Thalamus
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Describe the region where the Thalamus (Diencephalon) is found
Found between the Telencephalon (cerebrum) and the Mesencephalon (midbrain)
Diencephalon is separated by the third ventricle
Medial to the posterior limb of the internal capsule
Involves 3 structures:
Thalamus: sensory relay, motor coordination, higher cognitive functions
Hypothalamus: body homeostasis through autonomic and hormone functions
Subthalamus: motor coordination (as part of the basal ganglia)
What are the primary function of the Thalamus?
Sensory
Thalamic neurons are the final neurons in all sensory pathways to the cortex (except for olfaction!)
Plays an important role in sleep - decreasing cortical activation, and therefore, our conscious perception of sensations
Motor
Takes part in motor circuits interconnecting basal ganglia and cerebellum with the motor cortices
Involved in planning, execution, coordination, and control of movement
Limbic
Connections with limbic areas of the cortex for memory and emotion
Plays a role in linking memory and emotions to sensations and behaviours
Cognitive
Facilitates attention, alertness, and consciousness through connections with the prefrontal cortex
Supports higher cognitive functions like learning, memory consolidation, and decision-making
Describe the general structure of the Thalamus - Groups and overall structure
Thalamus is separated into 4 regions:
Intralaminar Group
Anterior Group
Medial Group
Lateral Group
Which nuclei are characterised as ‘Specific Sensory’ nuclei? What are their general functions?
Ventral Posterior Lateral Nucleus
Receives input from Medial Lemniscus and Spinothalamic tract
Outputs through superior thalamic radiations to ‘body regions’ of S1
Ventral Posterior Medial Nucleus
Receives input from Trigeminothalamic tract (principal and spinal trigeminal nuclei)
Outputs through superior thalamic radiations to ‘head regions’ of S1
Lateral Geniculate
Visual Pathway
Output to V1 via retrolenticular part of internal capsule
Medial Geniculate
Auditory Pathway
Output to A1 via sublenticular part of internal capsule
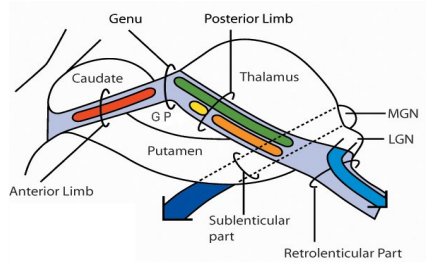
Which nuclei are characterised as ‘Specific Limbic’ nuclei? What are their general functions?
Anterior Nucleus
Input from limbic areas (hippocampus) of the temporal lobe via the hypothalamus
Outputs to the limbic areas (cingulate gyrus) via anterior thalamic radiations
Which nuclei are characterised as ‘Specific Motor’ nuclei? What are their general functions?
Ventral Anterior Nucleus
Receives input from basal ganglia motor loop (GBi)
Ventral Lateral Nucleus
Receives input from cerebellum (interposed and dentate nuclei)
Output to all motor cortices via superior thalamic radiations
Which nuclei are characterised as ‘Association’ nuclei? What are their general functions?
Medial dorsal and Lateral posterior nuclei
Connections between limbic areas and parietal cortices
Lateral dorsal nucleus
Connections between basal ganglia, limbic areas, and prefrontal cortex via
anterior thalamic radiation
Through its connections with the basal ganglia and association cortices, it
may play a role in the decision-making process in habitual target selection
Pulvinar Nucleus
Connections between association cortices of frontal, temporal, parietal and
occipital lobes
Role in sensory integration
Which nuclei are characterised as ‘Association’ nuclei? What are their general functions?
Intralaminar and Midline nuclei
Connections between reticular formation, basal ganglia, unimodal and
multimodal association cortices
May play a role in coordinating motor functions for goal-based movement sequences