SPAA 648 - Auditory Nerve Physiology - E5
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Cochlear Graded Potential
Graded Potential → exceeds threshold of auditory nerve fiber and creates an action potential
Amplitude increases in proportional to the amount of the stimulation
Ex. cochlear microphonic (OHCs) and summating potential (IHCs)
HC needs to reach threshold for depolarization for an action potential to be triggered
Auditory Nerve Action Potential
Resting → deporlaized → repolarizing → resting
All-or-none electrical discharge → meaning it MUST reach threshold to be triggered
*A stimulus increases the firing rate
Action Potential (Firing)
The discharge of a spike (action) potential
Action Potential (Firing/Discharge Rate)
The number of action potentials discharged per second
Action Potential (Spontaneous Rate (SR))
The rate at which a neuron fires on its own when there is no stimulation
Auditory nerve bundles encode what information?
Frequency and intensity of sound input
Need to preserve information from the cochlea to be send to a higher nuclei (auditory nerve)
Intensity Coding (Continued)
Fibers working together to encode a wide intensity range but for the same center frequency!
Frequency Coding (Depends On?)
The rate at which an auditory nerve fiber discharges depends on the intensity and frequency of the sound input
Depends on:
Characteristic Frequency (CF) of nerve fibers - where does it happen along the nerve fiber?
Firing Pattern of nerve fiber - afferent → Type 1 (1-8 fibers per IHC)
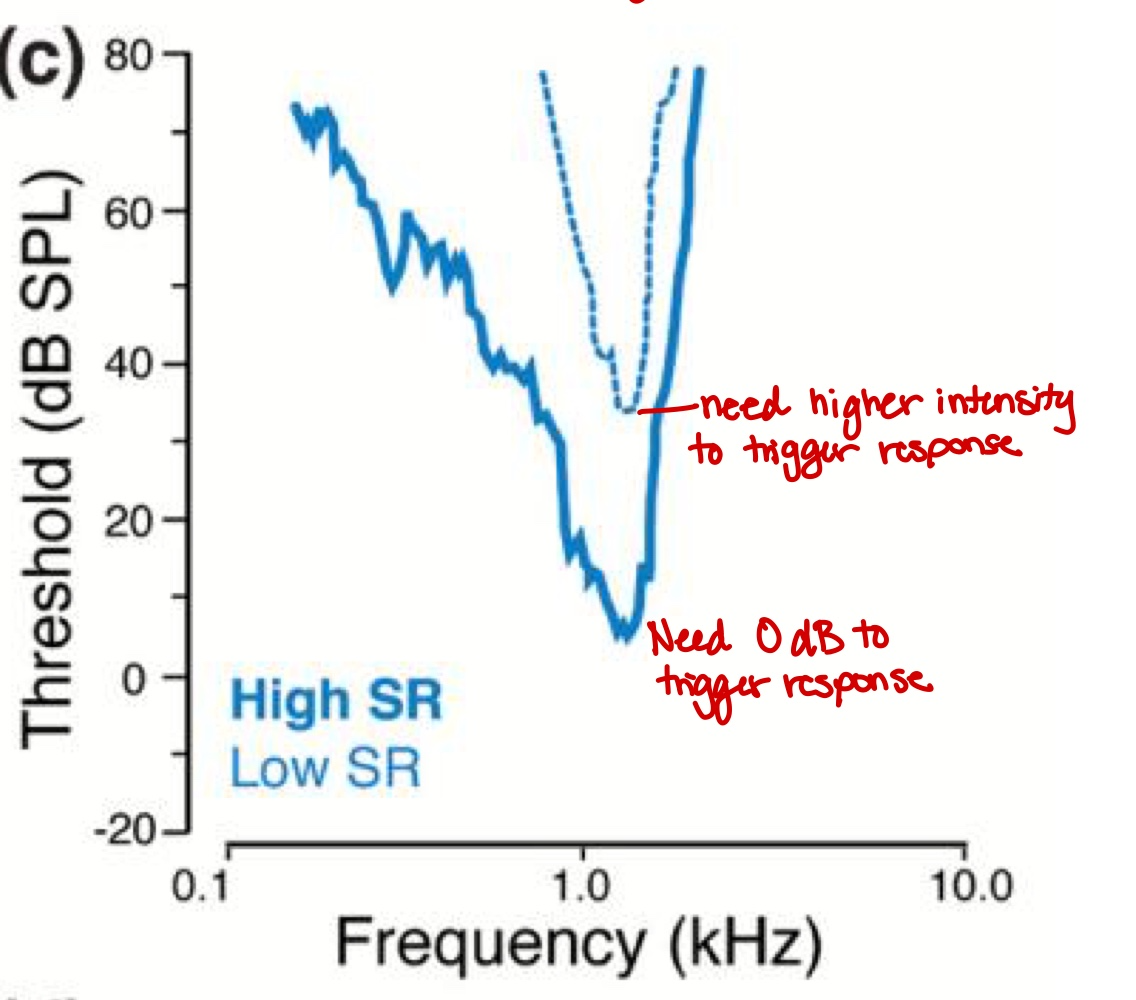
Characteristic Frequency (CF) of a Neuron (Tuning Curve)
The frequency of the lowest threshold/greatest firing rate
Tuning Curve - the threshold of an auditory nerve fiber plotted as a function of frequency
Low CFs - broader (not sharp) & symmetric
High CFs - narrower (more sharp) & asymmetric
Frequency Coding (Firing Pattern & PSTH)
Firing Pattern - the manner in which spikes are elicited over time (after there’s a stimulus)
Shows were the highest amplitude for the peak is
Post-Stimulus Time Histogram (PSTH) - number of spikes that occurred during a period of time after an acoustic stimulus is applied
Can revealed firing patterns
Spikes are phase-locked to cycles of the sine wave
Frequency Coding (Phase Locking)
Phase Locking of Auditory Nerve Fiber - the time locking of neural discharges to the acoustic waveform
Low Frequency - might be okay to fire and stop at each peak
High Frequency - maximum firing rate is around 5000 Hz and anything higher will be hard for the nerve fibers to fire this fast at each peak
Frequency Coding (Volley Principle)
For a high frequency sound, other nerve fibers are recruited into action when one nerve fiber reaches its maximum firing rate
Group of neurons have to work together for high freq. sounds to encode the sound wave
Intensity Coding (Dynamic Range & Saturation)
Dynamic Range of a Neuron: (humans -10 dB to 110 dB; total range of 120 dB)
The range of intensity over which the auditory nerve fiber continues to respond with increasing magnitude
Dynamic range for MOST neurons is about 40 dB
Saturation - when the neuron’s response no longer increases as the stimulus level goes up
Related to the spontaneous rates (SRs) of the nerve fibers, until we have an action potential!
*Nerve fibers work together to encode for the intensity of a sound!
Intensity Coding (Spontaneous Rates)
Low: 0-0.5 spikes/s
Low SR Fibers - smaller in diameter, usually towards the modiolus, high thresholds, and wide dynamic range (40-60 dB range)
High: > 18 spikes/s
High SR Fibers - larger in diameter, usually towards the tunnel of Corti, low thresholds (0 dB), and narrow dynamic range (around 20-30 dB they STOP firing)