fungal infections
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PEBC
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
fungals infections
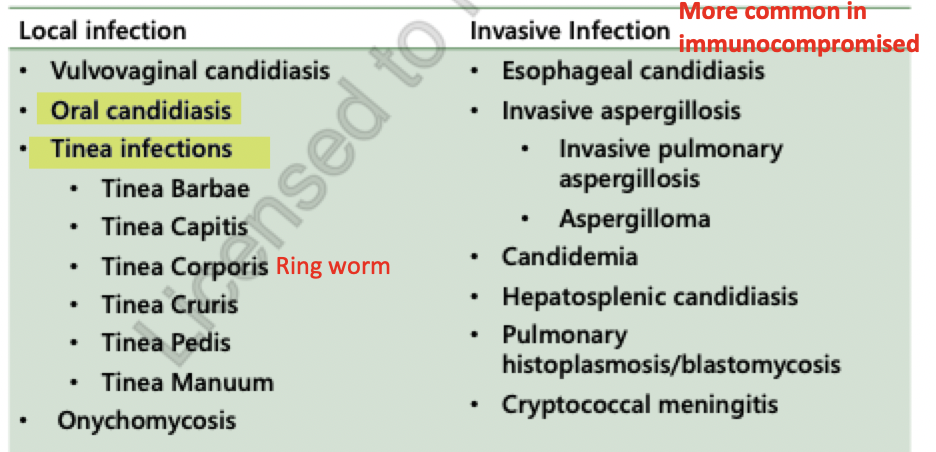
dermatophyte (tinea infections)
tinea barbae = on beard
on coarse beard hair
spread by animals to farm workers
unilateral lesions = scaly patches, follicular pustules
tinea capitis = scalp
scalp hair follicles and adjacent skin
children = common
also common in low socioeconomic and crowded environments
through direct contact, animals, contaminated clothing
annular patch of scaling and itchy skin along with hair loss
tinea corporis = ringworm
trunk or limbs excluding face, hands, feet, groin
flat, circular scaly spot with central clear portion with raised red border
common in athletes with skin-to-skin contact (wrestlers)
tinea cruris = jock itch
groin area
scrotum and penis are spared
in men during summer months
often a reservoir for infection found on feet
bilateral, scaly, red-brown centers with clearly defined raised borders
tinea pedia = athletes foot
white scaling between toes, skin maceration, odour present
late-teens, adults
in moist environments (swimming pools, occluded footwear and excessive sweating)
tinea mannum = hand ringworm
not common
dorsal surface of hands
dermatophyte/ tinea infection treatment
non pharm:
keep skin clean and dry to discourage fungal proliferation
wear loose fitting clothing for ventilation
nonmedicated powders can be used to absorb excess perspiration BUT AVOID CORNSTARCH b/c it promotes fungal proliferation
use talc with caution around neonates/ infants or those w respiratory conditions
topical treatment = clotrimazole 1%, ketoconazole 2%, Miconazole 2%, terbinafine 1%, ciclopirox 1%
azoles:
tinea cruris (jock itch) = 2-4 weeks
corporis (ringworm), pedis (athletes foot) = 4 weeks
terbinafine:
tinea cruris (jock itch) and corporis (ringworm) = 1 week
tinea pedis = treatment should continue for at least 1 week after symptom resolution
candidiasis
fungal infection or mycosis due to Candida sp
most common cause is Candida albicans
can cause oral or esophageal candidiasis
diagnosis:
history and physical examination
can do biopsy and endoscopy
oral candidiasis
Microbiology:
Candida albicans = 70-80%
non - albicans = 17% → increases to 50% in immunocompromised pts (c. glabrata, c. tropicalis, c. krusei, c. guilliermondi, c. paeapsilosis)
clinical presentation:
pseudomembranous with “cottage cheese” appearance = thrush
soft white plaques overlying areas of erythema (red) —> can be removed with vigorous rubbing but leave red/bleeding sites
lesions on tongue, gums, throat
symptoms:
cotton mouth
loss of taste
may have pain on eating and swallowing
burning sensation on tongue
metallic taste
dysphagia
esophageal candidiasis
clinical presentation:
extension of oral but esophagus can be the only site involved: distal 2/3 of esophagus (the lower part) rather than the proximal
symptoms:
dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
odynophagia (pain on swallowing) = HALLMARK
retrosternal chest pain
epigastric pain (rare)
signs:
fever
plaques (can be ulcerated or edematous)
advanced cases present with narrowing of lumen
local risk factors (for candida)
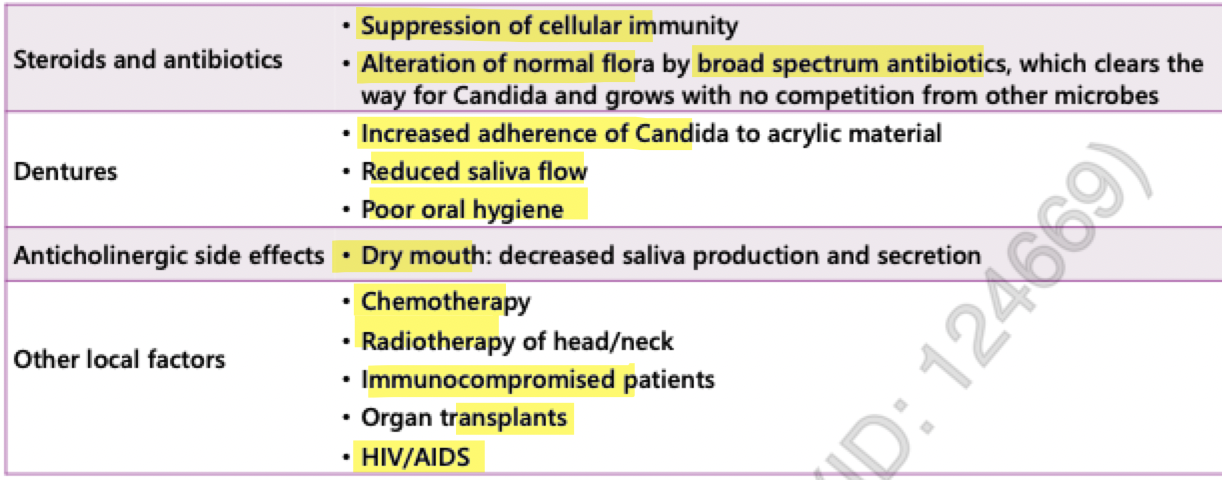
systemic risk factors (candida)

drug causes (candidiasis)
steroids
xerostomia inducing agents:
anticholinergics
radiation
broad spectrum antibiotics = alter normal flora
decreased environmental and nutritional competition for Candida causes candidal overgrowth
chemotherapy = altered rate of mucosal regeneration, xerostomia, neutropenia
PPIs = inhibition of gastric acid allows overgrowth, decreased salivation
goals of therapy (candida)
cure fungal infections: eliminate signs and symptoms
prevent complications related to fungal infection
minimize adverse effects and manage drug-drug interactions
treatment (candidiasis)
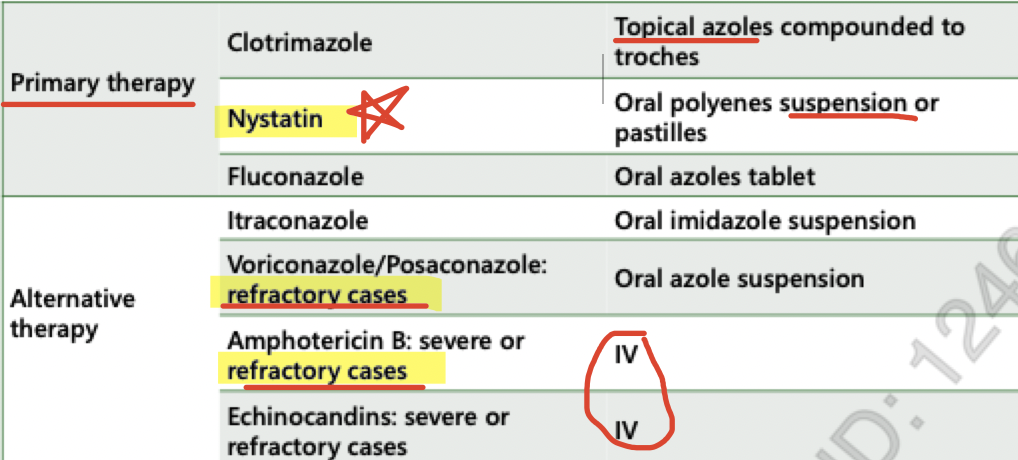
topical agents:
1st line in uncomplicated oral candidiasis with no underlying conditions
include oral rinses (suspensions) and troches (lozenges)
need to be administered frequently with short contact time
need enough saliva to dissolve troches (can be issue in dry mouths)
irritating
suspensions
can be better for patients with dry mouth but the contact time is short
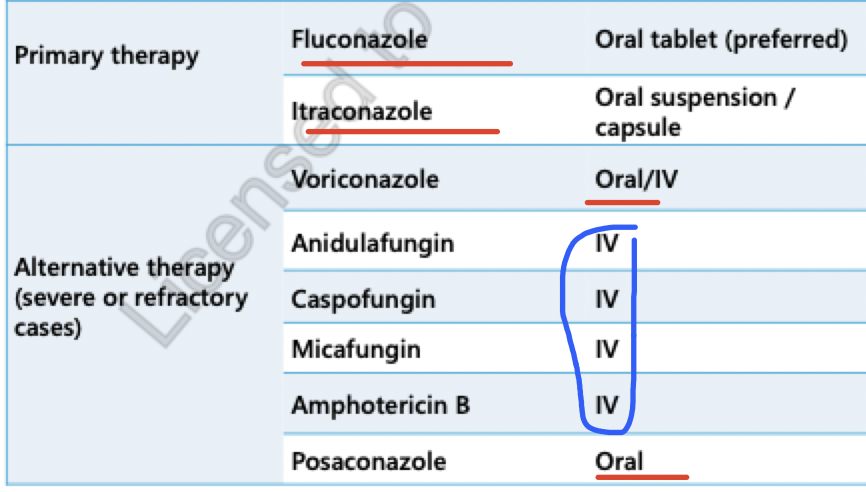
systemic agents:
needed for for esophageal candidiasis
trouble swallowing = give IV formulations
mucocutaneous candidiasis = fungal infection on mucous membranes:
Imidazole and triazole antifungals: fluconazole (IV, PO), itraconazole (po), voriconazole (IV, PO), Posaconazole (po)
effective and more convenient and better tolerated vs topical
preferred in:
patients at high risk for disseminated systemic or invasive candidiasis (ex. neutropenia due to leukemia and bone marrow transplantation)
who cant tolerate topical agents due to dry mouth or swallowing issues
refractory to topical treatment
severe odynophagia
treatment options (oropharyngeal candidiasis)
treatment options (esophageal candidiasis)
azoles
2 classes:
Imidazoles = 2-N azole ring
clotrimazole, ketoconazole
Triazoles = 3-N azole ring, better pharmacokinetic properties
fluconazole = older
itraconazole = older
voriconazole, posaconazole
voriconazole, isavuconazole and posaconazole = newer and made to:
overcome limited efficacy of fluconazole against Aspergillus and other non-albicans Candida sp
improve absorption, tolerability and safety vs itraconazole
interactions:
CYP3A4 inhibitors = itraconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole
CYP3A4, 2C9/19 = Fluconazole
increased: cyclosporines, tacrolimus, sirolimus, CCBs, most BDZ, statins, steroids, warfarin, rifampin
itraconazole and posaconazole = inhibitors of PgP (EFFLUX PUMP)
CYP450 inducers (CBZ, Phenytoin, Phenobarbital, rifampin and rifabutin) = decreases azoles
s/e:
N/V
LFTs increase
gynecomastia (at high doses, longer duration except fluconazole)
fluconazole
not affected by food or GI pH
dose adjust for renal dysfunction
Hepatic CYP2C9 = metabolism
penetrates into body fluids and CSF
s/e:
GI upset
hepatitis
increased LFTs
interactions (least drug interacting azole) = CYP3A4 / 2C9/ 19 inhibitor
rifampin = decreases its efficacy
increases toxicity of cyclosporin, contraceptives, prednisone, sulfonylureas, theophylline and warfarin
itraconazole
capsule= best absorbed with food
oral solution = best absorbed on empty stomach
metabolized by liver
interactions= Strong inhibitor of CYP3A4
does NOT penetrate CSF
s/e:
N/V
hepatotoxicity
Congestive heart failure , pulmonary edema = Black box warning!
voriconazole
more efficacious vs fluconazole for invasive aspergillosis and non-albicans Candida
oral= tablet or solution
metabolized in liver by CYP2C19, 3A4 and less 2C9
affected by CYP2C19 genetic variability (19% asians and 2% caucasians are poor metbaolizers)
interactions:
sirolimus, tacrolimus, cyclosporine, midazolam, ributamin/rifampin, ergots
levels are decreased by: CBZ, Rifampin, barbiturats and phenytoin
s/e = mainly eye disturbances and hepatitis
visual field disturbances = altered perception, acuity, photophobia
visual and auditory hallucinations
hepatitis
posaconazole
only as a suspension for oral use
for invasive aspergillosis prevention and treatment
absorption is increased by food, esp fatty meals
not affected by antacids
metabolized by liver
moderate inhibitor of CYP3A4
s/e:
Diarrhea, headache, nausea
ketoconazole
least effective of all azoles due to poor bioavailability
low pH is needed for absorption = acid suppression decreases absorption
not used systemically bc = greater toxicity, lower efficacy, drug interactions
replaced by fluconazole and itraconazole
interactions = most interacting of ALL azoles —> potent 3A4 inhibitor
s/e:
gynecomastia
N/V
abdominal pain
itching
headache
hepatotoxicity
endocrine effects
lichenoid mucosa reactions
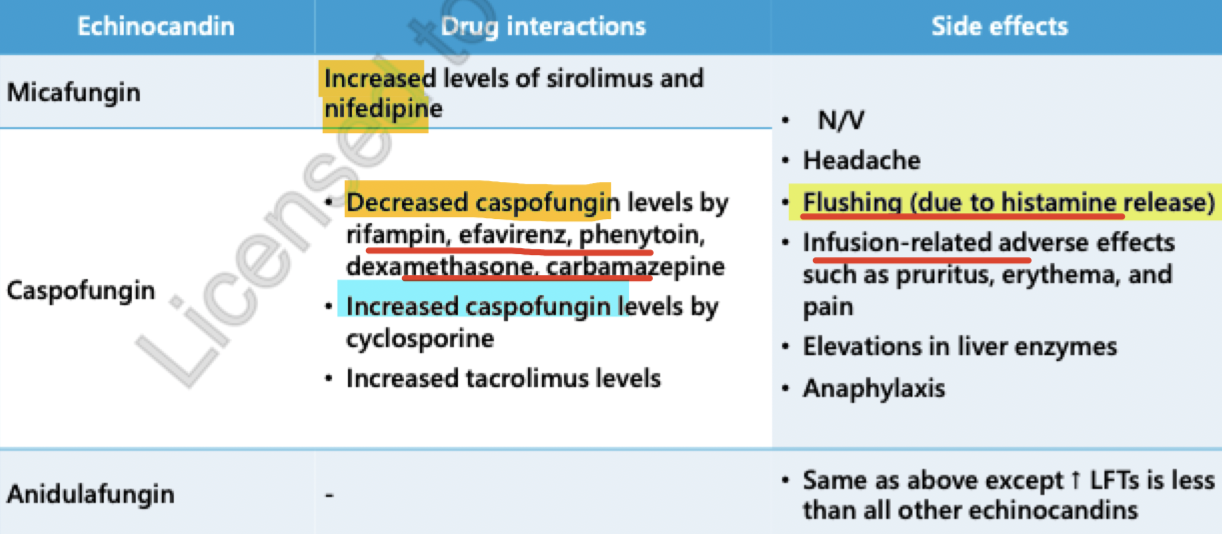
echinocandins
include: Caspofungin and Micafungin
as efficacious as fluconazole, amphotericin B or lipid amphotericin B against candidemia
resistance is infrequent
only available as parenteral formulations
effective against candida and Aspergillus
drug interactions = none are major inducers, substrates or inhibitors of CYP450 or PgP
caspofungin and micafungin
used in combo w azoles and polyenes (these are echinocandins)
can be used more in immunocompromised patients
narrow spectrum of activity
Fungicidal against Candida spp
s/e:
very few toxic s/e bc their MOA is not found in mammalian cells
increase LFTs
HA
histamine release (rash)
phlebitis (due to IV administration)
fever
advantages:
extremely safe antifungals, relative to other antifungal classes
do not need dose adjustments
disadvantages:
high cost
IV
nystatin
polyene antifungal
only non-absorbable topical form
effective in oral candidiasis but less effective vs oral azoles
produces channels through fungal membranes = leakage of essential cell contents
amphotericin b
widest spectrum of activity among all antifungals
polyene antifungal
lipid based formulation = better safety profile (less nephrotoxic) and better PK parameters
s/e:
N/V
diarrhea
infusion related s/e
monitor electrolytes due to occurrence of hypokalemia, hypomagnesia, hypophosphatemia
monitor renal function = nephrotoxic drug