Protozoa
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
How many species in protozoa? Are they eukaryotes? What do they consist of?
65 000 species. Yes they are. Consist of a single cell but many species contain more than one nucleus during all or portions of their life cycles and certain stages such as spores may be built from more than one cell
What are most protozoans important parasites of?
The gastrointestinal tract and blood
What are two relevant genera in Euglenozoa phylum?
Trypanosoma and Leishmania
What are two species in the genera Trypanosoma? What about leishmania?
Trypanosoma: T.brucei, and T. brucei gambiense
Leishmania: L.donovani, L. tropica
What is a relevant genus for the phylum apicomplexa? What are four species in this genus?
Plasmodium. Species include: P. malariae, P.ovale, P.falciparum, P.vivax
What are three genera in the phylum metamonada?
Chilomastix, Giardia, and Trichomonas
What is one important species in each of the three genera for the phylum metamonada?
Chilomastix mesnili, Giardia lamblia, and Trichomonas vaginalis (or muris)
What is a genus and a species in the phylum Cilliophora?
Genus: Balantidium
Species is Balantidium coli
What are three genera associated with the phylum Amoebozoa? What is an associated species with each genera?
Genus: Entamoeba, Endolimax, Iodamoeba
Species: Entamoeba coli and histolytica, Endolimax nana, Iodamoeba butschlii
What do trypanosomes possess?
6 basic morphological forms based on shape and position of the kinetosome and kinetoplast
Describe the amastigote morphological form
It has a spheroid shape with a very short flagella projecting just above the flagellar pocket.
What is the definitive morphology for Leishmania in the vertebrate host?
Amastigote
Describe the choanomastigote morphological form
The flagellum emerges from the collar. Kinetosomes and kinetoplasts are anterior to the nucleus.
What genus has the choanomastigote form?
Crithidia
Describe the promastigote morphological form. What is an example of a genus that has this form?
Flagellum extends forward and the kinetsome and the kinetoplast are anterior to the nucleus. Leptomonas
Describe the opisthomastigote morphological form. What is an example of a genus that has this form?
Kinetosome and kintoplast are found between the posterior and the nucleus. Have a long flagellar pocket and no undulating membrane. Herpetomonas
Describe the epimastigote morphological form. What is an example of a genus that has this form?
Similar to promastigote as the kinetosome and kinetoplast are between the nucleus and anterior end. But they have a short undulating membrane found along the basal or proximal part of the flagellum. Blastocrithidia
Describe the trypomastigote morphological form
Kinetoplast and kinetosome are near posterior of body. The flagella runs along the surface of the body generally continuing as a whip anterior to the body. Has an undulating membrane.
What genus has the trypomastigote as the definitive form in humans?
Trypanosoma
What is the size for trypanosoma lewisi? What morphological form is it in? Is the undulating membrane visible under 40X?
25 micrometers in length. Typical trypomastigote form. May not be
What is the definitive host for T.lewisi? Habitat? Phylum? Disease? Diagnostic feature?
Definitive host: Rat
Habitat: Blood
Phylum: Euglenozoa
Disease: Non-pathogenic
Diagnostic feature: Perform a blood smear
What is the size of Trypanosoma brucei gambinense? Describe morphological features. What morphological form is it in?
25-50 micrometers
Long and slender but can be broad and short if no flagellum is present or in an intermediate stage
Typical trypomastigote form in vertebrate host and epimastigote form in insect host
What is the definitive host? Habitat? Phylum? Diagnostic features of trypanosoma brucei gambiense?
Definitive host: Human
Habitat: Blood
Phylum: Euglenozoa
Disease: Trypanosomiasis, African sleeping sickness
Diagnostic feature: Perform a blood smear
What morphological form is Leishmania donovani in?
Typical amastigote form in vertebrate host and promastigote form in insect host
What is the definitive host? Phylum? Habitat? Diagnostic feature of Leishmania donovani?
Definitive host: Human and dogs
Habitat: Liver and spleen
Phylum: Euglenozoa
Disease: Kala-azar, dum-dum fever, and visceral leishmaniasis
Diagnostic feature: Perform a smear
What morphological form is leishmania tropica in?
Promastigote form when grown in culture and in insect host (gut of sandfly). Amastigote form in vertebrate host.
What is the definitive host? Phylum? Habitat? Disease? Diagnostic feature of leishmania tropica?
Definitive host: Human and dogs
Habitat: Dermal layer of the skin
Phylum: Euglenozoa
Disease: Dermal leishmaniasis, or Oriental sore
Diagnostic feature: Perform a culture
Where does the flagellum originate at for T.b.gambiense?
At the posterior of the organism but it is contained by the undulating membrane along the outside. It becomes free at the anterior part of the body.
What is the vector for African trypanosomiasis (T.b. gambiense)? What is the vector for T. lewisi?
The tsetse fly. No vector because it is non-pathogenic
What is the complete life cycle for African trypanosomiasis including diagnosis and infective stages
The tsetse fly takes a blood meal and injects metacyclic trypomastigotes (I)
Injected metacyclic trypomastigotes transform into bloodstream trypomastigotes which are carried to other sites
Trypomastigotes multiply by binary fission in various body fluids such as blood, lymph, and spinal fluid
Trypomastigotes are then in blood (D)
Tsetse fly will take a blood meal and blood stream trypomastigotes are ingested
Bloodstream trypomastigotes transform into pro cyclic trypomastigotes in tsetse flys midgut. The pro cyclic trypomastigotes multiply by binary fission
Procyclic trypomastigotes leave the midgut and transform into epimastigotes
Epimastigotes multiply in the salivary gland. They transform into metacyclic trypomastigotes and the cycle continues.
Does Leishmania donovani have a flagellum or undulating membrane? Where is the kinetoplast located?
No it does not. It is a dark rod-shaped inclusion near the round nucleus
What do leishmania like to attack? What are they seen as here?
Macrophages and are seen as the flagellate amastigote forms.
Does leishmania tropica have an undulating membrane? What about flagellum?
No undulating membrane or flagellum but has a flagellum when in promastigote form.
What are two distinguishing characteristics that can be used to distungish between Leishmania promastigote and the trypanosoma trypomastigote?
Leishmania do not have an undulating membrane while trypanosoma do.
KS and KP are anterior to the nucleus in Leishmania while KS and KP is posterior to the nucleus in trypanosoma
How can you distinguish the nucleus from the kinetoplast in the leishmania amastigote? In what host is the amastigote form found?
The kinetoplast is rod shaped near the nucleus in the amastigote form. It is in the amastigote form in the vertebrate host and promastigote in the insect host
What are the two genera of sand flies that transmit leishmania? New world? Old world?
New world- Lutzomyia spp
Old world- Phlebotomus spp
What is the life cycle of the sand fly that transmits leishmania? What stages are infective? Diagnostic?
Sandfly takes a blood meal and infects promastigote stage into the skin (I)
Promastigotes are phagocytozied by macrophages
Promastigotes transform into amastigotes inside macrophages (D)
Amastigotes multiply in cells (including macrophages) of various tissues until the infected cell ruptures (D)
The released organisms infect other cells and affect different tissues
A sandfly will take a blood meal and ingest an infected macrophage with amastigotes
Ingestion of parasitized cell
Amastigotes transform into promastigote stage in midgut
Divide in midgut and migrate to proboscis and cycle can now repeat itself
Define definitive host
It is a host where the parasite reaches sexual maturity
Define intermediate host
It is a host that is required for parasite development but one in which the parasite does not reach sexual maturity
What is schizogony/merogony?
It is where the nucleus divides multiple times before cytokinesis occurs, resulting in the simultaneous production of many daughter cells
During schizogony, what are the three possible names to call the cell?
Schizont, meront, or segmenter
What is excystment? Encystment?
Excystment is the process of rupturing the cyst to return to an active form. While encystment is when protozoa will form a cyst (protective covering) and go into a resting state to survive harsh conditions.
What is a cytostome?
It is a specialized cell structure used for phagocytosis that protozoa have
What is ammonotelic?
It is where most of their nitrogen is secreted in ammonia and most of this diffuses directly through the cell membrane. It is a method for excretion and osmoregulation.
What is a kinetoplast?
It is a DNA containing organelle within the mitochondria and it is disc shaped
What is a kinetosome?
It is a self-duplicating organelle that is homologous to the centriole. It is responsible for the formation of flagellum or cilia.
What is the undulating membrane?
It is a lateral expansion of the plasma membrane in flagellates that is usually associated with the flagellum
What is an axostyle?
It is a sheet of microtubules that arises from the base of the flagellum
What is gametogony?
It is the sexual phase of the life cycle in which the gametes are formed
What is sporogony?
Formation and maturation of infective stages. It gives rise to sporozoites
What is a zygote?
It is the first cell formed when a sperm fertilizes an egg
What is a vector?
It is an organism that transmits the causative agent from the reservoir to the host
What is a karyosome?
It is a knot of condensed chromosomes joined together in a limited volume of the oocyte nucleus
What is a merozoite?
It is a small amoeboid sporozoan trophozoite produced by schizogony that is capable of initiating a new sexual or asexual cycle of development
What is a karyomastigont?
It is an organelle system in some primitive protists that consist of a nucleus, one or more basal bodies, and flagella all linked together
What is a basal body?
They are barrel-like micro tubular structures found at the base of cilia or flagellum
What is a commensal?
It is an organism that benefits and the host is neither benefitted or harmed.
What is an isogametes? Anisogamete?
Iso- is morphologically identical to the other gamete it fuses with
Aniso- differs from the other in size or form
What is a trophozoite?
It is the active, feeding, and reproducing stage of protozoan parasites
What is syngamy?
It is the fusion of two cells or their nuclei in reproduction
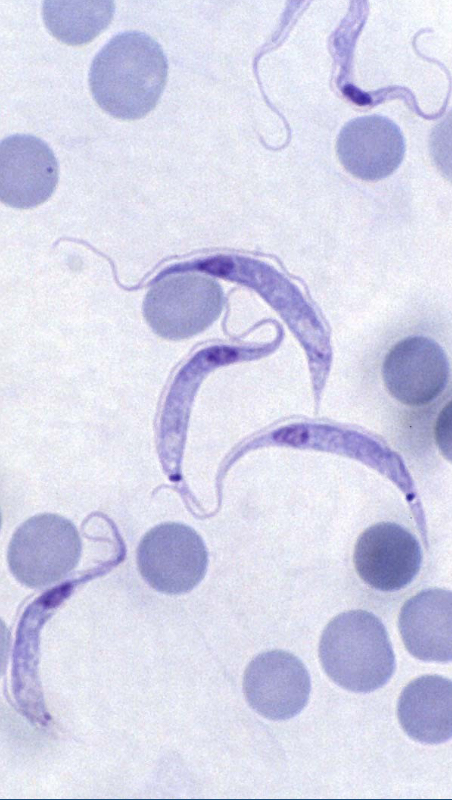
What parasite is this?
Trypanosoma lewisi
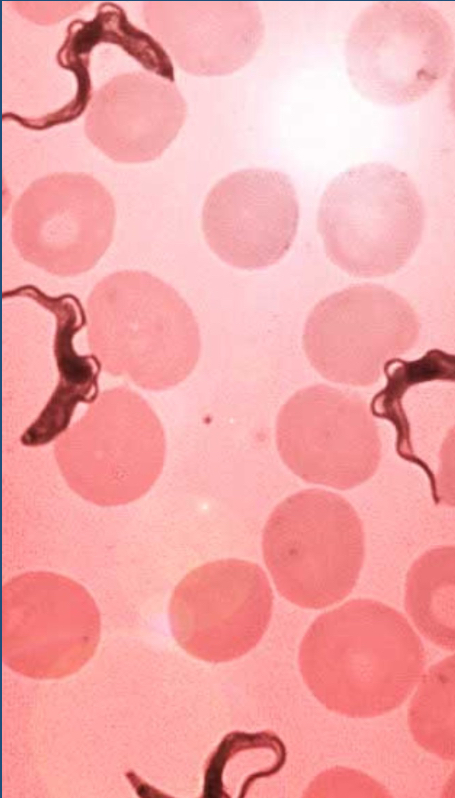
What parasite is this?
Trypanosoma brucei gambiense
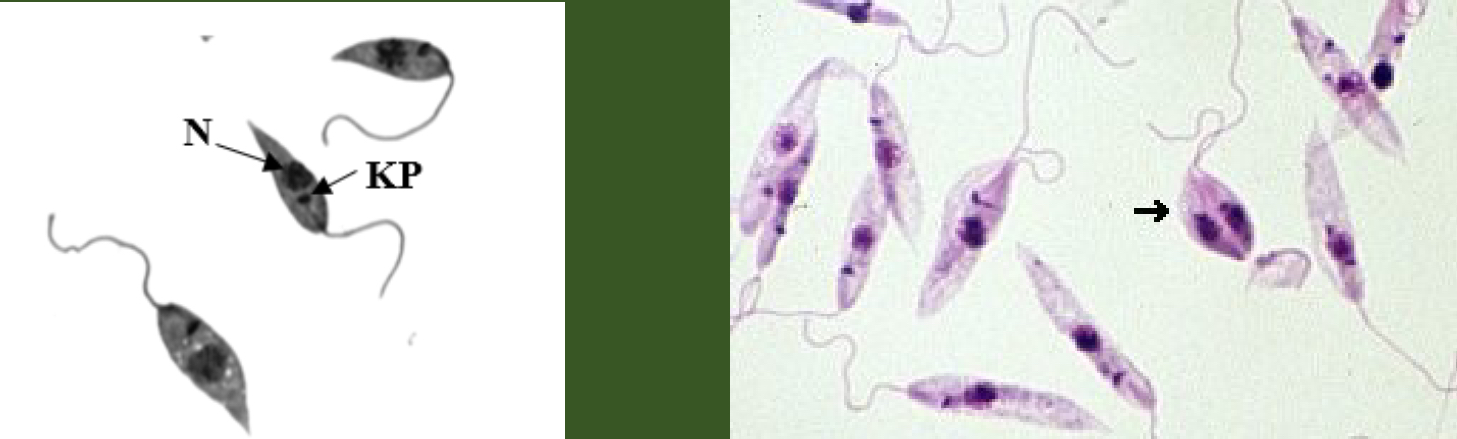
What parasite is this?
Leishmania tropica
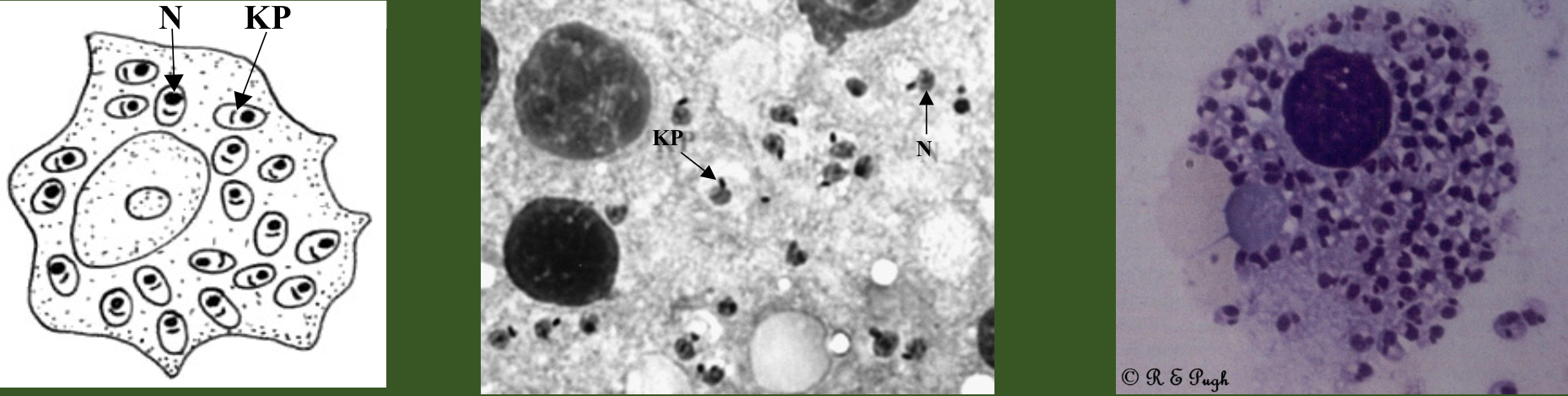
What parasite is this?
Leishmania donovani