international logostics exam 1
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Control decisions
are about executing and monitoring the plan
Design decisions
are about what to make and how to make it
Open systems
Changes in the business environment affect operations, competitors can get at similar resources, and customers have choices.
Predictive logistics
Companies use predictive logistics to ship goods ahead of purchase orders in the next three to five years
Service operations
can't be shipped or inventoried, but still require inputs and processes
Supply chain tiers
-Tier 1: Module or system supplier
-Tier 2: Manufacturer supplier
-Tier 3: Raw materials supplier
Supply chain vs value chain
-Supply chain focuses on logistics and production and ends with the customer
-Value chain looks for ways to enhance the product's value as it moves along that supply chain
Value chains
Enhancing the product at each stage to gain competitive advantage
Customer service, satisfaction and success
-Customer service: focus is on what the firm can do; customer service measures internal service levels. The firm hopes that by performing well along these internal measures customers will be please
-Customer satisfaction: focus is on understanding what the customer views as important; measures of customer satisfaction are externally oriented. The firm seeks feedback from its key customers and uses this feedback to design its value-added processes and measurement system.
-Customer success: focus is on helping customer succeed
The eight quality factors
-Performance
-Features
-Reliability
-Conformance
-Durability
-Serviceability
-Aesthetics
-Perceived quality
The four utilities
o - Form (acquiring products and services to transform to value)
o - Possession (translating needs, promoting, and facilitating the exchange)
o - Time (when product needs to arrive)
o - Place (Delivering item where it needs to be)
Offshoring and Outsourcing
o They are not the same thing
o Offshoring involves moving production on your own or a suppliers from a domestic location to another country.
o Outsourcing involves moving from make to buy, asking a supply chain partner to perform a specific task that the company itself used to do.
The Pareto principle
o Says that all customers are not equal, and they don’t necessarily fall in a strict 80/20 split
Balanced score card
-Scorecards translate vision into actionable behavior
-Scorecards communicate vision
-Scorecards are forward-looking
-Scorecards impose discipline
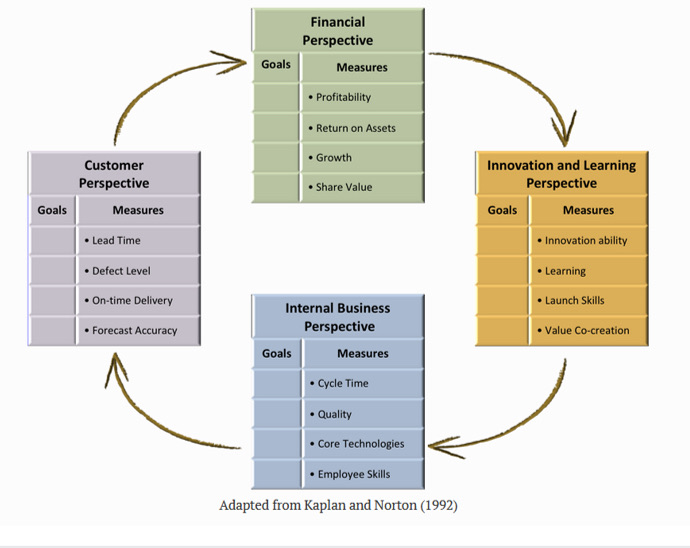
Critical success factors
essential elements for achieving goals
Key performance indicators
metrics to measure performance (industry standards, bench marks, customer feedback)
Four phases of project management
o Initiating
o Planning
o Delivery
o Closure
Dependencies
Some of the tasks have to be done before others
Gantt charts
o A bar chart that shows schedule information.
o Lists activities on the vertical axis and dates on the horizontal axis
Steps:
▪ List all of the activities for a work package
▪ Build you work breakdown structure
▪ Create an activity schedule
▪ Display activities in a bar chart format
Work breakdown structures
o Show all the major tasks that need to be completed and how they relate to one another
o Divide was has to be done into the smallest tasks possible
The five focusing steps (theory of constraints)
o Step 1: identify; easily spotted
o Step 2: exploit; remove any non-value adding work or interruptions o Step 3: subordinate; synchronize all other activities in the process to the bottleneck, so they are aligned with the support the bottleneck needs o Step 4: elevate; make investments to improve how the bottleneck process works or to increase its capacity
o Step 5: Repeat; constantly improve, aggressively removing one constrain and then moving on to the next
Process maps
o Step 1: define the process
▪ Ask why develop a process map
o Step 2: identify the trigger
▪ Ask what triggers or starts the process
o Step 3: identify key activities
▪ Observe the process and how it really works
o Step 4: show flows
▪ Connect linked activities
o Step 5: define the ending point
▪ Follow the process through
Process maps (flowcharts)
o Double arrow: arrival into process
o Single arrow: process direction flow
o Ovals(Beginning/end): show input to start the process or output at the end of the process
o Boxes: show task or activity performed in the process
o Triangle: waiting
o Diamonds: process where a yes/no question is asked or a decision in required
The product process matrix
o Links a product’s life cycle to the OSCM capabilities needed to produce the product
o Matrix points out that product variety and product volume define process efficiency and depocts five process structures along the diagonal: project, job shop, batch, assembly line, and continuous flow
Days of inventory outstanding
The amount of days you have left of inventory if you stopped producing right now
Kaizan (continuous improvement)
tells people to focus on continuous incremental waste elimination, improving the flow and quality of the work
Kanban (visual sign or card)
visual communication to show what is needed in the different stages of production. If it gets low, someone refills it
Muda
not doing processes well
Mura
uneven processes
Poka-yoke
basically dummy proofing a project
Takt time
how long does it take to complete a process