Computer Organization (IB HL CS)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
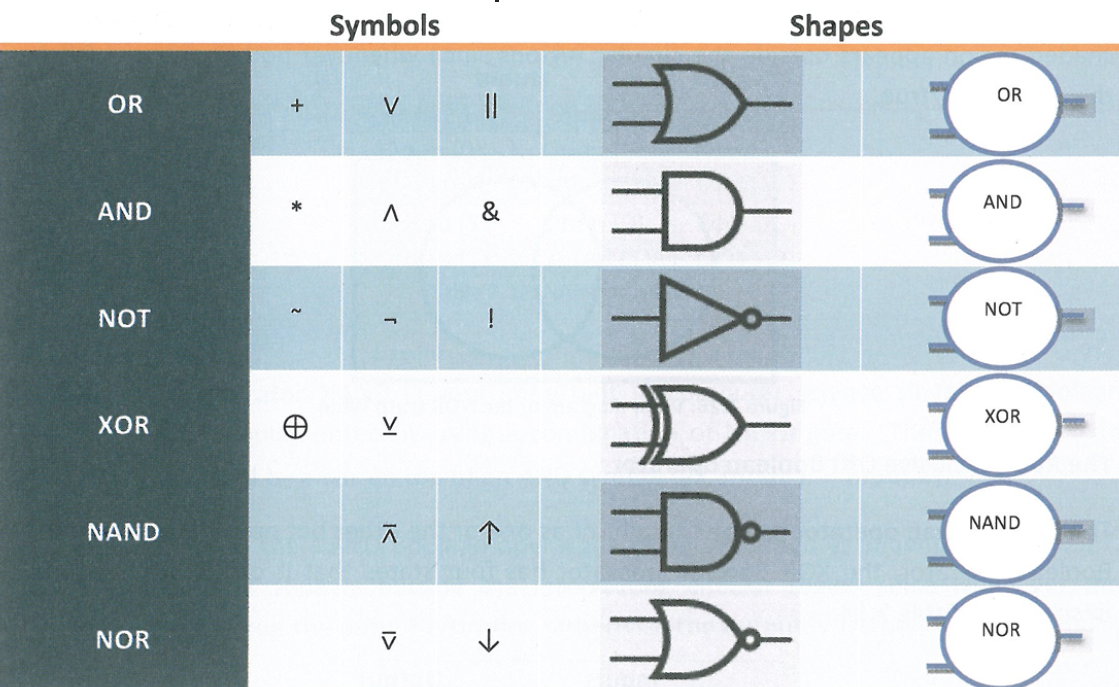
CPU
Central processing unit
Uses arithmetic and logic operations to process input and output useful information
ALU
Arithmetic logic unit
Performs all basic arithmetic, logic, and I/O operations
CU
Control unit
Retrieves/decodes instructions for CPU
Directs data flow for ALU
MAR
Memory address register
Connected to address bus
Contains RAM address of the next instructions
MDR
Memory data register
Connected to data bus
Holds data that will be written to/was read from RAM
CPU Diagram
RAM
Random access memory
Also known as primary memory
General-purpose storage, can be overwritten
Directly accessible by CPU
Stored in binary
ROM
Read only memory
Stores instructions/data
Cannot be overwritten
Address bus
Connects MAR to ALU
Data bus
Connects MDR to RAM
Differences between RAM and ROM
RAM is volatile memory used for temporary storage, while ROM is non-volatile memory that stores permanent instructions.
DRAM
Dynamic RAM
Preferred for the main RAM of a computer system
SRAM
Static RAM
Faster, more expensive
A small amount is placed between RAM and processor
AKA the cache
Cache memory vs RAM
Cache memory is a smaller, faster type of volatile memory located between the CPU and RAM, used to temporarily store frequently accessed data for quick access, whereas RAM provides larger temporary storage for active applications and data.
Machine instruction cycle
Fetch: CPU sends address to primary memory through address bus. Data bus copies this address’ instruction and sends it to CU.
Decode: CU decodes instructions and fetches required data from primary memory. Data’s addresses are placed into memory bus and data is received by CPU through data bus.
Execute: CPU executes the instructions.
Store: CPU stores the result of instructions in primary address through buses then checks for the next instruction.
Persistent storage
AKA secondary memory
Can be written to, is non-volatile
Hard drive, USB, floppy disk, ZIP drive, etc.
Virutal memory
A memory management technique that uses disk space to extend RAM by swapping data in and out as needed, allowing for larger applications to run on limited physical memory.
AKA using secondary memory as a backup for primary memory
Primary vs secondary memory
Primary = small amount, volatile, expensive, faster, directly accessed by CPU
Secondary = large amount, retains data when powered off, inaccessible by CPU
Operating system
Provides a user interface
Does memory management
Does peripheral management
Allows multitasking
Provides security
Word processors
Programs for storing, manipulating, and formatting text-input from keyboard then providing a printout
Spreadsheets
Program to arrange data in rows/columns and can be manipulated for calculations
DBMS
Database management systems
Systematic way to create, retrieve, update, and manage data
CAD
Computer aided design
1 byte (B)
8 bits (b)
Negative binary

Decimal binary

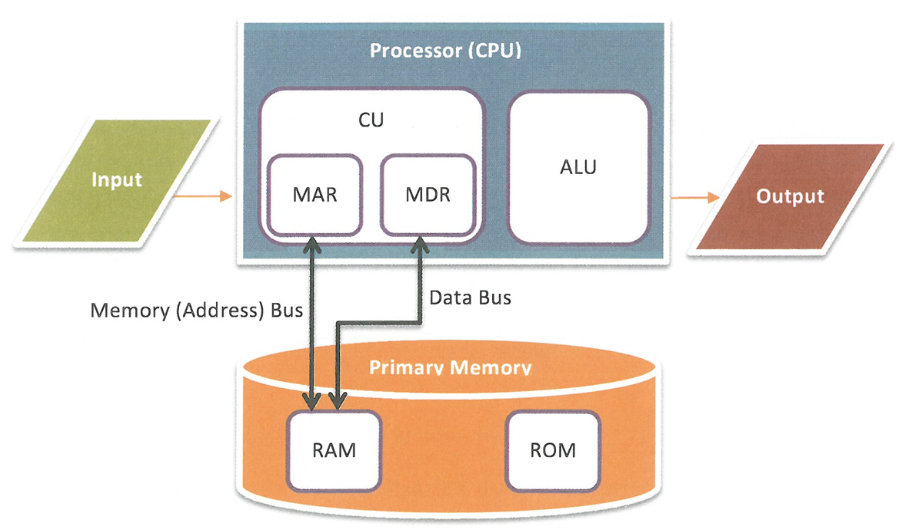
Different data types take up more space
NAND, NOR
NOT and, NOT or
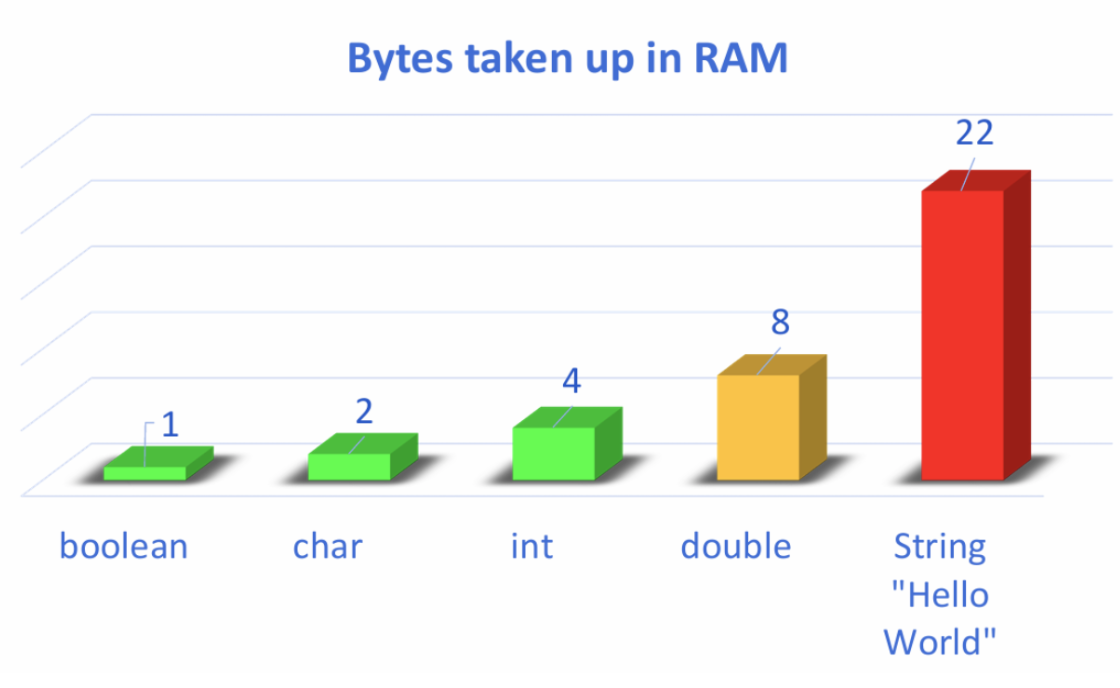
XOR
One or the other, but not both
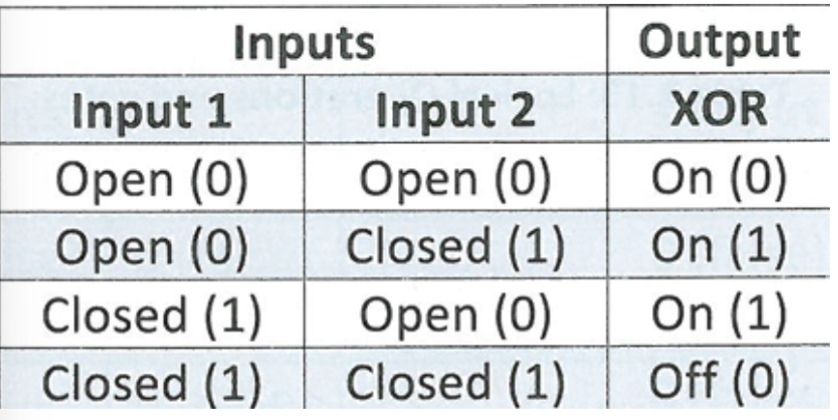
Common symbols for logic gates