Exam 2 (with Review Quizzes, Study Tips, & Quiz 2 study tips)
1/393
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
394 Terms
True or False:
Animals affected by Cryptosporidia parvum can only shed the organism if they are still having diarrhea. Once they have stopped having diarrhea, they can no longer shed the organism.
false
True or False:
Giardia causes diarrhea in all species that are affected by it.
true
Which strain of salmonella is predominately associated with enteritis?
S. typimurium
What is the word used to describe a dermatophyte that can be transmitted from animal to man?
Zoophilic
Human cases of leptospirosis are often associated with exposure to what?
Contaminated water
True or False:
Coxiella burnetii can be found in milk. This is a reason why it is important to pasteurize milk.
true
All strains of Brucellosis are zoonotic except....
B. ovis
Brucella abortus can be transmitted by contact with an infected animal's...
*separate answers with a comma
milk, aborted fetus, vaginal discharge, placenta
What is the name for the chronic, recurrent febrile illness that Brucellosis causes in people?
Undulant fever (Undulating fever)
What is the most common disease form of Anthrax in people?
Cutaneous (wool sorters disease)
Majority of bovine lameness is in the... BE AS SPECIFIC AS POSSIBLE!!!
The lateral claw of the hind feet
laminitis where the corium swells within the hoof which becomes very painful; there are no obvious changes to the hoof wall or sole; the foot is warm and digital pulses are prominent...
Acute Laminitis
laminitis where there is visible deformity of the hoof wall
chronic laminitis
What is the first clinical sign of a sole ulcer?
sole hemorrhage
True or False:
Sole abscesses are a primary condition and are not usually due to any other complication.
false
This condition commonly affects one or both lateral hind claws. It is caused by hemorrhage into or separation of the white line. Heavy, high-yielding dairy cattle kept under confined conditions are at a higher risk for the development of this.
White line disease
This is a mild inflammatory condition of the interdigital skin. It is seen most often when cattle are housed where they are continuously exposed to moisture and manure slurries. The lesions are painful to the touch, but usually do not cause any lameness.
Interdigital dermatitis
This is a highly contagious, erosive, and proliferative infection of the epidermis proximal to the skin-horn junction in the flexor region of the interdigital space. It can be spread by newly acquired animals, contaminated boots, or hoof trimming equipment. Lameness is seen with this.
digital dermatitis
This is the result of bacteria being sequestered in a joint. It causes severe lameness and distension of the joint. The affected joints are visibly swollen and warm to the touch.
septic arthritis
What is the name of the bacteria that is involved with interdigital dermatitis?
Fusobacterium necrophorum
After a digit amputation, what is the herd retention time for that animal?
less than a year
What is the name of the guide that we use to determine which animals need to be treated for parasites? (by using it appropriately, it will decrease the rate of the development of anthelmintic resistance).
FAMACHA Chart
What is the term given to a decline in the efficacy of an anthelmintic against a population of parasites that is generally susceptible to that drug.
Anthelmintic Resistance
What is the causative agent for Foot Scald/ Strawberry Foot Rot in small ruminants?
Dermatophilus congolensis
True or False:
Foot rot in sheep is infectious. Animal that are infected should be separated. They are treated by using foot baths with 10% zinc sulfate plus systemic antibiotics.
True
What is the causative agent for Foot Rot in sheep?
Dichelobacter nodosus
What is the causative agent for Johnes Disease?
Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis
This condition results when a piece of metal pierces the reticulum and leads to a localized peritonitis.
traumatic reticulitis
This condition results from a piece of metal piercing through the diaphragm and into the pericardium.
traumatic pericarditis
A cow suffering from this condition will have a papple shaped appearance from the rear. With this condition, ingesta does not pass through one or more of the forestomachs due to a dysfunction in rumen motility.
Vagal Indigestion (Reticulo-omasal transport).
This disease is caused by cattle swallowing a sharp piece or metal. What is is called? (lay term)
Hardware disease
True or False:
When dealing with pasture bloat, can you relieve the issue with with stomach tubes or trocars?
false
True or False:
Neonates with GI issues tend to be more alkalotic, while adults with GI issues tend to be more acidotic.
false
What are the 4 viruses that contribute to the bovine respiratory disease complex?
(DON'T PUT ABBREVIATIONS)
*separate answers with a comma
Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis, Parainfluenza 3 Virus, Bovine Respiratory Syncitial Virus, Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus
This respiratory virus can cause a viral pneumonia on its own. It is more common in calves 3-12 months old.
Bovine Respiratory Snycytial Virus
This respiratory virus can cause immunosuppression, EED, abortion, fetal mummification, and can cause persistently infected calves.
Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus
Calves that are persistently infected due to Bovine Viral Diarrhea infection inutero were infected between _________________ days gestation.
45-125
True or False:
We use an ear notch test to detect BVDV in calves.
true
What is the period of time between the last treatment and when meat, milk, or eggs may be marketed called?
Withdrawal time
This swine respiratory condition is caused by Bordetella bronchiseptica &/or Pasturella multocida. Pigs affected have deviated snouts and epistaxis. It is commonly seen post weaning.
Atrophic rhinitis
This swine respiratory condition is causes an acute, severe pneumonia. Pigs affected have "thumps" and blue ears. Acute death is also associated with this. It is commonly seen in larger pigs.
Actinobacillus pleuropneumonia
This swine respiratory condition is the most common cause of chronic pneumonia. Pigs affected usually don't die, but they don't grow either. It is commonly seen in late-nursery to early finishing areas. Lincomycin is the drug of choice for this.
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae
This swine respiratory disease was first known as "mystery swine disease". It is classified as the BVD of swine. Clinical problems appear and disappear without logic. Clinical signs can very drastically from one herd to another. It does cause reproductive failure and severe enzootic pneumonia.
Porcine Respiratory and Reproductive Syndrome
What is the name of the only FDA-approved antibiotic used to treat caprine pneumonia?
Ceftiofur (Naxcel)
When talking about GI issues in cattle, adults tend to have more (diarrhea/forestomach) _______________ problems.
*Choose the correct one
forestomach
When talking about GI issues in cattle, neonates tend to have more (diarrhea/forestomach) _____________ problems.
*Choose the correct one
diarrhea
A calf that is 2 weeks old should be fed _________% of its body weight daily.
Correct!
8
True or False:
Calves born in the last week of calving season have the lowest death rate.
False
What is the term given to excess gas accumulation in the rumen?
Bloat
True or False:
Pre-dipping is done to control contagious pathogens, and post-dipping is done to control environmental pathogens.
false
What type of heart failure is associated with intermandibular and brisket edema?
Right sided heart failure
What is the most common congenital heart defect of cattle?
Ventricular Septal Defect
What is the most common form of valvular disease in cattle?
Bacterial Endocarditis
What is the normal pH range for milk?
6.5-6.8
What is the legal limit of somatic cells in the bulk tank?
750,000 cell/ml
Tell me what the CMT (California mastitis test) does.
Estimates the number of white blood cells (somatic cells) in the milk
True or False:
When preparing an udder and collecting milk samples, you should prep the udder by cleaning the far teats then the near teats and obtain your sample by collecting from the near teats first then the far teats.
true
In this form of mastitis, there is dysfunction of the mammary gland that results in inflammation, abnormal milk, an ill cow, and production losses.
clinical mastitis
In this type of mastitis, there is inflammation of the mammary gland, loss in production, loss in milk quality, increase in somatic cells, and no clinical signs.
subclinical mastitis
With contagious mastitis, the primary source of infection is...
the mammary gland of other cows
With environmental mastitis, the primary source of infection is...
the environment
This contagious mastitis pathogen lives in the infected quarter, respiratory tract, and reproductive tract. It can cause joint problems and lameness issues, and it is unresponsive to treatment. If this pathogen is found in a milk culture, the animal is culled.
Mycoplasma bovis
What are the contagious mastitis pathogens?
*separate answers with a comma
Staphylococcus aureus, Mycoplasma, Streptococcus agalactiae
What is the meat withdrawal time for phenylbutazone?
21 days
What is the milk withdrawal time for phenylbutazone?
120 hours
Which drug has a milk withdrawal time of 120 hours and a meat withdrawal time of 21 days?
Phenylbutazone
What is the meat withdrawal time of banamine?
4 days
What is the milk withdrawal time of banamine?
72 hours
Which drug has a meat withdrawal time of 4 days and a milk withdrawal time of 72 hours?
banamine
What is the meat withdrawal time of oxytetracycline?
28 days
What is the milk withdrawal time for oxytetracycline?
96 hours
Which drug has a milk withdrawal time of 96 hours and a meat withdrawal time of 28 days?
oxytetracycline
What is the meat withdrawal time for Naxcel?
4 days
What is the meat withdrawal time for excede?
13 days
Which drug has a meat withdrawal time from 4-14 days and no milk withdrawal time?
ceftiofur
What is the meat withdrawal time for penicillan in cattle?
10-30 days (dose dependent)
What is the meat withdrawal time for penicillin in sheep?
9 days
What is the meat withdrawal time for penicillin in pigs?
7 days
What is the meat withdrawal time for Benzathine penicillin G?
30 days
What is the meat withdrawal time for Tulathromycin?
18 days
What is the meat withdrawal time for Tylosin?
21 days
What is the meat withdrawal time for spectinomycin?
11 days
What is the meat withdrawal time for sulfadimethoxine?
5 days
What is the meat withdrawal time for Baytril?
28 days
What is the meat withdrawal time for lincomycin?
48 hrs
Which drug has a meat withdrawal time of 28 days, but no milk withdrawal time?
baytril
Which drug is used to treat swine and has a meat withdrawal time of 48 hours?
Lincomycin
What is the meat withdrawal time for ivermectin?
35 days
Bovine lameness
-90% of bovine lameness is in the hindfoot lateral claw
Sole lesions
Due to trauma, abnormal growth/wear and/or nutritional
Heel erosions
most likely due to bacterial agents
Interdigital lesions
due to bacterial agents or trauma
Wall lesions
Due to trauma, abnormal growth or wear and or nutritional aspects
Laminitis
-result of the disturbance of the corium of the claw
-most common noninfectious door condition in cows
-3 different forms: acute, subacute, and chronic
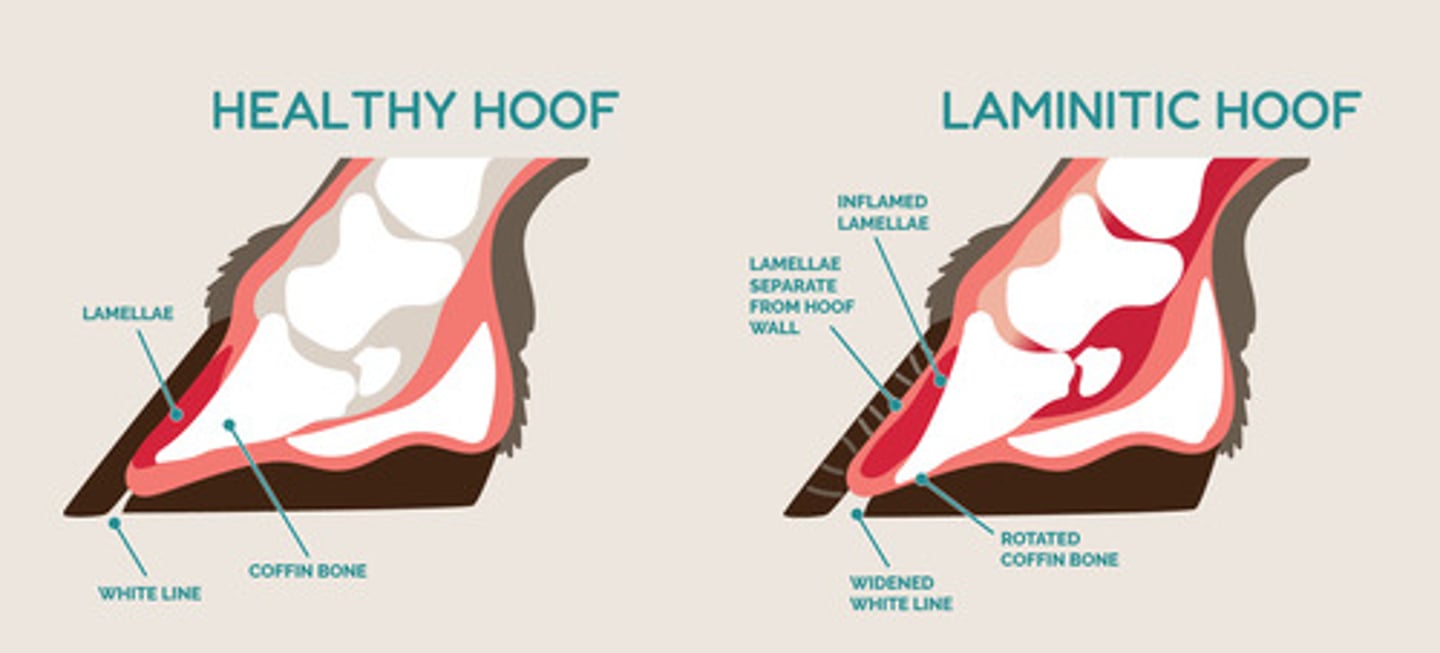
Treatment for acute laminitis
Pain meds(Flunixin meglumine-Banamine) and cold water hydrotherapy
Treatment for chronic laminitis
corrective foot trimming
What is the first clinical sign of a sole ulcer?
sole hemorrhage
Sole ulcers
-full thickness break in sole that exposes the corium
-can be found at the axial heel sole junction, toe, or heel
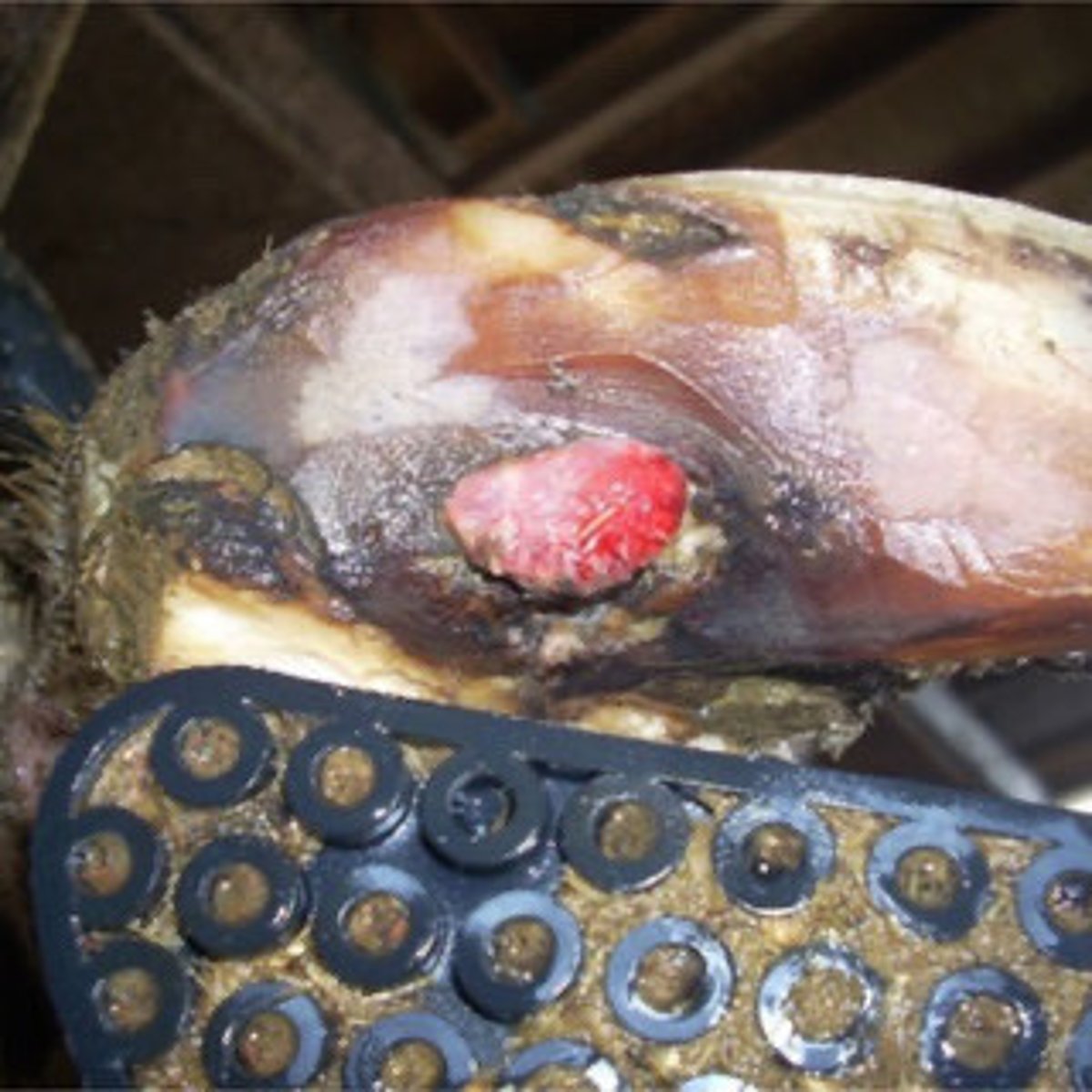
What is the treatment for sole ulcers?
relieve all weight from affected claw with wooden block, removing necrotic tissue and prescribing pain relief and healing aids such as antibiotic dressings (oxytetracycline)
What is the treatment for sole abscess?
Remove all loose horn around the abscess and put a block on hoof