The liver
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/53
Last updated 7:55 PM on 4/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
1
New cards
What are liver cells called?
Heapatocytes
2
New cards
What connects the liver to the small intestine and supplies it with nutrients?
Portal vein
3
New cards
What supplies the liver with oxygenated blood?
Hepatic artery
4
New cards
What histological structures is the liver made up of?
lobules
5
New cards
How many lobes does the liver have?
2, left and right
6
New cards
Where is the liver located?
Right side of the abdomen, below the diaphragm
7
New cards
What transports deoxygenated blood away from the liver?
Hepatic vein
8
New cards
What main nutrients can the liver store?
* glycogen
* iron
* vitamin A
* vitamin D
* iron
* vitamin A
* vitamin D
9
New cards
What are the 4 main functions of the liver?
1. controlled storage and release of key nutrients
2. detoxification of harmful ingested substances
3. breakdown of blood cells and production of bile salts
4. production of plasma proteins
10
New cards
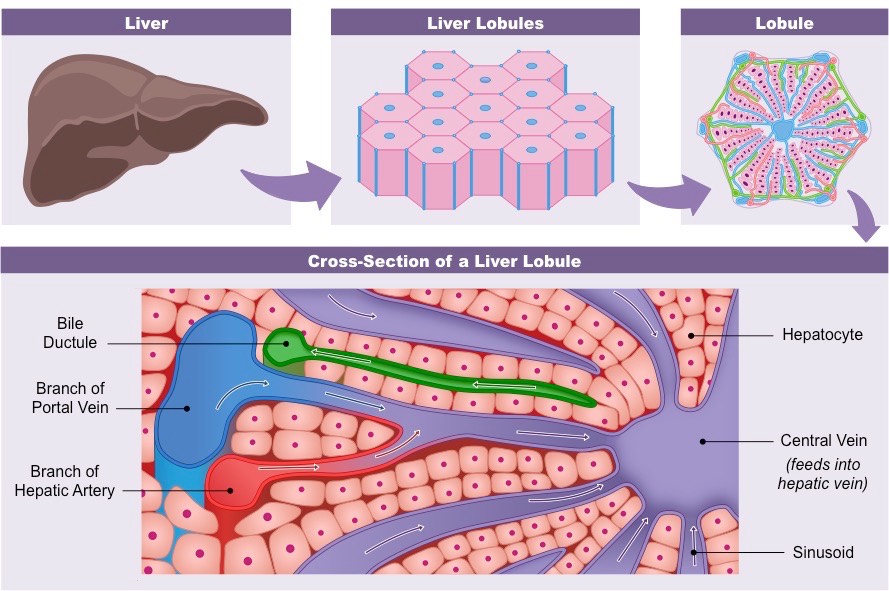
Describe the following picture and what is happening.
* hepatic artery provides oxygen
* portal vein provides nutrients
* hepatocytes produce bile which drains into the bile ducts
* sinusoids allow for the exchange of materials within the hepatocytes
* portal vein provides nutrients
* hepatocytes produce bile which drains into the bile ducts
* sinusoids allow for the exchange of materials within the hepatocytes
11
New cards
What vessels transport bile t bile ducts?
Caniculi
12
New cards
What are sinusoids?
Capillaries (blood vessels) with increased permeability (incomplete basement membrane and intercellular gaps)
13
New cards
Why is permeability of sinusoids important?
It allows for larger molecules to pass through
14
New cards
What are the two layers of a capillary and how are they different in sinusoids?
* Endothelial layer (inside)
* Basement membrane (outside)
* In sinusoids there are intercellular gaps in the endothelial layer and the basement membrane is incomplete
* Basement membrane (outside)
* In sinusoids there are intercellular gaps in the endothelial layer and the basement membrane is incomplete
15
New cards
What does the liver do with nutrients received from the portal vein?
1. It converts the nutrients into forms that can be stored or used
2. Mediates transport of nutrients in various tissues
16
New cards
What 3 biological molecules does the liver metabolise?
1. Carbohydrates
2. Protein/amino acids
3. Lipids
17
New cards
How does the liver regulate blood sugar?
It takes up excess glucose in the bloodstream and stores it as glycogen
18
New cards
What does the liver do if blood sugar levels start to drop?
breaks down glycogen into glucose and exports it to body tissues
19
New cards
What happens when hepatic glycogen reserves become exhausted?
the liver synthesises glucose from other sources (eg fats)
20
New cards
What pancreatic hormones aid the liver in regulating blood sugar?
Insulin (high blood sugar)
Glucagon (low blood sugar)
Glucagon (low blood sugar)
21
New cards
How many essential amino acids are there?
9
22
New cards
What is the difference between an essential amino acid and a “regular” amino acid?
The body can only get non-essential amino acids through the diet whereas “non-essential” amino acids can be synthesised through transamination (if essential amino acids are in excess).
23
New cards
Why is it important that the liver metabolises amino acids?
They can not be stored by the body and must be broken down. The nitrogen of the amine group (NH2) can be toxic.
24
New cards
What are the steps of amino acid metabolism?
1. Transamination
2. Deamination
3. Urea synthesis
25
New cards
What happens in transamination?
Amino acid 1 + Keto acid 2
26
New cards
What happens in deamination?
The amine group is removed from the amino acid which forms ammonia and a keto acid
27
New cards
What two things are necessary for the occurrence of deamination?
Electron/Hydrogen carriers (NAD)
Enzymes (eg glutamate dehydrogenase)
Enzymes (eg glutamate dehydrogenase)
28
New cards
What happens in urea synthesis?
ammonia is converted to urea (through the urea cycle) which can then be excreted by the kidneys
29
New cards
What molecule is needed to convert ammonia to urea?
ATP (3 per molecule)
30
New cards
What does the liver do to excess carbohydrates and proteins?
converts them to into fatty acids and triglycerides
31
New cards
What important molecules does the liver synthesise (other than amino acids)?
cholesterol
phospholipids
phospholipids
32
New cards
What do LDL and HDL stand for?
Low density lipoprotein
High density lipoprotein
High density lipoprotein
33
New cards
What is the role of LDLs?
Transports/stores cholesterol within the blood stream
34
New cards
Why can the transport/storage of cholesterol in the bloodstream by LDLs be problematic?
Excess can cause plaque or blockages which clogs arteries and harms the circulatory system
35
New cards
What is the role of HDLs?
Regulate LDL storage and promote excretion (prevent blockage of bloodstream)
36
New cards
What happens to surplus cholesterol?
It is converted into bile salts by the liver which can be excreted via the bowels
37
New cards
When will the liver break down amino acids?
When they are in excess
38
New cards
What group of enzymes mediates the conversion of toxins in the liver?
Cytochrome P450
39
New cards
What is a conjugation reaction?
Attaching a group (hydrophilic) to a molecule that was toxic to make the molecule water soluble
40
New cards
Where in hepatocytes are plasma proteins synthesised?
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
41
New cards
Where are plasma proteins found?
In the blood (blood plasma)
42
New cards
What are the three major types of plasma proteins?
Albumin, Globulins, Fibrinogens
43
New cards
What is the function of the plasma protein Albumin?
Maintains osmotic pressure in the blood
44
New cards
What is the role of Fibrinogens in the blood?
Involved in blood clotting
45
New cards
Why do R.B.Cs need replacing?
They die due to not being able to divide (no nucleus)
46
New cards
What is the medical term for red blood cell?
Erythrocyte
47
New cards
What cells in the liver are responsible for breaking R.B.Cs down?
Kupffer cells
48
New cards
What is a Kupffer cell?
Type of phagocyte (white blood cell)
49
New cards
What do Kupffer cells break haemoglobin down into?
Globin and a iron containing haem group
50
New cards
An iron containing heme group is broken down into?
Bilirubin and iron
51
New cards
How does bile travel from the gall bladder to the small intestine?
Bile duct
52
New cards
What do the sinusoids connect to?
A central vein which connect to the hepatic vein
53
New cards
What causes Jaundice?
A build up of Bilirubin
54
New cards
What are symptoms of Jaundice?
Yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes