Unit 5.3 : Money Growth & Inflation ; Unit 5.4 : Gov Deficits & Nat Debt; Unit 5.5 : Crowding Out
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
MV = PY
Quantity Theory of Money
2
New cards
money supply
M
3
New cards
velocity of money
V
4
New cards
velocity of money
the average times a year money is spent and re spent in a year; ex. if Real GDP is $400B but amount of money in economy is $100B
5
New cards
price level
P
6
New cards
quantity of output
Y
7
New cards
V; Y
Assume ____ is relatively constant because people's spending habits aren't quick to change and ____ isn't affected by quantity of money because it's based on production, not value of stuff produced
8
New cards
the price level increases unless we can increase Y
If the government increases amount of money (M), what will happen to P?
9
New cards
Short-run spending eventually leads to higher resource prices and inflation. If inflation is bad enough, banks don't lend and economy tanks
What happens in the long-run when the central bank increases in money supply?
10
New cards
Monetary policy can increase real output in short-run
If the last question is true, why do many economists support expansionary monetary policy?
11
New cards
deficit spending
What's the trade off of increasing government spending without increasing taxes to close a recessionary gap?
12
New cards
budget deficit
when annual government spending and transfer payments are greater than tax revenue
13
New cards
budget surplus
when annual government spending and transfer payments are less than tax revenue
14
New cards
National Debt
the accumulation of all budget deficits over time
15
New cards
annual deficit; national debt
If the government increases spending without increasing taxes they'll increase the _____ and the _____
16
New cards
entitlements
a federal program that requires payments to any eligible person or unit of government; this mandatory spending must be paid (ex. Social Security)
17
New cards
crowding out
adverse effect of government borrowing on interest-sensitive private sector spending
18
New cards
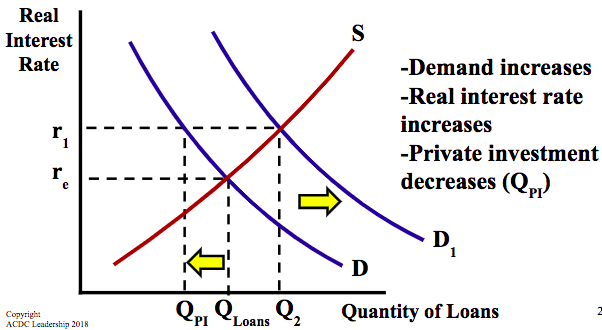
demand increases, real interest rate increases, and investment decreases (Qpi)
Assume government increases deficit spending, what happens to demand of loanable funds, real interest rate, and private domestic investment?
19
New cards
falls
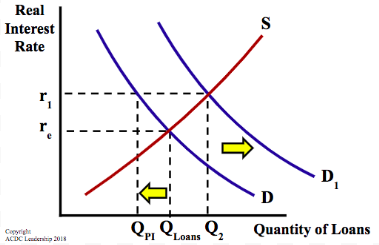
the total number of loans increases to Q2, but that was due to public borrowing; private borrowing ____ to Qpi
20
New cards
less economic growth because investment decreases ... less capital stock
What is the long run impact of a higher real interest rate?