Forensics 2 Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/106
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:01 AM on 2/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
1
New cards
lab safety
closed toed shoes, read all instructions, follow universal safety precautions (treat everything like it’s contaminated, wear PPE (gloves, lab coat, face mask)
2
New cards
Public Labs
may be police staffed, civilian staffed or a mix of both. Often funded through police departments-may lead to a sense of bias towards prosecution a court of law.
3
New cards
Private labs
funded by those seeking analysis. Often used for outsourcing from public labs or for defense re-analysis. Also paternity labs, personal info labs
4
New cards
private research facilities
develop and market testing supplies (chemicals and equipment). Funded by profits from sales
5
New cards
Academia
research methodologies, new tests, train new forensic scientists, etc.
6
New cards
evidence clerks
schedule evidence transfer appointments with lab analysts, track/record evidence submission/transfers; answer general questions concerning each discipline; maintain complete and correct records
7
New cards
analyst
obtain evidence form clerk; examine evidence; take notes; sample/test/observe; interact with prosecutors, LEO, analysts; write reports, review reports, testify; maintain work space
8
New cards
CSI
collect and submit evidence to clerk; discuss collection/evidence with analyst; package evidence; write reports; testify
9
New cards
microscope
A lens, or series of lenses, used to magnify and resolve fine details of an object. Used by drug chemists (marijuana exam), Biologists (takayama, semen, hair,fiber), trace analysts(paint glass hair fibers etc.) documents
10
New cards
light microscope
most common in forensics. Glass lenses. May be compound, dissecting, phase contrast, polarizing (used to examine optical properties), comparison (2 scope connected by optical bridge. Virtual image produced.
11
New cards
electron microscope
not widely used in forensics, mostly in trace analysis. Use circular magnets and beams of elections
12
New cards
refraction
Bending or Change in direction/velocity of light when it passes from one transparent medium to another-long wavelengths bend less than short ones
13
New cards
dispersion
Separation of white light into component colors
14
New cards
diffraction
The spreading of a wave motion as it passes an obstacle and then expands into the area behind the object
15
New cards
destructive interference
2 waves vibrate in the same plane 180o out of phase-Darkness occurs
16
New cards
constructive evidence
Two waves vibrate in phase-Increased brightness
17
New cards
objective lens
Forms an inverted, side reversed image of observed object
18
New cards
ocular
Eye piece gathers the immediate image produced by the objective lens
19
New cards
magnification of ocular and objective
multiply together for total magnification
20
New cards
field of view
area visible in the ocular
21
New cards
compound light microscope
2D, very small objects (hairs, cells)
22
New cards
dissecting/stero microscope
3D, larger objects (crack in knife blade)
23
New cards
resolution
The shortest distance between two points that the microscope can define as clearly being separate
24
New cards
1857 France
first forensic hair study published-Questions about accuracy soon followed
25
New cards
locards exchange principal
every touch leaves a trace, even if not visable to the eye
26
New cards
1900’s ____ principal
locards
27
New cards
1980
witnesses start to question hair evidence
28
New cards
1984
FBI questions direct match based on a single hair
29
New cards
1990s
DNA enters the picture (hair roots only)
30
New cards
hair
a slender threadlike outgrowth from the follicles of the skin of mammals, composed essentially of keratin and having three anatomical regions: The cuticle, the cortex and the medulla
31
New cards
root
growth point of hair
32
New cards
shaft
projects from skin, made of dead cells, keratin, melanin
33
New cards
cuticle
layers of scales covering shaft, clear to translucent
34
New cards
medulla
central core of cells, appears dark under transmitted light. May be fragmentary, discontinuous or absent in people usually present in animals. Amorphous in humans, other species may be vacuolated, serial ladder, lattice. Narrow in human hair, broad in animal hair
35
New cards
cortex
main body of hair, made of spindle shaped cells. May have corticle fusi (air spaces), pigment granules and/or ovoid bodies
36
New cards
root
pulled hair, large soft root with skin tag; mature hair, small tight root, no skin tag
37
New cards
proximal
root end VS distal-tip (may be cut, split, worn)
38
New cards
fiber
smallest unit of a textile material that has a length many times greater than its diameter. Fibers can occur naturally as plant and animal fibers, but they can also be man-made
39
New cards
common fibers not valuable for analysis
white garment cotton, blue denim
40
New cards
natural animal fibers
sheep wool, angora, alpaca, mohair, silk, feathers
41
New cards
natural plant fibers
cotton, flax, hemp, jute
42
New cards
synthetic fibers
easier to trace, polyester, rayon, nylon, acrylic
43
New cards
serology- medical field
the scientific study or diagnostic examination of blood serum, especially with regard to the response of the immune system to pathogens or introduced substances.
44
New cards
serology- forensics
the detection, classification and study of various bodily fluids such as blood, semen, fecal matter and perspiration, and their relationship to a crime scene
45
New cards
presumptive test
very sensitive screening tests but can only say maybe a particular fluid
46
New cards
confirmatory test
less sensitive, may require more sample or be expensive but can ID a fluid definitively
47
New cards
adults have __ to __ liters of blood
4-6.5
48
New cards
what is blood composed of
plasma, RBC, WBC, platelets
49
New cards
blood
Dynamic tissue, extracellular fluid, delivers nutrients, oxygen, clears waste
50
New cards
blood functions
transport dissolved gases, nutrients, hormones and waste; regulate pH and ion composition; restrict fluid loss; provide immune system; stabilize body temperature
51
New cards
antigens
Substance that may trigger a response from the immune system
52
New cards
antibodies
Protein substance that forms in response to exposure to foreign antigens
53
New cards
plasma
half of blood volume, mostly water with hormones, proteins, glucose and minerals.
54
New cards
plasma is water _____
soluable
55
New cards
red blood cells
25% of body cells, transports oxygen using hemoglobin, lacks a nucleus and organelle, flexible biconcave disks
56
New cards
white blood cells
Nucleated cells, 1 WBC for every 1000 RBC. Neutrophils, Eosinophils , Basophils, Monocytes, and Lymphocytes
57
New cards
types of lymphocytes
T, B, NK cells
58
New cards
platelets
Small, membrane bound packets of cytoplasm and enzymes responsible for clotting
59
New cards
blood typing
Most common forms are Rh factor (+/-) and ABO typing (Karl Landsteiner developed) becoming a less common tool due to sample size needed and lack of specificity (rarest type 250,000 Americans), most common (over 100 million Americans). Blood type may be secreted into other body fluids
60
New cards
sperm
head (side view elongated pear shape, front view ovoid with acrosomal cap), midpiece and tail (midpiece and tail may be missing on degraded samples) ejaculated will be clearish to whitish to yellowish.
61
New cards
aspermatic males
normal semen except lacking spermatozoa (illness, obstruction, vasectomy). Cells from reproductive tract lining provide DNA component.
62
New cards
acid phosphate test
found in many body fluids, highest levels in semen. reacts to components of seminal fluid that rely on diet, may be tested ouchterlony or PSA cartilage
63
New cards
sperm confirmatory test
look for spermatozoa under microscope-phase contrast or Christmas tree stain
64
New cards
differences within sperm
may have different shapes, sizes, midpiece size, tail length
65
New cards
amylase
Enzyme that digests starch, in elevated levels in saliva, also in urine, semen, sweat, feces, vaginal secretions and blood.
Radial diffusion, phadebas or cartridge tests.
Does not inherently have DNA, but often cells that have nuclei can be found where amylase levels are high.
Radial diffusion, phadebas or cartridge tests.
Does not inherently have DNA, but often cells that have nuclei can be found where amylase levels are high.
66
New cards
vomit
Acidic, destructive to most cells, spermatozoa often can with stand it. No confirmatory test
67
New cards
urine
Sterile liquid, contains urea and ammonia which may inhibit DNA
68
New cards
feces
Solid waste. Poor source for DNA, solid stool may have outer surface swabbed for cells from intestines
69
New cards
vaginal secretions
Presumptive test-periodic acid-Shiff reagent to stain cellular glucose (high levels in vaginal secretion)
70
New cards
mucous/tears/sweat
All rely on cell transfer from other sources, no confirmatory tests.
71
New cards
locus
particular location of genome
72
New cards
allele
valid coding sequence of loci
73
New cards
polymorphic
many variable gentic options
74
New cards
homozygous
two identical alleles at locus
75
New cards
heterozygous
two different alleles at locus
76
New cards
electrophoresis
separates molecules according to size and electical charge
77
New cards
fluorescence detection
detection of fluorescently tagged DNA fragments by exciting the fluorophore with a laser and the light emitted is captured by a camera
78
New cards
RFU
relative fluorescent units. unit of measurement in electrophoresis
79
New cards
hardy-weinberg equilibrium
Population gene and genotype frequencies remain constant from generation to generation all assumptions are meet (roughly). This is robust, and certain issues can be resolved with the application of a theta value
80
New cards
gregor mendal
rules of heredity - something is causing relatives to inherit traits in a reliable fashion
81
New cards
watson, crick, Franklin
determined structure of DNA
82
New cards
Sir Alec Jeffreys
British geneticist developed genetic fingerprinting methods originally used in casework…you don’t need a full genome to compare people
83
New cards
Kary Mullis
American Biochemist, PCR that allowed for automation and widespread use-part of the team that incorporated Taq polymerase
84
New cards
purines
Adenine and Guanine
85
New cards
pyrimidines
thymine and cyosine
86
New cards
Chargaff’s rules
A to T and G to C
87
New cards
introns
polymorphic useful for forensics
88
New cards
loci nomenclature
D=DNA; #=Chromosome number; S=single copy sequence; long#=locus number
( ie D3S1358) or named after a near-by gene
( ie D3S1358) or named after a near-by gene
89
New cards
DNA exam
have source material (found by serology) blood, semen, hair, etc. Take a small sample, lyse cells, separate DNA from other cell bits, quantify the DNA in the sample, Amplify the sample, electrophorese, analyze
90
New cards
automation kits
becoming more popular, phenol chloroform isoamyl alcohol still the gold standard. Can use different filters/columns to further purify.
91
New cards
differential extraction
separates sperm cells from other cells
92
New cards
peak height ratios
the RFU ratio between two peaks within a locus. Dependent on amount of DNA contributed, modelled by STRmix. Imbalance can (and will) occur. Peak height will vary between loci
93
New cards
stochastic effects
Preferential amplification of one allele occurs with Low concentration samples
94
New cards
shutter
“strand slippage” When template or replicate loops and reanneals. Results in a strand either one repeat shorter (n-4, n-5) or longer (n+4, n-5) than the true allele.
95
New cards
spike
Much sharper than allele peaks. Usually appears in all colors. Caused by dust or urea crystals in the capillary
96
New cards
dye blob
Much broader than allele peak. Usually appear in one color. Caused by dissociated primer dyes
97
New cards
binary genotyping
Either it is an allele or it isn’t. Visual interpretation of electropherogram (epg) using thresholds; stutter percentages; etc. Easiest for single source samples, less useful for mixtures. Calculate CPI or (m)RMPs
98
New cards
probabilistic genotyping
Allows for complex mixture interpretation using Continuous biological modelling. Alleles can be maybes. Calculate LRs
99
New cards
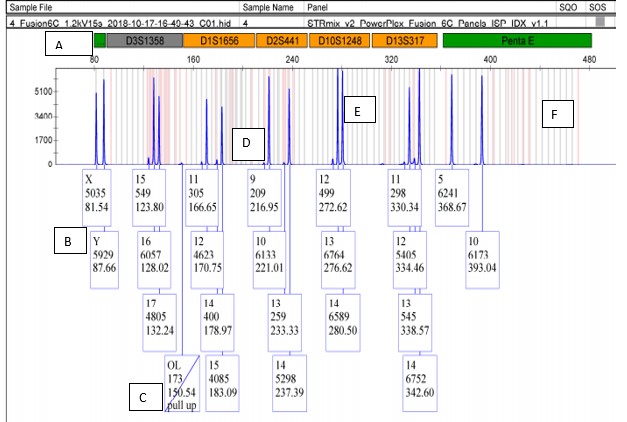
Box A
indicate the Locus you are analyzing (ie D3S1358). The space below the box represents all of the alleles that are possible for that locus.
100
New cards
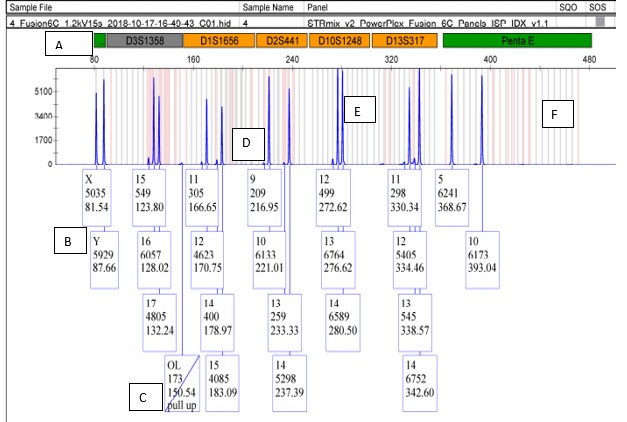
Box B
the peaks indicate the allele call (here X and Y), the peak height in rfu (5035 and 5929) and the position (81.54 and 87.66) as determined by the ILS. This sample is a male (XY).