Mammalian Paleontology Final Exam
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
5 Changes during the Eocene-Oligocene Transition and the Impacts
1. Tectonic separation between Antarctica and Australia - new oceanic gateway and Antarctic circulatory current —glaciers form in antarctica
2. Falling eustatic sea levels - glacier formation sucks up seawater; Turgai strait retreats between Asia and Europe
3. Biotic interchante between Asia and Europe — imbalanced exchange, Asia had larger land area and greater diversity so Asian taxa did better than European taxa
4. Grand Coupure - Eu taxa that went extinct— paleotheres, apatemyids and pseudosciurid rodents
5. Balkanatolia Archipelago - continent of islands that included African and Laurasian taxa— was getting colonized from everywhere
Balkanatolia Colonization Patterns (why its a necessary first step to reach europe)
a. ruminants & rhinocerotoids colonize balkanatolia before reaching europe AFTER the grand coupure
b. after they leave, brontotheres and other rhinocerotoids come to balkanatolia then to EU
Faunal Changes of Eocene-Oligocene of North America
Brontotheres & Primates go extinct
primates like tropical but Olig of N.Am is too cold
Hypertragulus appears — selenodont artiodactyl
Floral & Faunal Changes of Eocene-Oligocene of Asia
Floral Changes: hardwood forest to sage brush biome
Faunal Changes: from large perissodactyls to lagomorphs
Differential Survival Pattern of Primates in Eocene-Oligocene
Eocene: anthropoids do good in Asia & lemurs do good in Africa
Oligocene: lemurs do good in Asia & anthropoids do good in Africa
Timing of Collision between Eurasia and Africa
Debated, but occurred in the Oligocene-Miocene boundary
African Taxa Present BEFORE Collision with Eurasia
Arsinotherium (Embrithopods)
Hyracoids
Chilgatherium & other proboscideans
Hyaenodonts
What is the ‘Proboscidean Datum’?
The first appearance of proboscideans outside of Africa (late oligocene)
Aftermath of African Taxa after Eurasian Collision with Africa (Extinctions & Immigrations)
Extinctions:
Embrithopods
Ptolemai-ids
Some Marsupials
Antilohyrax (afrothere that looks very similar to artiodactyls)
Immigrations:
Perissodactyls—chalicotheres & rhinos
Artiodactyls—suidae & ruminants
Lagomorphs
Rodents—Anomalurids, Hystricomorphs, Pedetidae, Porcupines, Mice
Pedetidae & Anomaluridae are closely-related rodent taxa, but Anomalurids are found in Africa before Pedetids, why may this be?
Anomalurids are arboreal, which is better for sweepstakes dispersal than the ground-living pedetids.
Which taxa shows evidence for a late Oligocene (28 Ma) split between old world monkeys and apes? list 2 features it has that are characteristic of apes
Saadanius — prognathic face & tubular ectotympanic bone
List 2 opposing theories for island evolution and descibe what they say dictates island evolution
Macarthur and Wilson model — rapid turnover ; colonization and extinction are mediated by distance from mainland and island size
disregards in situ speciation
Vicariance biogeography — stability ; tectonic movement
“Island Effects” in regards to evolutionary trends
Large taxa get small & small taxa get large
adaptations to avoid predation are lost (flying,running)
brain size reduction (minimize energy cost of maintaining brain tissue)
4 Factors Affecting Island Evolution
Limited resources
limited space
geographic isolation
less or no predation
There are only 4 orders of mammals on Madagascar today. List them. Which of these lineages is monophyletic on Madagascar. Why is this important?
Rodents
Primates
carnivorans
afroinsectiphiles
All four are monophyletic and it’s important because it means each order only colonized Madagascar one time.
List the 4 Great American Biotic Interchange Events & when they occurred. State how many S.Am taxa moved north & how many N.Am taxa moved south for the first half (1& 2) and the second half (3 & 4).
GABI 1 (2.5 Ma) & GABI 2 (1.8 Ma)
S.Am taxa moving north — 7 (rodents, cingulates, ground sloths)
N.Am taxa moving south — 8 (rodent, carnivores, proboscidean, perissodactyls, artiodactyls)
GABI 3 (0.8 Ma) & GABI 4 (125 Ka)
S.Am taxa moving north — 1 (opossum)
N.Am taxa moving south — 6 (mustelids, cervids, peccaries, rabbits, horses, carnivorans)
How could glacial oscillations affect the dispersal ability of North and South American taxa? What did Central America look like during interglacial and glacial periods?
Glaical oscillations coincide with the 4 interchange intervals. Glacial periods increased the dispersal ability of taxa.
During interglacial periods, Central America was characterized by rainforest biomes, which stifled the dispersal of taxa, particularly large taxa.
Glacial period Central America was characterized by savannah biomes, which made it easier to disperse.
Also, glacial periods took up sea water, lowering the sea level around the Panama connection between North and South america. The larger land mass aided in easier dispersal.
How many taxa that originated in North America and how many taxa that originated in South America went extinct at the end of the Pleistocene? What are the 4 possibilites postulated for this differential extinction? Finally, what 3 factors impact these possibilites
N.Am: Gomphotheres only
S.Am: Many; toxodonts, glyptodonts, ground sloths, etc.
4 possibilites:
higher dispersal of N.Am taxa
higher speciation of N.Am taxa
more extinction of S.Am taxa
larger pool of N.Am taxa
3 factors impacting the differential extinction:
competition - S.Am outcompeted by N.Am ungulates
predation - absence of efficient mammal S.Am predators meant S.am taxa were not prepared for incoming N.Am carnivores
cyclical climate change
Final Results of the Great American Biotic Interchange:
4 taxa in North America are derived from South American ancestors
53% of living South american taxa are derived from North American ancestors
What are the two proposed factors responsible for the megafaunal collapse at the end of the Pleistocene? What were the impacts of both factors?
Humanity and climate change.
Humanity:
predation/hunting - Blitzkrieg overkill
habitat alteration - fire, etc.
hunting & disease caused by commensal animals (dogs & rats)
Climate:
habitat loss
changing floral diversity - coevolutionary disequilibrium
What is the problem with climate change as an explanation for the late-Pleistocene megafauna collapse?
why didn’t the previous climate oscillations cause a megafaunal collapse?
Give 2 reasons and 2 pieces of evidence that humans were the main cause of the late-Pleistocene megafauna collapse.
carribean ground sloths persisted longer than mainland groundsloths—they lived until humans arrived in carribean, then went extinct
less genera went extinct in Eurasia & Africa— humans originated in Africa & were already present in Eurasia prior to megafaunal collapse
evidence of hunting: mastodon rib embedded with a projectile
evidence of habitat alteration: reduction in numbers of megafauna (lowered concentration of poop fungus) followed by increase in human activity (increased concentration of charcoal)
Living and Extinct Clades of Perissodactyls (7 total)
Equids
Tapirs
Rhinocerotids
Brontotheres
Chalicotheres
Rhinocerotoids
Paleotheres
2 Stem/Close Relatives of Perissodactyls
Cambaytheres & Phenacodontids
3 Synapomorphies of Perissodactyls
mesaxonic— odd number of toes
concave navicular facet on astragalus
pi-shaped upper molars
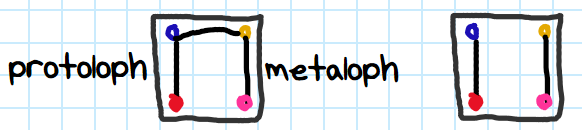
Which taxa do these belong to?
Tapir
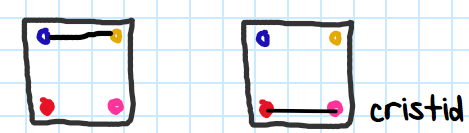
Which taxa do these belong to?
Rhinos

Which taxa do these belong to?
Brontotheres
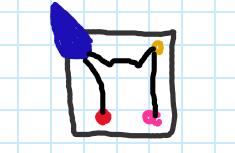
Which taxa do these belong to?
Chalicotheres
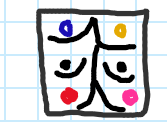
Which taxa do these belong to?
Paleotheres
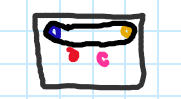
Which taxa do these belong to?
Rhinocerotoids
Which taxa is though to be the ancestor of all perissodactyls?
Hyracotherium
Give the 2 major features of equid evolution and explain the adaptive benefit of each. What are these two things associated with?
monodactyl limbs (one toe) with elongated metacarpal — aids in running
hyposodont cheek teeth (high crowned teeth) — eating grass
these things are associated with the spread of grasslands during the Miocene
When and what is the Hipparion Datum? Where did equids evolve?
10-11 Ma; appearance of equids throughout the old world. Equids evolved in North America.
4 Living Clades of Artiodactyls
Suids & Peccaries
Camels
Hippos & Whales
Ruminants
5 synapomorphies of artiodactyls
double pulley astragalus
paraxonic — even number of toes ( axis passes btwn digits 3 & 4)
deciduous p4 “baby tooth” has 3 lobes
selenodont upper molars
tall greater trochanter of femur and narrow patellar groove
Basal artiodactyls are thought to either be Wutuhyus of China or Diacodexis of Wyoming. Describe features of both taxa. Which taxon is more derived?
Wutuhyus is pig-like with bunodont teeth. Diacodexis has a double-pulley astragalus and artiodactyl femur morphology, as well as paraxonic toes. Diacodexis is more derived than Wutuhyus
List the 2 living clades of Cetacea and the 4 extinct Archaeocete clades
Living:
Mysteceti - baleen
Odontoceti - teeth and sonar
Extinct Archaeocetes:
Pakicetids - most basal
Ambulocetids
Protocetids
Basilosaurids - 1st fully aquatic
Necessary changes for Cetaceans to become marine
Reproductive changes: tail first birth (ancestral mammal is head first)
Skeletal changes:
a. elongated vertebral column
b. shorter limbs and longer skull
c. osteosclerotic bones
Hearing changes:
a. remove eardrum
b. auditory bullae enlarged and separated from skull w/ Involucrum to conduct sound
Living (7) and Extinct (1) Clades of Afrotheria (the two general clades and then the Orders within)
Paeungulata:
Proboscidea - elephants
Sirenia - manatees
Hyracoid - hyrax
Embrithpods (extinct)
Afroinsectiphilia:
Tubulidentata - aardvarks
Macroscelidea - elephant shrews
Chrysochloridae - golden moles
Tenrecidae - tenrecs
2 synapomorphies of Afrotherians
large cotylar fossa of astragalus
transverse ectal facet on calcaneus
3 Paleocene African Mammals:
Todralestidae
Eritherium — oldest potential relative of proboscideans
Ocepeia — transitionary from insectivorous to herbivorous
Dispersal btwn Africa and Eurasia was possible, but limited in the paleocene. Which taxon shows us this?
Hyaenodonts found in both Africa and Asia in late paleocene
5 Afrotherian taxa present during the Eocene of Africa and features of each
Numidotherium — early proboscidean with aquatic affinity
Nementchatherium — macroscelidean
Hyracoids — looked similar to early perissodactyls; W-shaped ectoloph as well
Embrithopods — made it out of Africa before collision with Eurasia (perhaps Balkanatolia?)
Tubulidentata — aardvark; confined to Africa until collision w/Asia
Describe the dentition of aardvarks (Tubulidentata). What challenge does this dentition raise in regards to their position in the Afrothere phylogenetic tree?
Dentition is highly simplified with smooth cheek teeth. aardvarks are placed at the base of Afroinsectiphilia, but with such derived teeth, it makes this position unstable. Many Afroinsectiphiles have teeth adapted for insectivory and are less derived than aardvark teeth.
Sirenian adaptations to life in water:
swollen ribs & dense bones (pachyosteosclerosis)
changing body proportions:
neck shortened
center of buoyancy equal to center of gravity; body axis is aligned with water—more efficient swimming
larger thoracic cavity
forelimbs are flippers and hindlimbs are gone
What taxon do these teeth belong to?
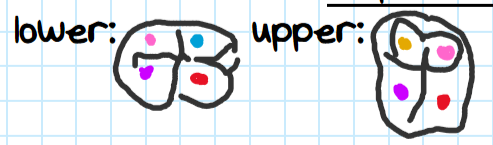
Elephant shrew
Which taxon do these teeth belong to?


Dimaitherium (hyracoid)
Which taxon do these teeth belong to?
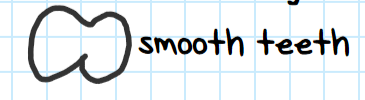
Tubulidentata (aardvark)
Which drawing represents the body of modern manatees? What does the B &the G represent in these drawings? What is important about their position relative to each other?
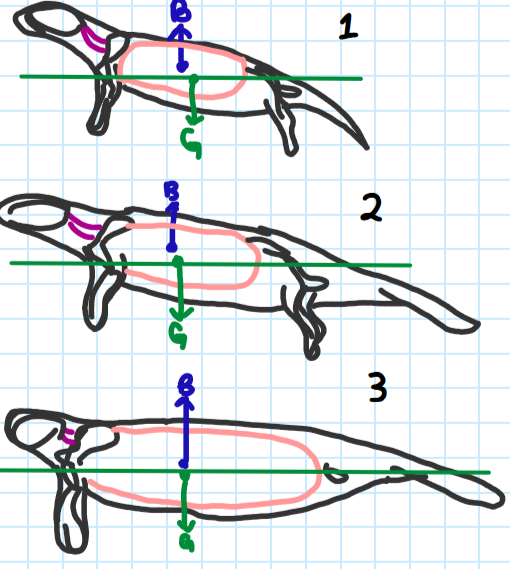
Number 3; The b is the center of buoyancy and the g is the center of gravity. As the center of buoyancy is shifted to be equal in position to the center of gravity, the axis of the body becomes aligned with the water (green line), which makes swimming more efficient
Clades of Xenarthra:
Cingulata — armadillos & glyptodonts
Vermilingua — anteaters
Folivora — tree sloths & ground sloths
2 Synapomorphies of Xenarthra
Xenarthrous joints — accessory joints between vertebrae that fortify the skeleton
simplification or loss of teeth
Who is sister to Xenarthra? What do we know about the ancestor of Xenarthra?
Afrotheres
Xenarthran ancestor was likely a good digger
Cingulata: give one synapomorphy & describe the dentition
carapace made of osteoderms
dentition: euhypsodont (ever growing & closed roots) ; no enamel—only dentine
What are Glyptodonts? How are they related to others in their clade? What unique morphological trait are they hypothesized to have used for intraspecific combat?
Large, armored cingulates that are nested within living cingulates.
Most closely related to the pink fairy armadillo.
They are thought to have used their giant club tail for intraspecific combat.
3 Examples of Extinct Ground Sloths
Megalonyx
Megatherium
Paramylodon
Fun facts! Briefly describe the historical story around the discovery of ground sloths in America.
Thomas Jefferson found the claw of Megalonyx and thought it was a lion that may not be extinct, which catalyzed the expedition of Lewis and Clark.
List two diagnostic skull features of tree sloths and describe the two living groups and their differences
Skull features:
incomplete zygomatic arch
extended processes on zygomatic arch
Living Groups:
Bradypodidae — 3 toed sloth; peg like upper teeth
Choloepus — 2 toed sloth; canine-like 1st cheek teeth; scoopy part at symphysis of dentary
Are tree sloths more closely related to each other or to extinct ground sloths? Did they evolve suspensory arboreality independently or is it homologous?
Tree sloths are more closely related to ground sloths and evolved suspensory arboreality independently.
When did South America and Africa split? When did South America and North America connect?
S.Am and Africa split 120 Ma in Cretaceous and S.Am and N.Am collided 2.5 Ma in Pleistocene.
Four South American fossil groups that survived the meteor impact (cretaceous-paleocene boundary):
Monotremes
Gondwanatheres — similar molars to multituberculates (corn)
Molinodus — oldest S.Am placental; condylarth that emigrated from N.Am; duplicated protocone
Notoungulates — external shearing
Give the main synapomorphy of Notoungulates and list & briefly describe the 8 groups.
Main synapomorphy: external shearing
Pyrotheres — bilophodont; high nasal opening on skull
Toxodon — hypselodont tusks; hypsodont molars; largest notoungulates
Notioprogonian — buccal shearing
Typotheres — teeth look like a face 🥴
Hegetotheres — extremely hypsodont upper teeth; rabbit like
Litopterns — primitive dentition but evolved extreme monodactyly earlier before horses did
Astrapotheres — lightning beasts
Xenungulates — “foreign ungulates” ; maybe convergent with Uintatheres
Eurohippus messelensis
pregnant perissodactyl mare and fetus from germany
Embolotherium andrewsi
late Eocene brontothere; no brontotheres made it to the Oligocene
Diacodexis metsiacus
early Eocene artiodactyl
Rodhocetus kasrani
semiaquatic cetacean from Pakistan
Ocepeia dauoiensis
old Afrotherian taxa but neither small nor insectivorous
Pezosiren portelli
quadruped Sirenian of Jamaica
Litovoi tholocephalos
dome-headed multituberculate from an island; tiny brain
Arsinotherium giganteum
Embrithopod from right before collision of Africa & Eurasia
Nesodon taweretus
toxodont with rhino-like dentition
What structure are these? What group do they belong to and what is their function?
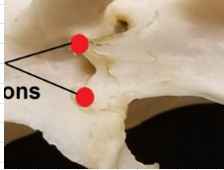
Xenarthrous joints; belong to xenarthrans; fortify vertebrae for digging
Which group do these teeth belong to?

Cingulates / armadillos
Which group do these teeth belong to?

Glyptodonts
Whose skull is this?

Glyptodont skull!
Whose skull is this?
Bradypopodidae — 3 toed sloth
Whose skull is this?
Choloepus — 2 toed sloth
Whose phalanges are these?
Fossil anteater
Which taxon has this skull and teeth?

Pyrotheres
Which taxon do these teeth belong to?
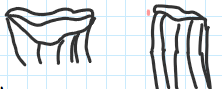
Toxodon
Which taxon do these teeth belong to?

Notioprogonian
Which taxon do these teeth belong to?

Typotheres
Which taxon do these teeth belong to?

Hegetotheres
Which taxon does this skull and these teeth belong to?

Astrapotheres
Which taxon do these teeth belong to?
Xenungulates
Which taxon do these teeth belong to?

Arctostylopids
Which taxon do these teeth belong to?
Molinodus
Review: earliest ancestor of mammals
Synapsids
Review: 3 basic mammal teeth prior to tribosphenic teeth
Triconodont
Symmetrodont
Docodont
Review: What did the ancestral mammal likely look like?
small and insectivorous
Review: The 2 evolutionary innovations of mammals
unique jaw joint (dentary-squamosal) and 3 middle ear bones — allows greater bite force and better hearing
enlarged brain — neocortex and olfactory bulb larger
Review: Name the 4 Paleocene North American Ages
Puercan, Torejonian, Tiffanian, and Clarkforkian
Review: What likely caused the rapid warming at the paleocene-eocene boundary?
Carbon isotope excursion due to thermally-induced release of methane hydrates from ocean column & sediment
Review: List the 3 Clades of Euarchontoglires and the 7 clades of Laurasiatheres
Euarchontoglires:
Primates
Rodentia
Lagomorpha
Laurasiatheres:
Lipotyphla
Perissodactyla
Chiroptera
Carnivora
Pholidota
Cetacea
Artiodactyla
Review: What factors allow an animal to be ‘eligible’ for sweepstakes dispersal? What climate conditions allowed for sweepstakes dispersal? Which 3 groups made it from Asia to Africa and South America through sweepstakes dispersal?
Factors:
arboreal or riverbank living
living in social groups
small body size
Climate conditions: monsoons made natural rafts & wind carried across ocean barriers
3 groups that won the sweepstakes:
Hystricognathous rodents
Anomalurid rodents
Anthropoid primates