Astro exam 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What are the main properties of light?
Ray/Beam
Reflection
Refraction
Wave Behavior
Diffraction
Dispersion
Polarization
Interference
Particle Behavior
Photoelectric Effect
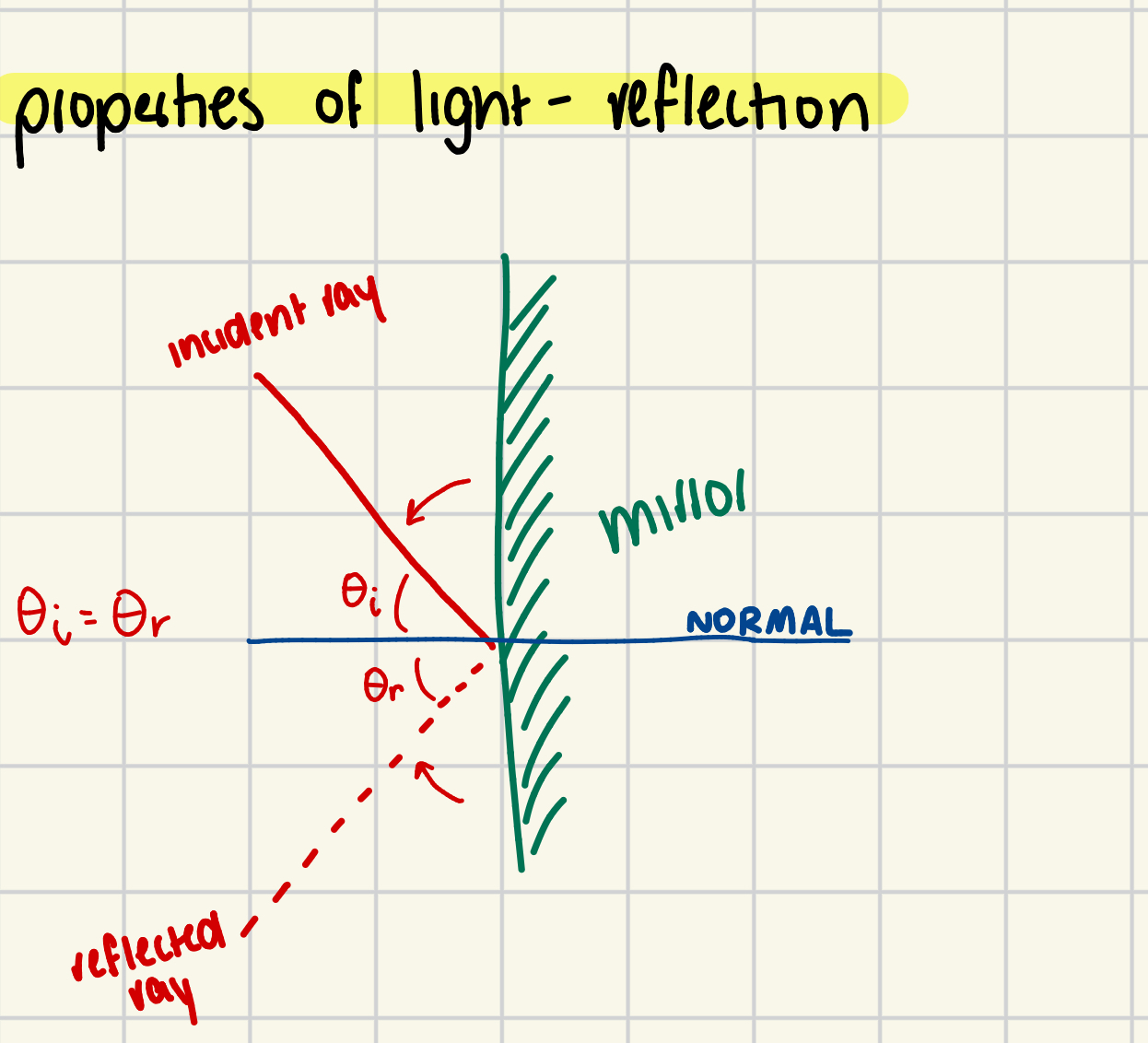
What is reflection in terms of light?
light bouncing off of a surface.
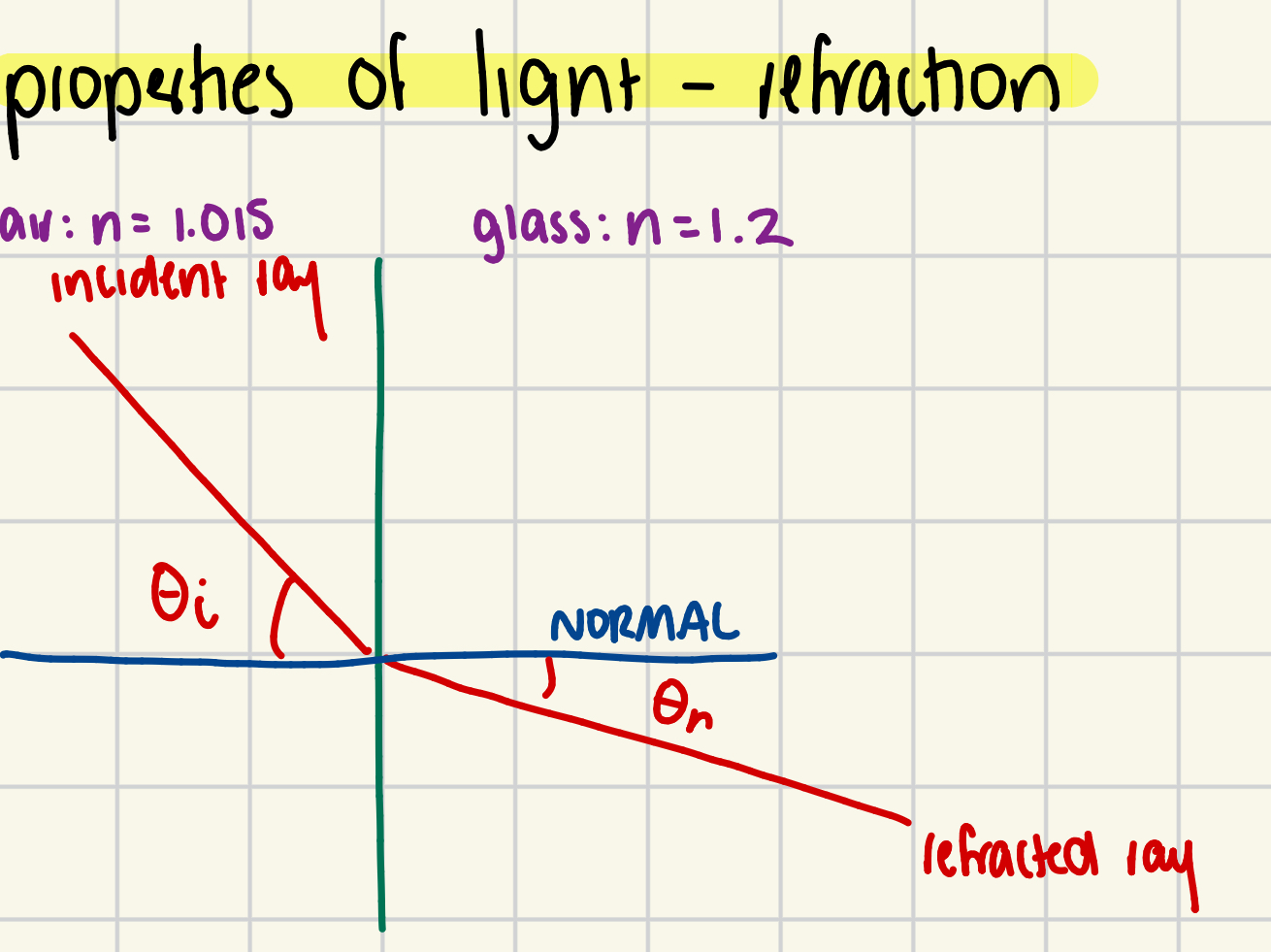
What is refraction in terms of light?
the bending of light as it passes through from one medium to another.
Small to large index of refraction (n) = light will bend toward normal
Large to small index of refraction (n) = light will bend away from normal
What is particle behavior in terms of light?
light behaves as photons, discrete packets of energy.
What is Constructive interference?
light waves overlap and amplify each other before continuing on their path.
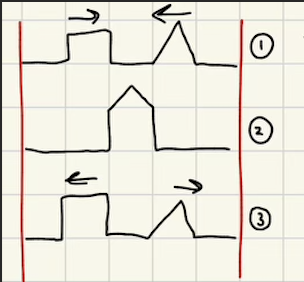
What is Destructive interference?
Opposite light waves cancel each other before continuing on their path.
What is the relationship between Wavelengths and photon energy?
shorter wavelength (higher frequency) → more energy & refraction/bluer light; longer wavelength (lower frequency) → less energy/redder light.
Subproperties of light as a ray?
reflection and refraction
Subproperties of light as a wave?
Diffraction
Dispersion
Polarization
Interference
Constructive
Destructive
What are the different kinds of interference (light as a wave)?
Constructive and destructive
Subproperties of the Particle properties of light?
Photoelectric effect
photon energy formula?
E = hc/λ
hc = light constant
λ = wavelength
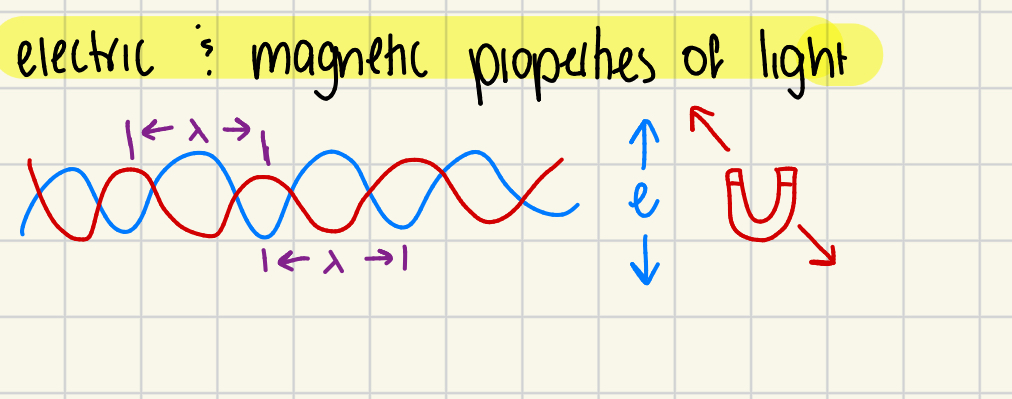
What are the electromagnetic properties of light (waves)?
• Light consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields perpendicular to each other.
- Electric and magnetic fields are always at 90° to each other.
• does NOT require a medium to propagate (generate).
WAVELENGTH = λ
How does light interact with human vision?
• Rods detect light intensity (brightness).
• Cones detect color; sensitive to red-green, blue-green, and violet-blue regions.
What is a light ray?
A straight-line path that light travels.
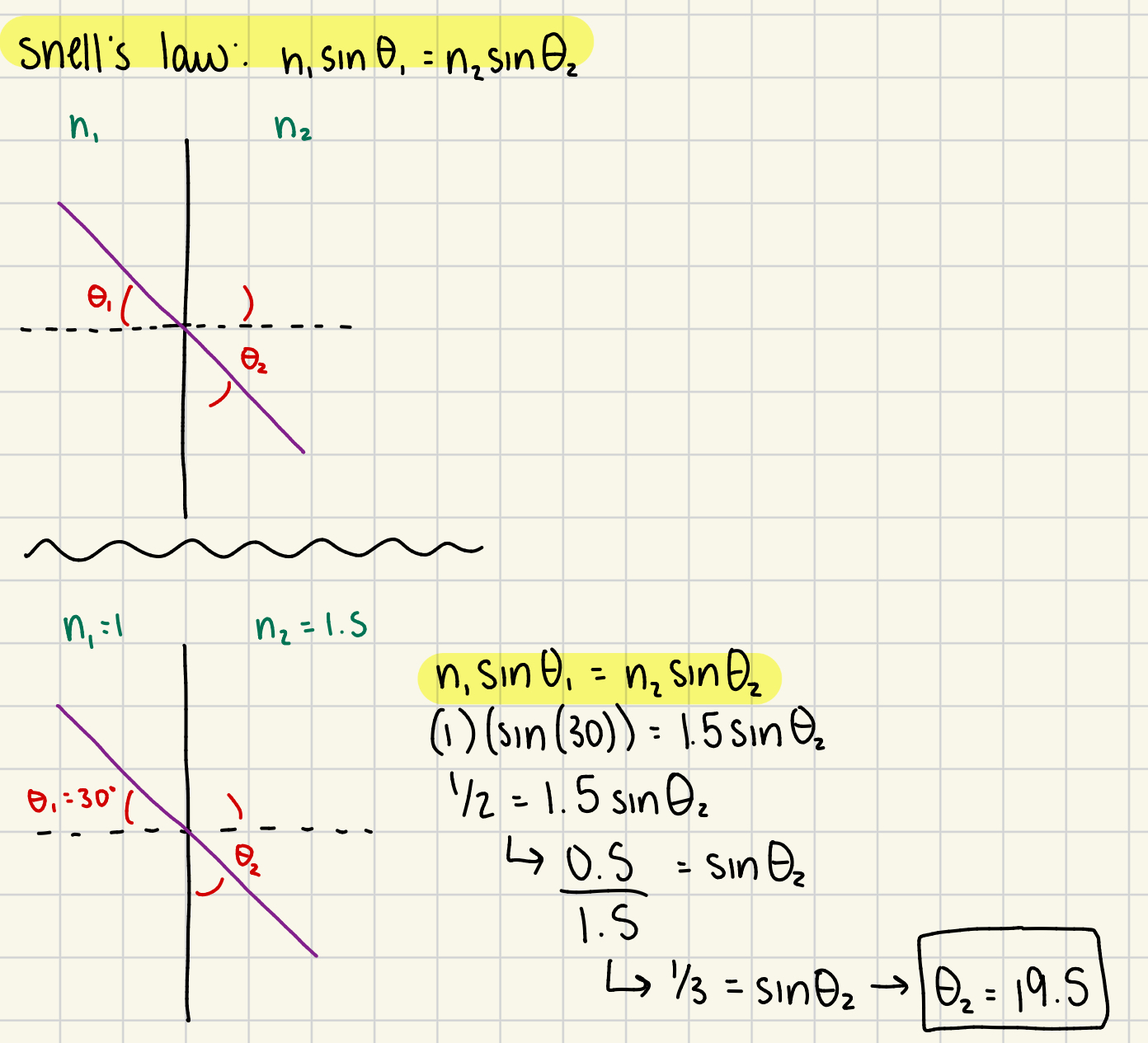
What is Snell’s law?
n1sin(θ)1 = n2sin(θ)2 - describes the angle of refraction between 2 media
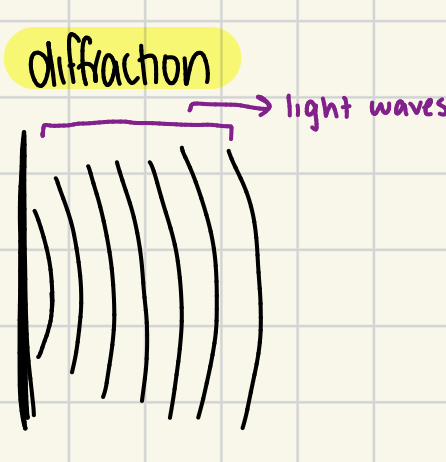
What is diffraction?
The spreading of light as it passes through an obstruction.
What is dispersion?
The splitting of white light into constituent colors under refraction through a prism.

What is polarization?
Restriction of the electric field components of light to a single plane.
What is interference?
Overlapping of light waves that can amplify (constructive) or cancel (destructive) each other.
What is the photoelectric effect?
When light with enough energy hits a surface, it can eject electrons; energy is carried by photons.
(Ephoton = hc/λphoton)

How does wavelength relate to photon energy?
Shorter wavelength → more energy; longer wavelength → less energy.
Order the visible colors from smallest to largest wavelength.
Violet (HIGH energy), Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red (LOW energy)
Order types of light waves from least to most energy.
Radio (LARGE wavelength), Microwave, Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet, X-ray, Gamma (SMALL wavelength)
What are the human-visible light wavelengths?
4000–7000 angstroms (400–700 nm).
What are rods responsible for?
Detecting light intensity.
What are cones responsible for?
Detecting color.
What is Kirchhoff’s FIRST law?
Any sound, liquid, or opaque gas that is heated above absolute zero will produce a continuous thermal radiation spectrum (LIGHT)
heated electrons produce light
How does tempurature affect molecular states?
increasing tempurature = solid → liquid → gas.
How does pressure affect molecular states?
Decreasing pressure = solid → liquid → gas.
Why is ice less dense than water?
Solid water molecules are less densely packed than liquid water molecules - cool tempuratures don’t agitate the molecules.
What is temperature?
Measure of atomic/molecular motion; quantifies kinetic energy.
What are the temperature points in degrees Fahrenheit?
0°F = coldest in Fahrenheit’s hometown, 32°F = water freezes, 100°F = cow’s internal temp, 212°F = water boils.
What are the Temperature points in degrees Celsius?
0°C = water freezes, 100°C = water boils.
What is the absolute scale (Kelvin scale)?
scales the same as degrees C;
absolute 0 = where ALL molecular motion stops.
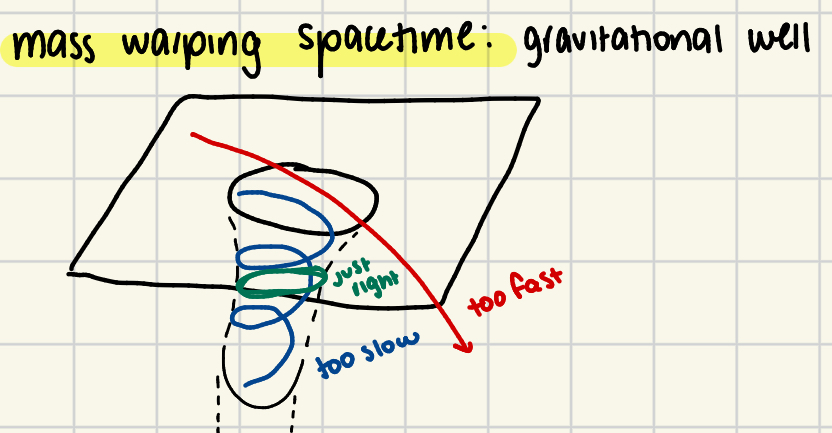
General Relativity Theory
Mass itself warps spacetime, creating gravitational wells.
What is an event horizon?
Boundary around a black hole beyond which nothing can escape.
What is spaghettification?
Stretching vertically and compressing horizontally due to strong tidal forces near black holes.
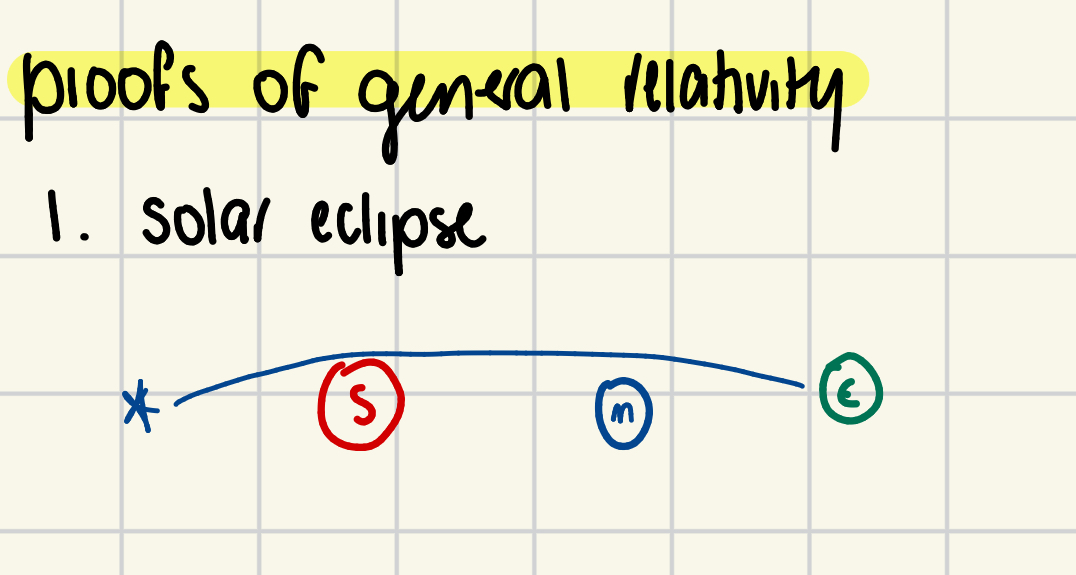
Name proofs of general relativity.
1) Solar eclipse starlight bending—the Sun’s gravity causes apparent positions of stars to shift during eclipse
2) frame dragging (gravity probe B)
Special Relativity Theory
Light speed is constant (300,000 km/s) for all inertial observers.
What is length contraction? formula?
objects moving close to light speed appear shorter in the direction of motion; L = L0 (➰)
L0: observed length
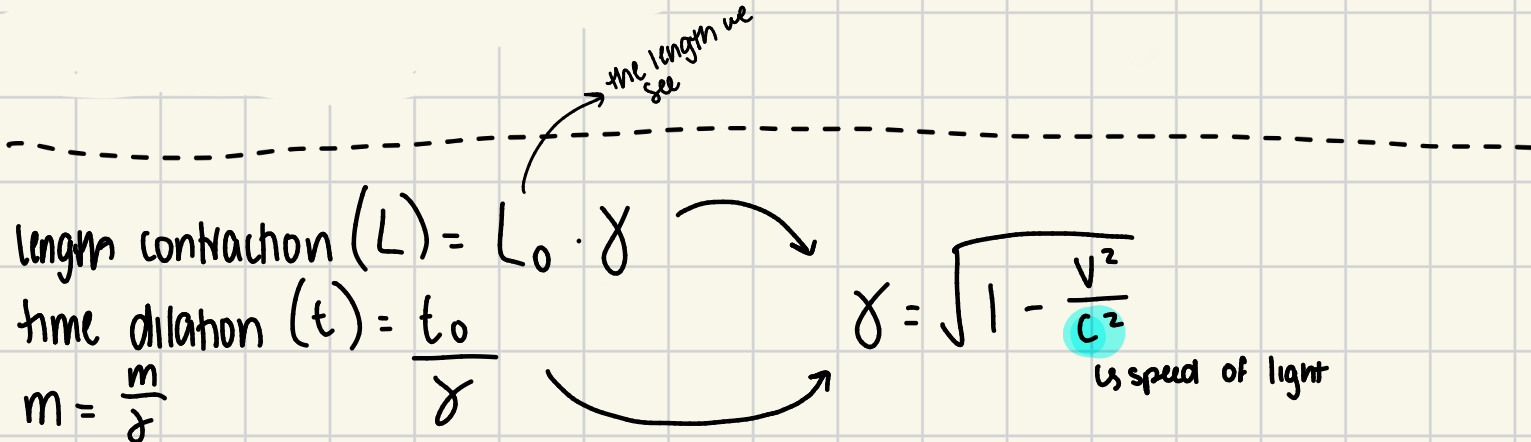
What is time dilation? formula?
time passes more slower for an object moving close to light speed (t = t0/➰)
t0 = observed time
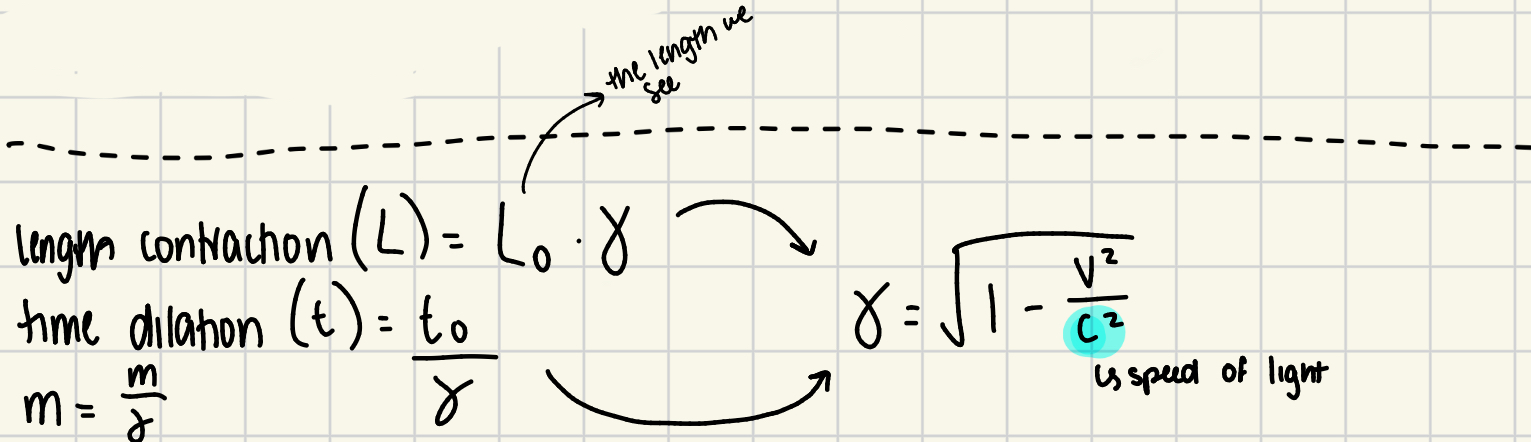
Name proofs of special relativity.
Muon decay experiment (length contraction), twin paradox (time dilation).
What is the muon decay experiment?
Because muons travel near the speed of light, their lengths contract (length contraction), allowing them to cover the distance to Earth before decaying - they normally don’t travel fast enough to make it to earth.
What is the twin paradox?
When one twin travels on a high-speed spaceship and returns, they are younger than the stay-at-home twin due to time dilation;
at near-light speed, time slows and distances contract, effectively shifting through many inertial frames.
IGNORE
Objects moving near light speed appear more massive.
What is momentum (p)?
quantification of how much movement a mass has; p = mv
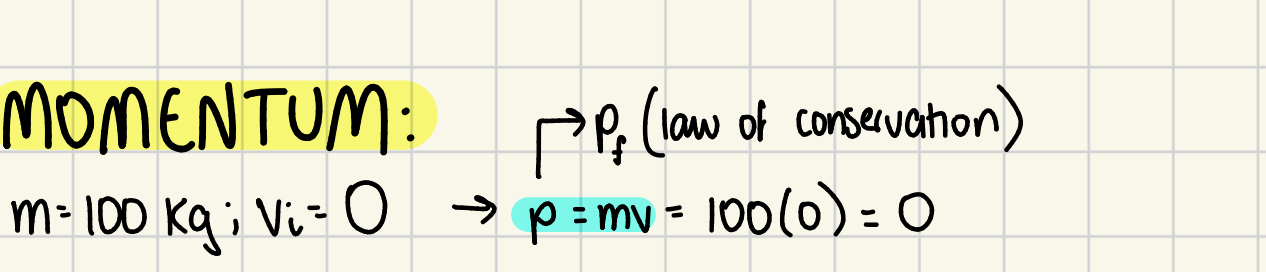
What is kinetic energy?
energy of motion; (KE = 1/2mv^2)
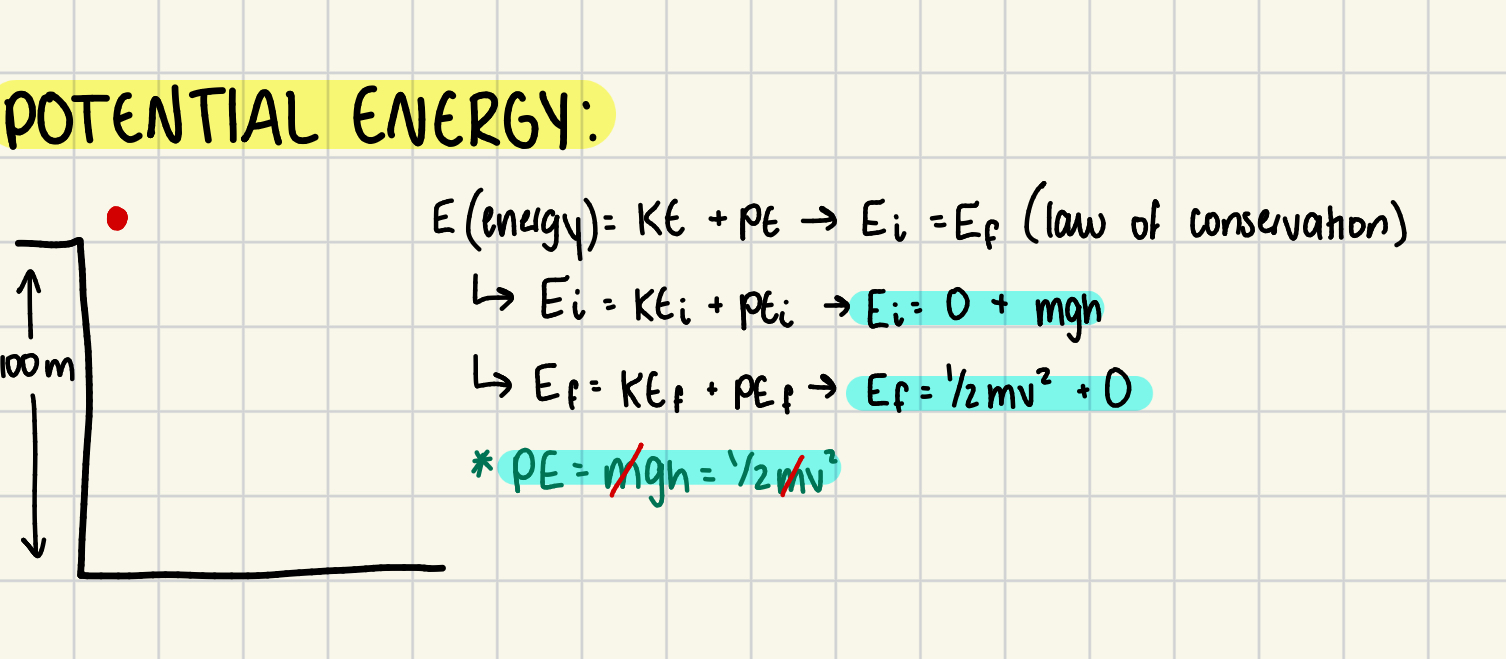
What is potential energy?
Energy stored due to position or state; (PE = mgh).
What is a conserved quantity?
A property that remains constant if not added or removed from a system.
mass
can’t be spontaneously made/taken away
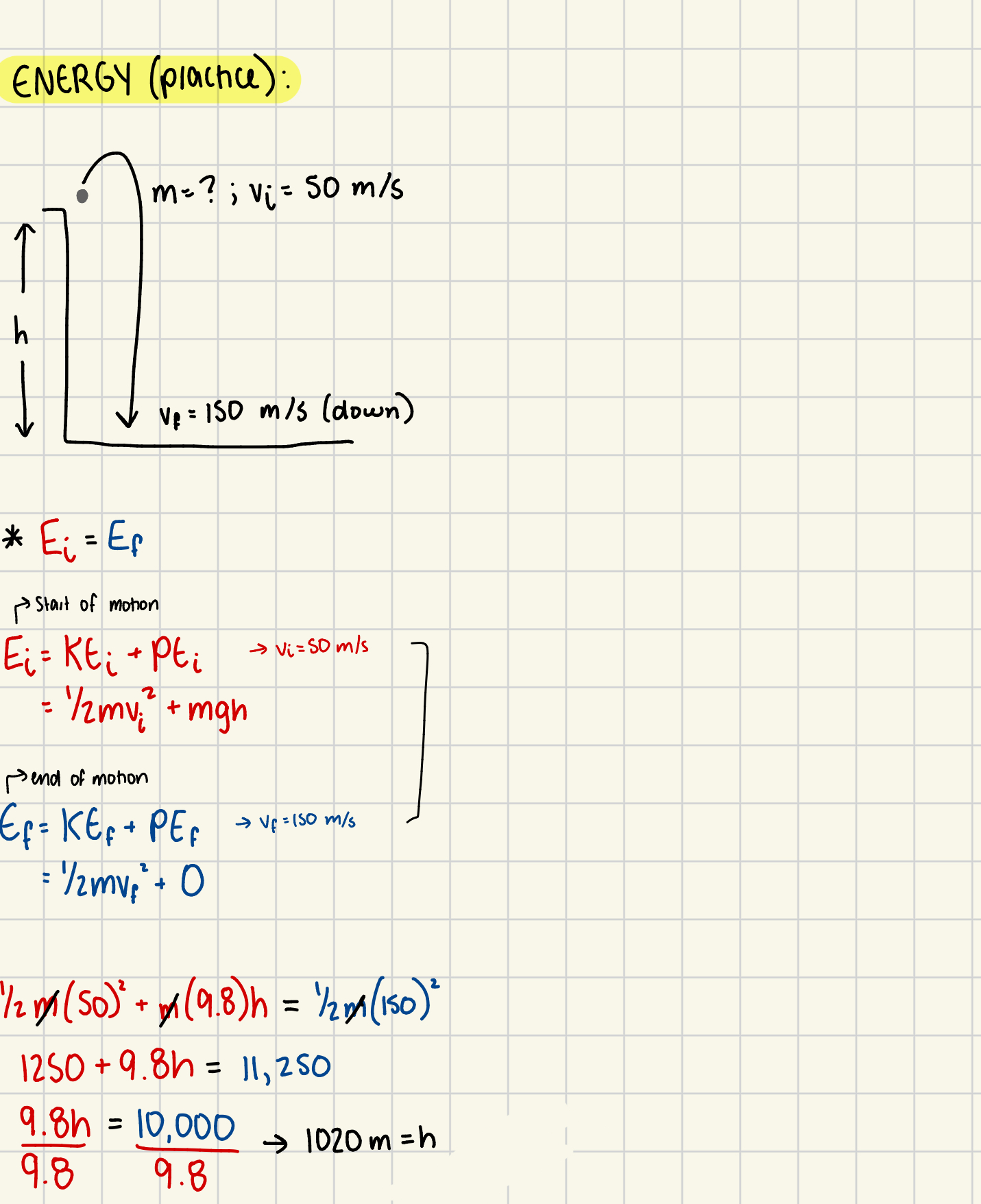
What are some rules in energy problems?
Ei = Ef
PE = 0 at the end of a motion
KE = 0 at the start of a motion
Ei = KEi + PEi = 1/2mvi² + mgh
Ef = KEf + PEf = 1/2mvf² + mgh
**MASS (m) CAN BE CROSS-CANCELLED WHEN IT’S NOT GIVEN
General theory of relativity
mass itself warps spacetime
Special Theory of Relativity
speed of light is constant for everyone, regardless of their motion
cannot see it on ourselves, only see it on object moving relative to us
frame dragging
is the effect where a spinning massive object causes spacetime to move along with it
mass twisting/warping spactime
How many degrees C/degrees F in 0 K?
0 K = -273.15°C; -456°F
Halflife
how long it takes for HALF of a sample to go through radioactive decay
Kitchhoff’s SECOND Law
Any transparent gas that is “excited” will produce an emissions spectrum
particles and quarks
Protons (+): 2 up quark, 1 down
Neutron: 2 down quark, 1 up
Electron (-)
Changes in intensity of light: brightness & colorr
Dimmer light = cooler, redder; LOW FREQUENCY
Bright = hotter, bluer; HIGH FREQUENCY
Sp notation
A (atomic mass = ΣpΣn)
Sp (species)
Z (atomic charge = Σp)
Peak wavelength formula
(λmax (R) = 30,000,000/Temp(K)
What is the sun’s peak wavelength?
λmax (Sun) = 5000 angstrom
Angstrom (Å)
unit that describes wavelength intensity
Wein’s law
peak wavelength has an inverse relationship with temperature
Total energy in thermal emissions (Total E(photon)) formula
Total E(photon) = σT^4
Higher temp = power of 4
σ: stefan-boltzmann constant
doubling T makes value 16x larger (σ(2T)^4 = σ⋅2^4⋅T^4=16σT^4)