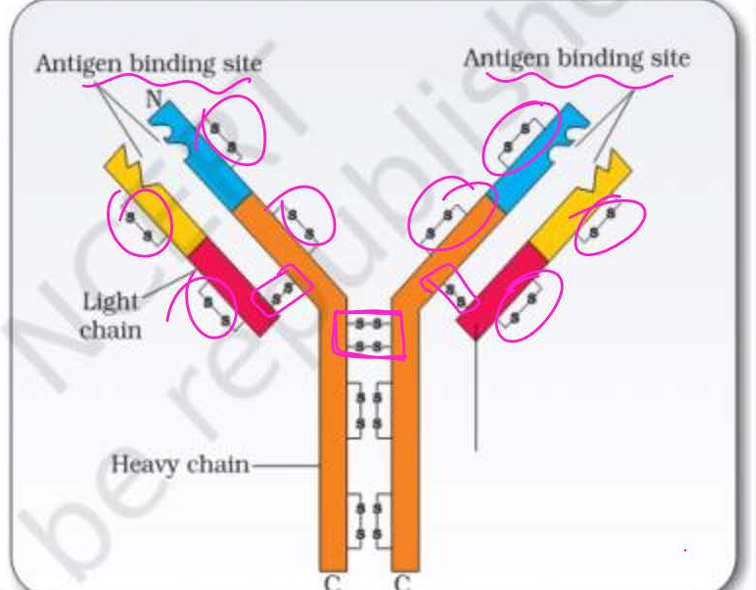
structure of immunoglobulins or antibody is made of
proteinaceous structure of glycoprotein
represented as H2L2
Heavy chain ~ 50 kDa
light chain ~25 kDa
antigen binding site also called____
present towards which terminal
Paratope
N terminal
1) between two heavy chain how many disulphide bonds
2) between one heavy and one light chain how many disulphide bonds
3) total disulphide bonds present
2
1
16
Type of Ig with percentage and function
Ig G: 75-80% crosses placenta barrier
Ig A: 10-15% found in colostrum and exist as dimer
IgM: 7-10% heaviest antibody and exist as pentamer
IgD: 1%
Ig E: less than 1% least
found in allergic reactions
primary and secondary immune response are controlled by special cells called
B lymphocytes
T lymphocytes
T lymphocytes produce an army of proteins in response to pathogen
true false
False
B lymphocytes produce an army of proteins in response to pathogen. The T lymphocytes do not produce antibodies but help B cells to produce them
when a host is exposed to antigens which may be in the form of living or dead microbes or proteins, antibodies are produced in host body
true false
true
conditions for organ transplant
blood type matching
tissue matching or MHC matching
Major Histocompatibility complex
Vaccines are prepared from
attenuated pathogens

a is false
b is true
not lymphoid organs
lymph nodes

immune system attacks its own body

both true

both true

both true
what is responsible for graft rejection
Cell mediated immunity or T lymphocytes
Active and passive immunity difference
Active Immunity
response is slow and long lasting
Body produces its own antibodies
passive immunity
response is fast and short lasting
readymade antibodies given
examples of natural and artificial active and passive immunity
natural active - when a pathogen enters a body
artificial active- vaccination by giving weak or killed pathogens so antibodies produced in body
natural passive- IgA by colostrum given to baby and IgG by placenta to foetus
artificial passive- Antivenom and anti-Tetanus serum
Good humor hypothesis was given by
Hippocrates
Balance of certain fluids make us healthy
who disproved Good humor hypothesis
William Harvey after discovery of double circulation
Person with ____ has hot personality and would have___
Blackbile
fever
Bacterial diseases examples and causal bacteria
Typhoid- salmonella typhi
pneumonia- streptococcus pneumoniae and haemophilus influenzae
diphtheria- cornybacterium diphtheri
plague- yersinia pestis
dysentry- shigella
Typhoid
location
mode of transmission
symptoms
its enters small intestine through contaminated food and water and migrates to other organs through blood
sustained high fever 39-40 stomach pain
Intestinal perforation and death may occur in serious cases
widal test confirms
typhoid
Typhoid mary did what?
Mary mallon was a cook by profession and spread typhoid for years
Pneaumonia
location
mode of transmission
symptoms
it usually affects the lungs and alveoli
spreads by aerosols and droplets and even by sharing utensils
symptoms
fever chill cough
fingernails and lips turn bluish in severe cases
1st 2nd and 3rd generation vaccine difference
1st- killed or weak/attenuated pathogen to generate immune response memory cells
2nd- protiens or toxins released by pathogen
3rd- DNA of pathogen
For Hepatitis, both 2nd and 3rd genenration vaccine used How?
Recombinant protein is made using rDNA within yeast
rDNA= recombinant dna technology
____ has allowed production of antigenic polypeptides of pathogen in yeast or bacteria
recombinant dna technology
Autoimmune diseases examples
myasthenia gravis
rheumatoid arthritis
graves disease
what is exaggerated immune response called and losing power of discriminating between self and non self cells?
1st is allergy
next is autoimmune disorder
symptoms of allergy
redness, sneezing, low blood pressure due to vasodilation, breathing difficulty due to vasoconstriction,
process of allergy
IgE released from B cells
IgE binds to mast cell or basophil to sensitize them
on encounter with allergen they release histamine and serotonin
to reduce the symptoms of allergy which drugs given
anti histamine
adrenaline
steroids
allergic reaction can be fatal resulting in
anaphylactic shock
state primary lymphoid organs and their characteristics
Bone marrow- site of production of both B and T cell, B cell mature here
Thymus- lobular structure of heart where T cells mature
primary and sec lymphoid organs difference
pri-production and maturation of lymphocytes occur and lymphocytes become antigen sensitive
sec- interaction of antigen and antibody encounter and antibody proliferate into effector cell
shape of spleen and it mainly contains
bean shaped
mainly contains lymphocytes and macrophages or phagocytes
spleen acts as
large reservoir for erythrocytes
filter for trapping blood borne microorganisms
examples of sec lymphoid organs
spleen
lymph node
MALT containing peyers patches of small intestine, tonsils, apendix
dengue and chikungunia is caused by rna virus or dna virus?
which mosquito causes
RNA virus
aedes mosquito causes both dengue and chikungunia
Ascariasis
location
mode of transmission
symptoms
small intestine
eggs of parasite are released through faeces and contaminates fruits or vegetables and passed to healthy person
MIA
muscle pain, internal bleeding, anaemia
Wuchereria/ Elephantiasis/ Filariasis
location
mode of transmission
symptoms
lymphatic vessels
bite of female culex mosquito
chronic inflammation of lymphatic vessels of lower body parts and genital area
protozoal diseases examples
Amoebiasis
malaria

asexual asexual
amoebiasis
location
mode of transmission
symptoms
large intestine
through contaminated food and water by housefly as mechanical carrier
excess mucous and blood in faeces
Host of malaria and their mode of reproduction
primary- mosquito- sexual stage
secondary- humans- asexual stage
life cycle of plasmodium
infective stage sporozoite enters liver hepatocytes
asexually divide and after some time cell rupture
the parasite reenters liver or mainly attacks RBC and asexually divide
RBC also burst and haemozoin released which causes chills and fever
parasite reenters RBC and forms sexual stage only formation mega and micro gametocyte
anopheles bites and picks these sexual stages
gametocyte forms ova and sperm in mosquitos gut. these are not formed in human due to high temp
form zygote then turns into sporozoite and stored in salivary glands of mosquito
1st case of AIDS reported in year ___ and has killed more than___
world aids day
1981 in us
killed more than 25 million
1 december
causative agent of aids and mode of transmission
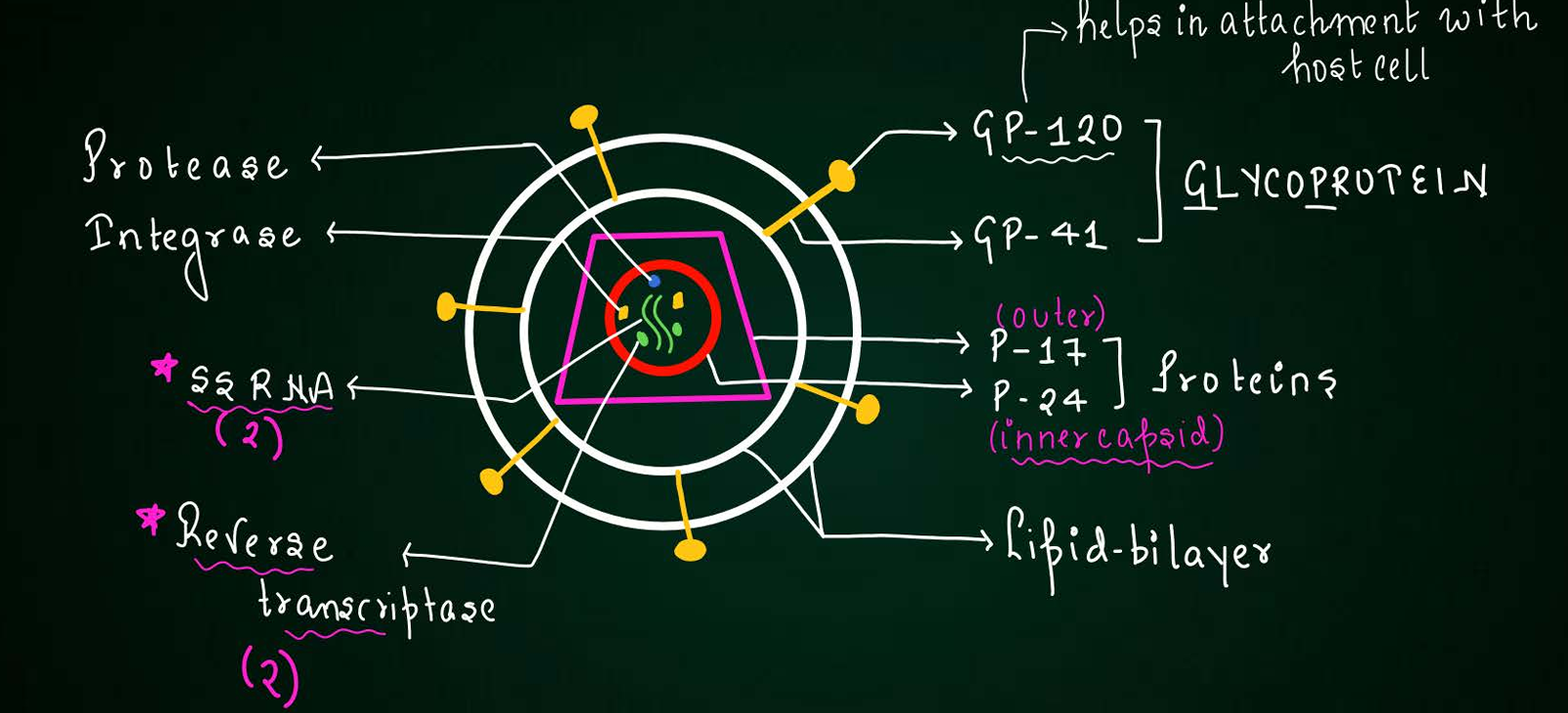
HIV a retrovirus
sexual intercourse
mother to child
sharing of needles and syringe
blood transfusions
structure of HIV
GP numbers
number of reverse transcriptase
ds RNA or ssRNA
AIDS is a congenital disease
true false
false
Diagnosis of AIDS can be done by
ELISA enzyme linked immuno sorbent assay
PCR
Western blotting confirmatory test
Anti retroviral drugs can cure AIDS
true false
false
it can only delay death
Process of HIV virus taking over cells in body
virus enters macrophage first and ssRNA replicated to form dsDNA with help of enzyme reverse transcriptase
this viral dna gets incorporated into host dna and directs the infected cells to produce virus particles
macrophages continue to produce virus and called HIV factories
virus attacks T helper cells and immune system gets weak. number goes from 1200 to 200
during this patients has bouts of fever diarrhoea and weight loss
Cancer 4 characteristics
Non infectious
Cancer cells do not die natural death ie Apoptosis
No contact inhibition, ie do not stop dividing on contact with young cells
Derive nutrition from normal cells and deprive them of nutrition
Regulatory genes present to prevent cancer
Protooncogenes or cellular oncogenes- these are normal genes of normal cells, on activation by cancer cells they convert into oncogenes
Tumor suppressor cells- these cells regulate and act as check point for the cell cycle. Do not let abnormal cell pass through cell cycle but if this gene gets mutated then cancer may occur