Upper Limb: Muscles, Nerves, and Vessels
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of flashcards covering the key concepts from Dr. Rex Barton-Smith's lecture on the upper limb, including muscular anatomy, nerve supply, and vascular structures.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are the major compartments of the upper limb?
Anterior and posterior compartments.
What is the primary function of the rotator cuff muscles?
To stabilize the humeral head in the glenoid fossa.
List the four rotator cuff muscles.
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres Minor, Subscapularis.
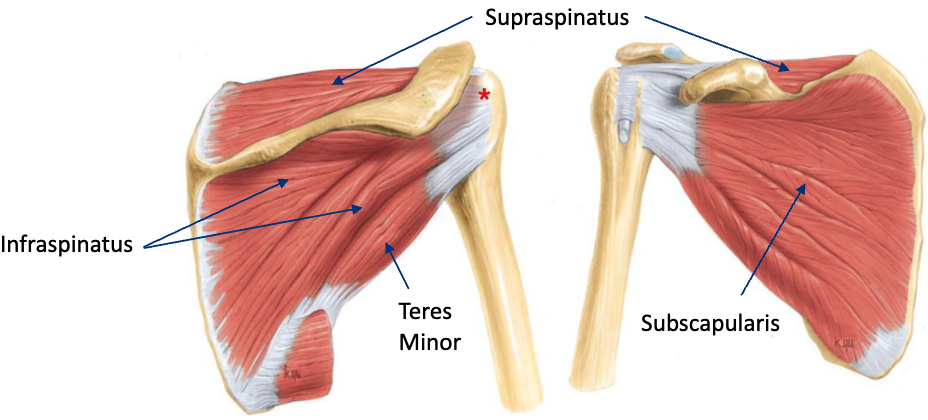
What action does the supraspinatus muscle perform?
Abduction of the arm.
Identify a major muscle found in the anterior compartment of the arm.
Biceps brachii.
What is the primary action of the biceps brachii?
Flexion at the elbow.
What is the main nerve supplying the anterior compartment of the arm?
Musculocutaneous nerve.
What muscle group is responsible for wrist flexion?
Flexor muscles of the forearm.
What is the role of the triceps brachii?
Extension of the elbow.
Which nerve is associated with the deltoid and teres minor muscles?
Axillary nerve.
What artery serves as the principal supply for the forearm and hand?
Ulnar artery.
What is the major role of the radial nerve?
Supply to the posterior compartment of the arm and forearm.
Identify the five terminal branches of the brachial plexus.
Musculocutaneous, Axillary, Median, Ulnar, and Radial nerves.
What is the function of the median nerve?
Supplies the anterior compartment of the forearm and some hand muscles.
What does the term 'musculocutaneous' refer to?
Relating to the musculature and overlying skin of the arm.
How does the ulnar nerve relate to elbow injuries?
Compression at the elbow can cause the sensation known as hitting the 'funny bone'.
What is the pathway of the brachial artery?
It traverses over the flexor side of joints.
Where does the cephalic vein originate?
From the dorsal venous arch of the hand.
What is the purpose of the intermuscular septa in the upper limb?
To separate muscle compartments.
What is the significance of the dorsal venous arch?
It is a common site for intravenous injections.
What muscle lies in the posterior compartment of the arm?
Triceps brachii.
Explain the primary action of the flexor musculature of the forearm.
Wrist and finger flexion.
What anatomical feature allows for attachment of deep muscles in the forearm?
The medial and lateral epicondyles of the humerus.
What is the primary action of the pronator muscles?
To pronate the forearm.
What key landmark provides attachment for wrist flexor muscles?
Medial epicondyle of the humerus.
How are deep veins classified in relation to arteries?
They accompany major arteries and are commonly found in pairs.
What is the function of the interosseous membrane?
To connect adjacent bones in the forearm.
What major function do the interosseous muscles serve in the hand?
Abduct and adduct the fingers.
Identify a major artery that anastomoses with the ulnar artery.
Radial artery.
What is the role of the upper limb's lymphatic vessels?
To follow the superficial veins and drain into the axillary lymph nodes.